Overview
The core capabilities of OceanBase materialized views include:
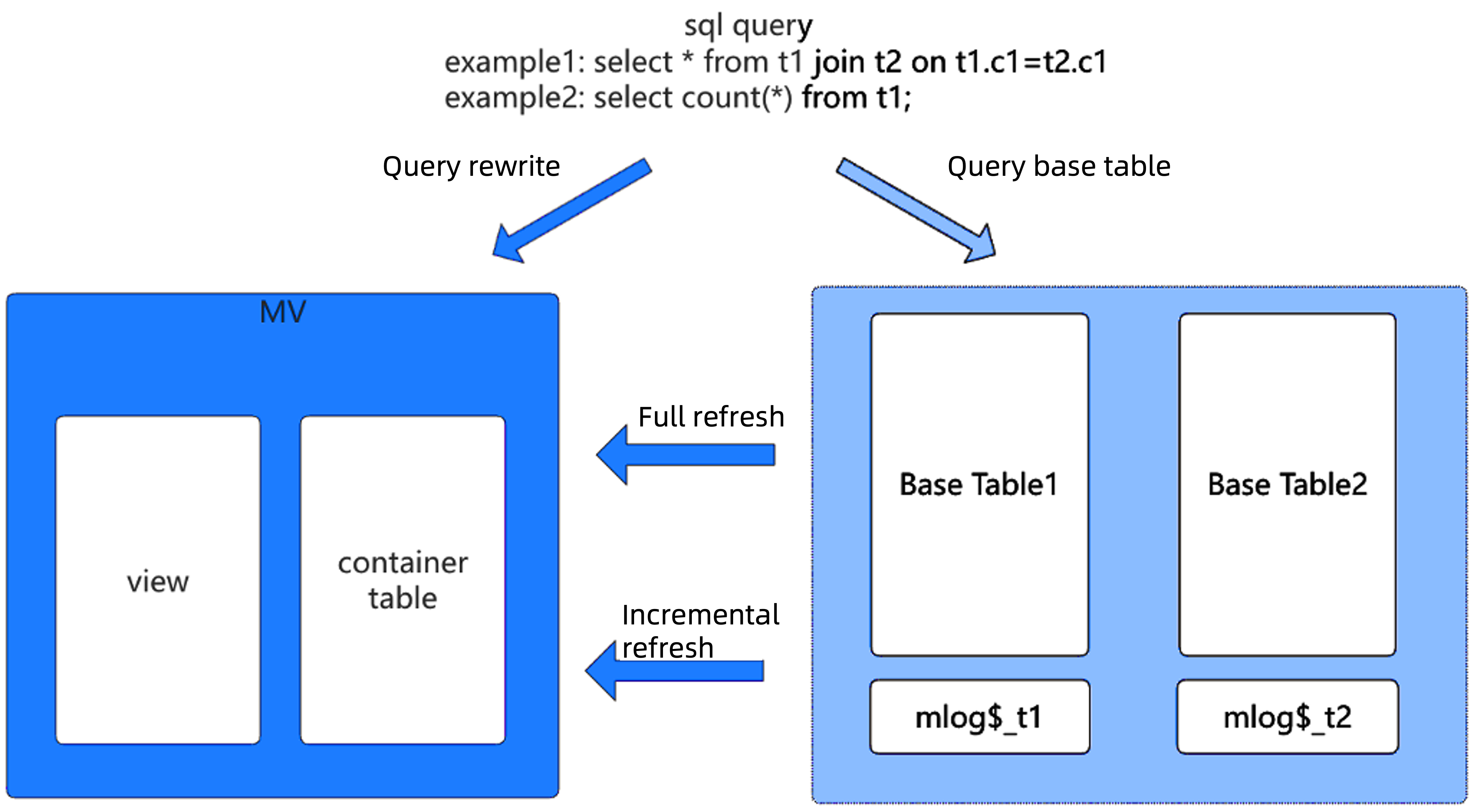
- Data precomputation: Accelerates analysis by precomputing and storing query results, reducing real-time computation overhead, and improving query performance.
- Refresh mechanism: Supports both full refresh (rebuilding all data) and incremental refresh (updating only changed data). Incremental refresh typically delivers better performance.
- Real-time query capability: When ENABLE ON QUERY COMPUTATION is enabled, queries automatically integrate incremental data to return real-time results.
- Nested and cascading refresh capability: Supports multi-level materialized views to facilitate the construction of complex ETL processes.
The table below categorizes the features of OceanBase materialized views by capability, helping users understand the technical implementation and applicable scenarios for each capability.
| Capability | Description |
|---|---|
| Basic capabilities | Supports primary key definition, partition creation, table group creation, index creation, and full refresh. |
| Advanced capabilities | Supports query rewriting, incremental refresh, columnar-format materialized views, use of views and external tables for base tables, and direct load. Supports refresh parallelism, scheduling intervals, resource isolation, monitoring and diagnostics, and ODC visual operations. |
| High-level capabilities | Supports real-time materialized views, nested materialized views, dimension table joins, DDL operations, automatic management of materialized view logs, and extended support for outer join/union all in incremental refresh. |
The test results from the best practice scenarios provided in this topic are for your reference only. Actual performance may vary depending on your business environment and system configuration.
Best practice scenarios
Scenario 1: Accelerate single-table aggregate queries
Applicable scenarios
- The business involves a single table with a large volume of existing data, resulting in high latency for direct queries.
- There is a need for frequent group aggregation queries (such as
COUNT,SUM, andGROUP BY).
Procedure
Create an incremental refresh materialized view:
CREATE MATERIALIZED VIEW mv1 PRIMARY KEY (a) PARALLEL 5 REFRESH FAST START WITH SYSDATE() NEXT SYSDATE() + INTERVAL '5' SECOND ENABLE ON QUERY COMPUTATION AS SELECT a, COUNT(b), COUNT(*), SUM(b) FROM t1 GROUP BY a;REFRESH FAST: enables incremental refresh. Since theREFRESH FASTmethod uses the information recorded in the materialized view log to determine what needs to be incrementally refreshed, you must create amaterialized view logon the base table before creating the materialized view.ENABLE ON QUERY COMPUTATION: automatically merges incremental data during real-time queries.
Verify the results:
- Non-real-time queries: Query the materialized view data directly, which has significantly lower latency compared to querying the base table.
- Real-time queries: The system automatically integrates incremental data and returns results, with significantly lower latency compared to querying the base table.
- Improved performance with data growth: As the amount of data in the base table increases, the performance improvement from using the materialized view becomes more pronounced (as shown in the figure below).
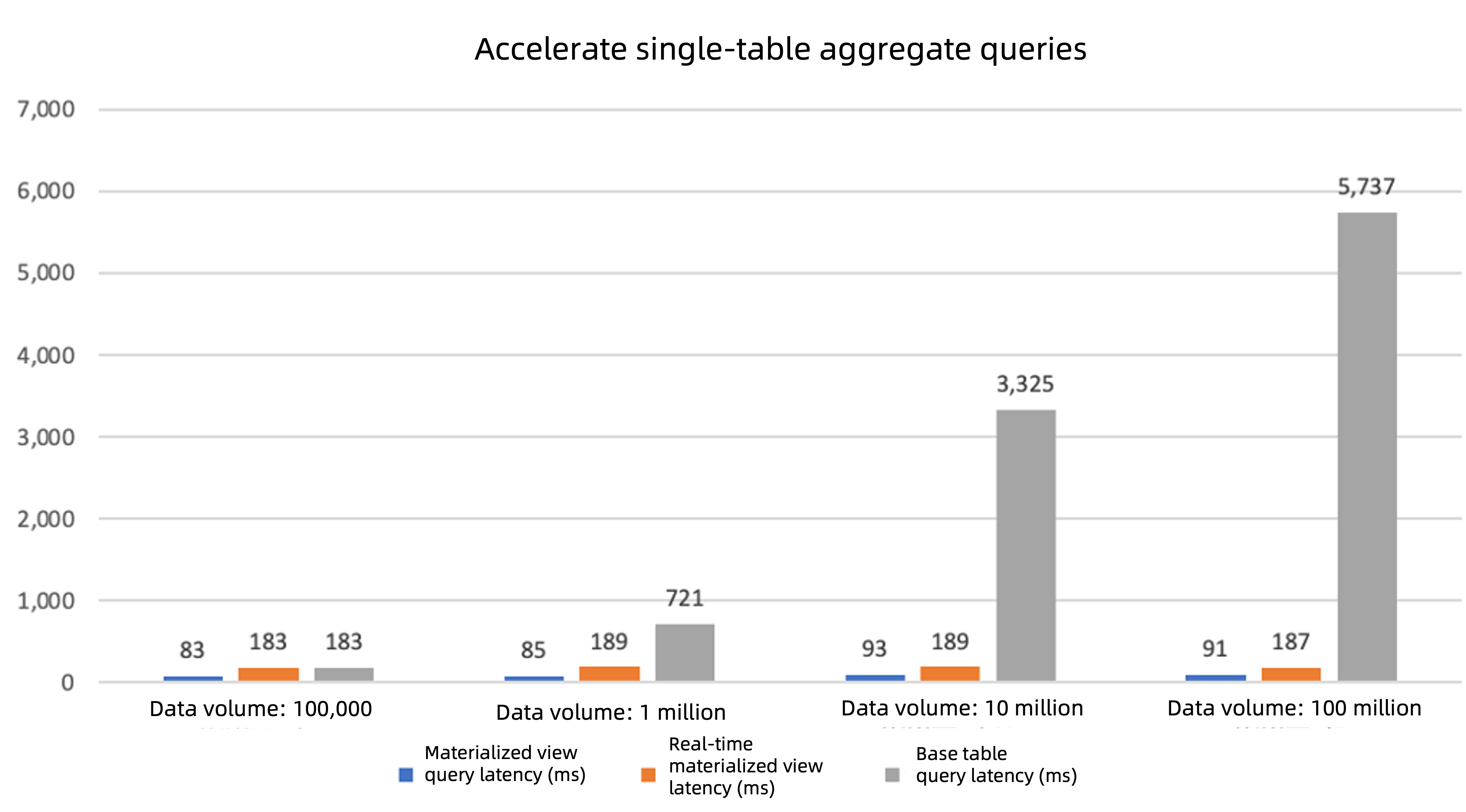
Scenario 2: Accelerate multi-table join queries
Applicable scenarios
- The business involves multiple tables with large volumes of existing data, resulting in high latency for direct queries.
- There is a need for frequent multi-table join queries (such as joins between two or three tables).
Procedure
Create an incremental refresh materialized view:
CREATE MATERIALIZED VIEW mv2 PRIMARY KEY (a, b) PARALLEL 5 PARTITION BY HASH(a) PARTITIONS 4 REFRESH FAST START WITH SYSDATE() NEXT SYSDATE() + INTERVAL 5 SECOND ENABLE ON QUERY COMPUTATION AS SELECT t1.a, t1.b, t1.c, t2.d, t2.e FROM t1 JOIN t2 ON t1.b = t2.d;REFRESH FAST: enables incremental refresh. Since theREFRESH FASTmethod uses the information recorded in the materialized view log to determine what needs to be incrementally refreshed, you must create amaterialized view logon the base table before creating the materialized view.PARTITION BY HASH: improves parallel execution efficiency through partitioning.PARALLEL: specifies the degree of parallelism to accelerate data processing.
Optimize queries:
- For the original query
SELECT * FROM t1 JOIN t2 ON ..., OceanBase Database automatically rewrites it to query the materialized viewmv2. - As the base table's data volume increases, the precomputed advantages of the materialized view become more pronounced (as shown in the figure below).
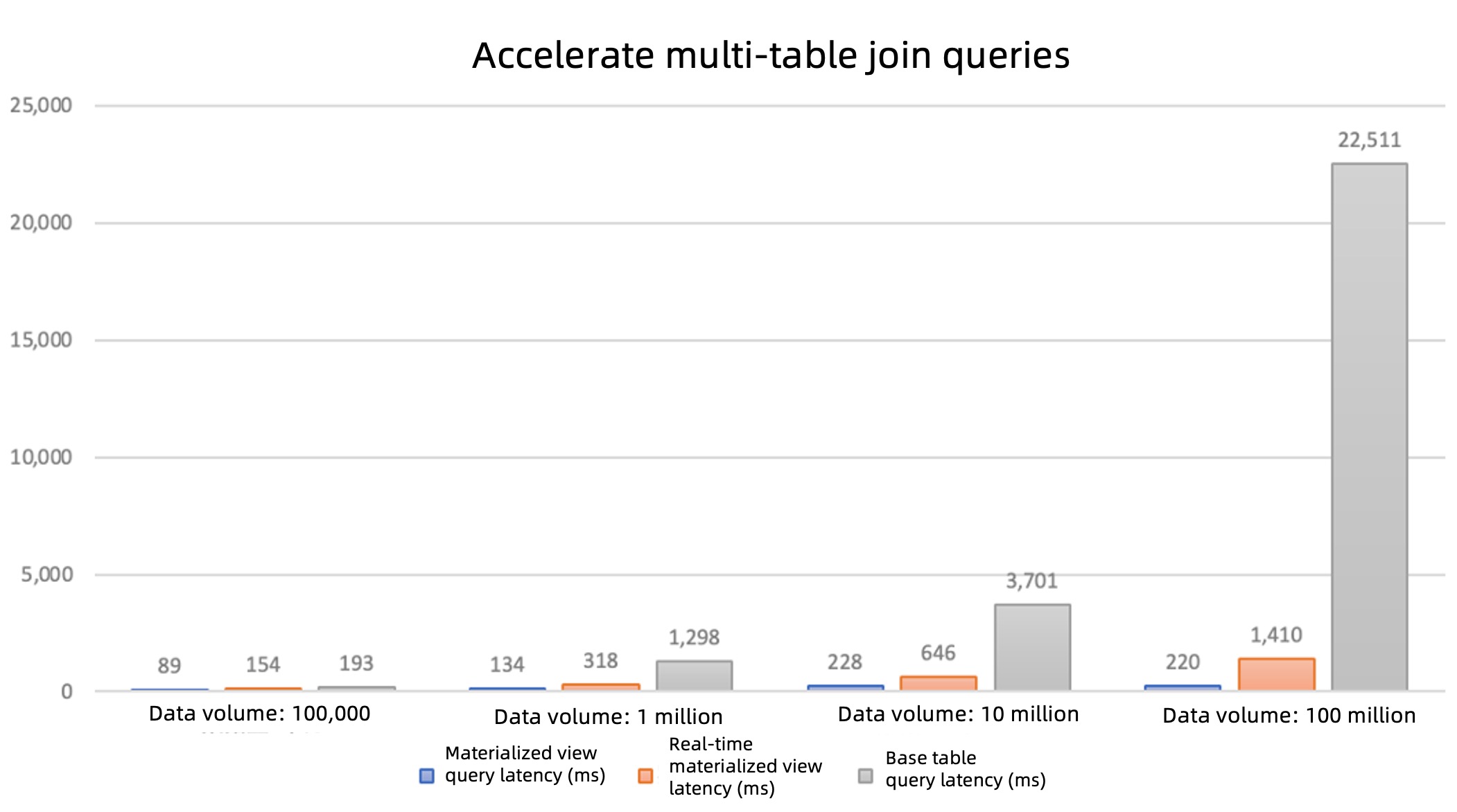
- For the original query
Scenario 3: Build a real-time data warehouse architecture
Key advantages
- Simplified ETL process: Define a simpler ETL process using SQL in the database.
- Stream-based incremental processing: Perform incremental refreshes and stream-based processing to achieve near-real-time data updates.
- ACID guarantees: Data stream tasks are implemented using transactions, ensuring ACID properties.
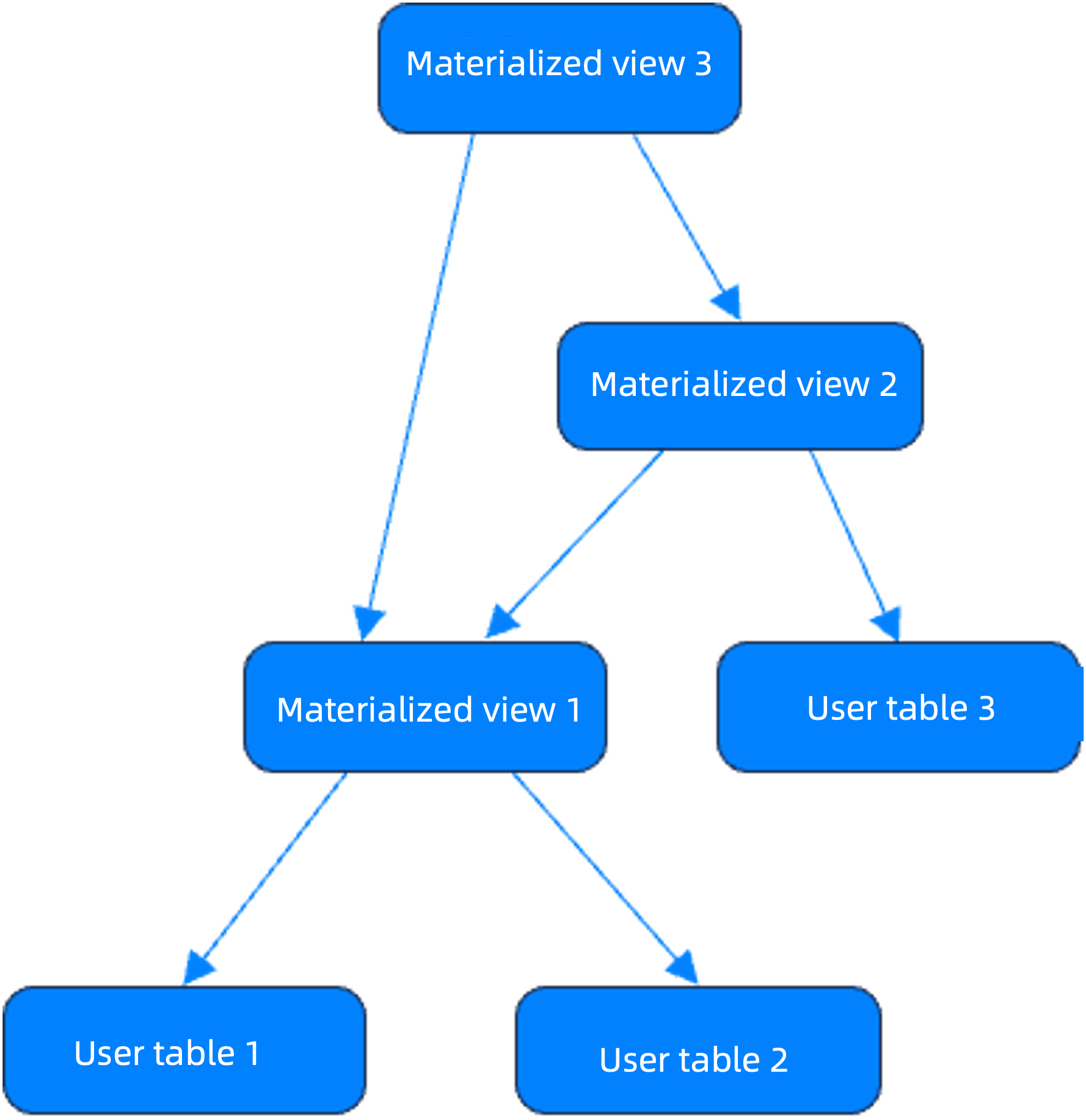
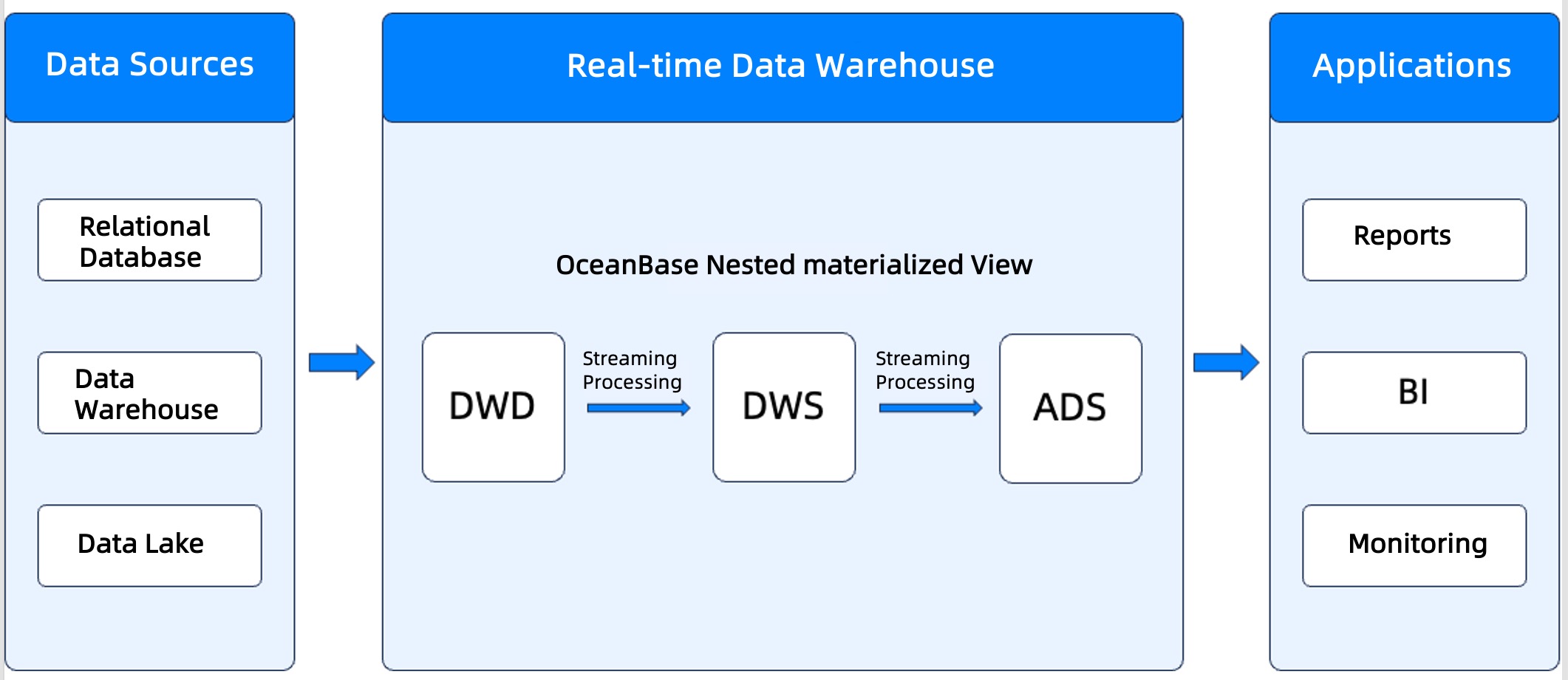
Procedure
Create a materialized view for multi-table joins and perform dimension expansion (multi-table join):
CREATE MATERIALIZED VIEW mv_join PARALLEL 5 REFRESH FAST START WITH SYSDATE() NEXT SYSDATE() + INTERVAL '5' SECOND AS SELECT t1.a, t1.b, t1.c, t2.d, t2.e, t3.f, t3.g FROM t1 JOIN t2 ON t1.b = t2.d JOIN t3 ON t1.b = t3.f;REFRESH FAST: enables incremental refresh. Since theREFRESH FASTmethod uses the information recorded in the materialized view log to determine what needs to be incrementally refreshed, you must create amaterialized view logon the base table before creating the materialized view.
Create an aggregate analysis materialized view based on
mv_join:CREATE MATERIALIZED VIEW mv_agg PARALLEL 5 REFRESH FAST START WITH SYSDATE() NEXT SYSDATE() + INTERVAL '5' SECOND AS SELECT b, SUM(c) AS sum_c, SUM(e) AS sum_e, SUM(g) AS sum_g, COUNT(*) AS cnt FROM mv_join GROUP BY b;Build a multi-layer ETL process.
- Use nested materialized views (such as
mv_aggbased onmv_join) to achieve complex data processing. - Set the refresh intervals independently for each materialized view.
- Use nested materialized views (such as
Key configuration considerations
Refresh strategy
Full refresh (
REFRESH COMPLETE): This strategy is suitable for scenarios where data changes are infrequent. However, it requires rebuilding all data during each refresh, which results in higher resource consumption.Incremental refresh (
REFRESH FAST): This strategy is designed to handle changed data and offers better performance. Currently, incremental refresh supports SQL statements for single-table aggregation, multi-table joins, and multi-table join aggregations. Starting from V4.3.5 BP3, it also supports single-table predicate filtering, left joins, and union all.
Real-time query capability
- Enable real-time query (
ENABLE ON QUERY COMPUTATION): When enabled, this option automatically merges the latest data from materialized views with incremental data during queries, providing real-time results. It is ideal for real-time analytics queries that require optimization.
Parallelism and partitioning optimization
PARALLEL: specifies the degree of parallelism to accelerate data processing.PARTITION BY: enhances query performance by distributing data across partitions.






