Exception symptom
When a tenant memory overrun error or a memory-related exception occurs in a cluster, OCP reports an alert, as shown in the following figure:
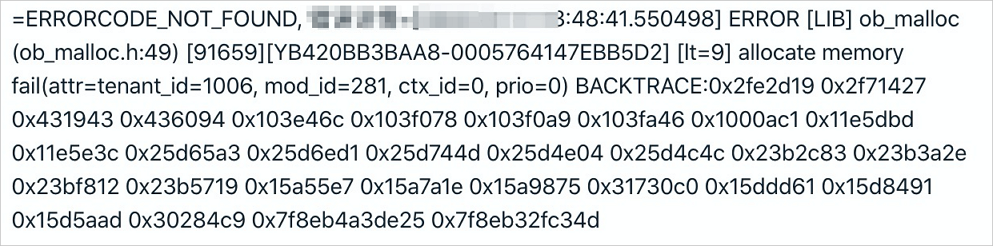
After the alert is received, the database administrator (DBA) needs to log on as the sys tenant of the OceanBase cluster where the alert target is located, to identify the cause.
Identify the cause
Usually, a tenant memory usage exception is related to user behaviors, and therefore can be identified by using the performance trend and SQL monitoring features on OCP.
Check tenant performance trends
Before you check the tenant-level performance monitoring information, log on to the OCP console as the sys tenant of the cluster, obtain the value of tenant_id from the error log, and run the following SQL statement to obtain the name of the tenant for which the memory usage alert is reported. In the log alert in the preceding figure, tenant_id is 1006. The corresponding SQL statement is:
obclient> SELECT tenant_name FROM __all_tenant WHERE tenant_id IN (1006);
After you obtain the name of the tenant, go to the Performance Monitoring page for the tenant on OCP. For more information, see Performance monitoring.
Pay attention to the QPS , Response time , TPS , Transaction response time , and MEMStore metrics on the Performance Monitoring page of the tenant. Identify the time when the alert was triggered, and check whether the alert is triggered by the following cases. Usually, variations of the preceding monitoring metrics near the occurrence time of the alert may encompass the following cases:
The transaction response time suddenly increases significantly, while other metrics show no obvious changes. In addition, the MEMStore metric is below the threshold for major compaction. This indicates that large queries exist and that the large queries have consumed memory exceeding the specified threshold, thus triggering the alert.
The transaction response time suddenly increases significantly, and the response time also increases, but other metrics do not change much. In addition, the MEMStore metric is below the threshold for major compaction. This indicates that the tenant has executed some large transactions, which have consumed memory exceeding the specified threshold, thus triggering the alert and affecting the query performance.
Both QPS and TPS decrease, but the transaction response time increases, while the MEMStore metric has reached the threshold for major compaction but does not drop. This indicates that the memory of the tenant cannot be released through minor compactions or major compactions. The log alert is probably caused by a minor compaction exception or a major compaction exception. For more information, see Handle major compaction exceptions.
Check SQL monitoring information
If the log alert is caused by large queries or large transactions but not major compaction exceptions, use the SlowSQL monitoring feature on OCP to identify the root cause. For more information, see SQL monitoring.
Solutions
The solution to a tenant memory overrun exception varies with the root cause. The following lists the solutions in descending order of preferences and benefits:
Turn large queries into small queries. For a tenant memory overrun caused by large queries or bad SQL statements, locate the SQL statement that causes the exception and optimize the SQL statements to reduce the memory consumption, thus preventing the alert.
Turn large transactions into small transactions. For an "insufficient tenant memory" error caused by large transactions or batch data import or export, locate the large transaction that causes the issue and optimize the transaction processing to eventually turn the large transaction into small transactions.
Optimize the related tenant variable. If the SQL statements and transaction sizes have been minimized to the greatest degree allowed, set
ob_sql_work_area_percentageto a larger value for the tenant to increase the memory allowed for a session. The default value is 5, indicating that 5% of a single memory resource unit of the tenant. The variable can be configured at the session level or global level. The recommended value range is [5, 80].Sample statements:
Session level
obclient> SET ob_sql_work_area_percentage = xxx;Global level
obclient> SET GLOBAL ob_sql_work_area_percentage = xxx;
- Scale out the memory resources for the tenant. If the alert persists after you have tried all the preceding methods, you may scale out the memory resources for the tenant. For more information, see Tenant management. If the alert is caused by a minor compaction exception or a major compaction exception, see Handle a major compaction exception.






