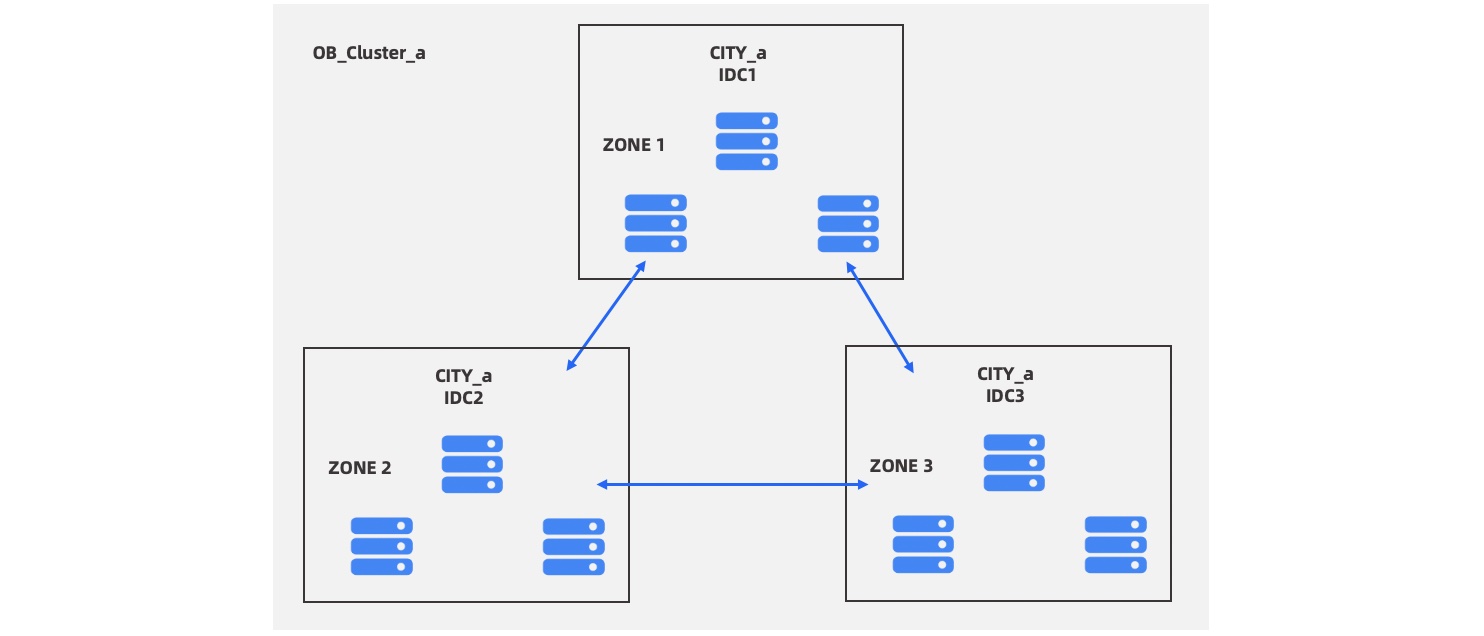
An OceanBase cluster consists of several zones. Zone is short for availability zone. A zone is a logical container that manages physical machines, usually a group of servers in the same IDC. At the physical level, a zone is usually equivalent to an equipment room, a data center, or an IDC. To deliver high-level data security and service availability capabilities, an OceanBase cluster is usually distributed in three IDCs in the same city. Three replicas of the same data are distributed in the three IDCs, which means three zones.
OceanBase Database supports cross-region deployment with the regions located far away from each other for remote disaster recovery. A region can have one or more zones. For example, an OceanBase cluster is deployed in three IDCs in a city (region), with three servers in each IDC. In this case, the three servers in each IDC form a zone.
Notice
A region is not an object in an OceanBase database but a key attribute of a zone. Tenants, databases, and data partitions (tables and indexes) at different levels are configured with primary zones for high availability and load balancing. The primary zone indicates a preferred location for scheduling the leader. If a primary zone is specified, the leader tends to be scheduled to the primary zone.
OceanBase Database supports the following two types of zones:
Read/Write zone
The zone that supports read/write operations. You can deploy full-featured replicas, read-only replicas, and common log replicas in the zone.
Encrypted zone
The zone that is encrypted. You can deploy only encrypted log replicas in the zone.
More information
For more information about the primary zone, see Primary zone.
For more information about replicas, see Replica overview.






