User tenants are a kind of tenants in database management systems. A user tenant is equivalent to a database instance. A system tenant can create user tenants.
The characteristics of a user tenant are the same as that of a database instance. Major characteristics:
A user tenant can create its users.
A user tenant can create all objects such as databases and tables.
A user tenant has a separate set of system tables and system views.
A user tenant has a separate set of system variables.
A user tenant has other characteristics of a database instance.
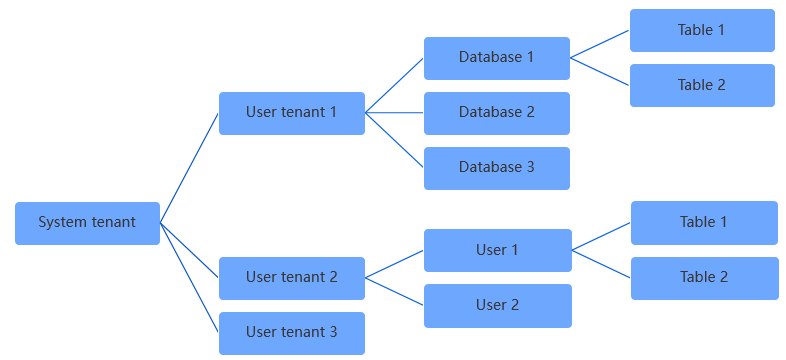
The metadata of all user data is stored in user tenants. Each tenant is assigned a unique namespace that is isolated from other namespaces. The system tenant manages all user tenants. The following figure shows the hierarchy between the system tenant and user tenants.
System tables for tenants
User tenants are independent of and are isolated from the system tenant. However, user tenants cannot perform bootstrap actions. The metadata of system tables for user tenants inherits the metadata of the system tenant. The location information about system tables for user tenants is stored in the __all_root_table table of the system tenant.
The following figure shows the tables that store object metadata or location information about system tables for a user tenant.

You can draw the following conclusions based on the preceding figure:
Replica location information
Location information about the user table for the tenant is stored in the
__all_tenant_meta_tabletable of the tenant. Location information about system tables for all tenants is stored in the__all_root_tabletable of the system tenant. Location information about the__all_root_tabletable is stored in the__all_core_tabletable. Location information about the__all_core_tabletable resides in the memory of RootService.To find the location of a replica of a user table partition, you must find the
__all_tenant_meta_tabletable. To find the__all_tenant_meta_tabletable, you must find the__all_root_tabletable, and then find the__all_core_tabletable based on the__all_root_tabletable. Then, you can identify the location of RootService.Object metadata
The object metadata of the user table for the tenant is stored in object metadata-related tables of the tenant. The object metadata of the system table for the user tenant inherits object metadata of the system table for the system tenant.
For example, the
__all_table_v2table of the tenant stores information about all user tables in the cluster. The object metadata of the__all_table_v2table inherits the object metadata of the__all_table_v2table of the system tenant. The object metadata of the__all_table_v2table of the system tenant is stored in the__all_core_tabletable. The schema of the__all_core_tabletable is hard-coded.
Create a user
Users that are created in a user tenant can log on to only the user tenant and are invisible to other tenants.
You can query user information about a MySQL-compatible tenant in the mysql.user view.
You can query user information about an Oracle-compatible tenant in the ALL_USERS view.
Create a user table
Other tenants cannot view the tables that are created in a user tenant.
You can query all user tables of a MySQL-compatible tenant in the information_schema.tables view.
You can query all user tables of an Oracle-compatible tenant in the ALL_TABLES view.
Modify system variables
A user tenant can modify only its own system variables.
You can query the system variables of a MySQL-compatible tenant in the information_schema.global_variables and information_schema.session_variables views. You can also execute the SHOW VARIABLES statement to query the system variables of a MySQL-compatible tenant.
To query the system variables of an Oracle-compatible tenant, execute the SHOW VARIABLES statement.
Location information
Each user tenant has a __all_tenant_meta_table table, which records the physical location metadata of user tables for the user tenant.






