Transport Layer Security (TLS) is a cryptographic protocol that provides end-to-end communications security over networks. In addition to TCP, OceanBase Database also supports the Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) and TLS protocols to implement communication encryption.
The following figure shows the architecture of OceanBase Database, which consists of three parts.
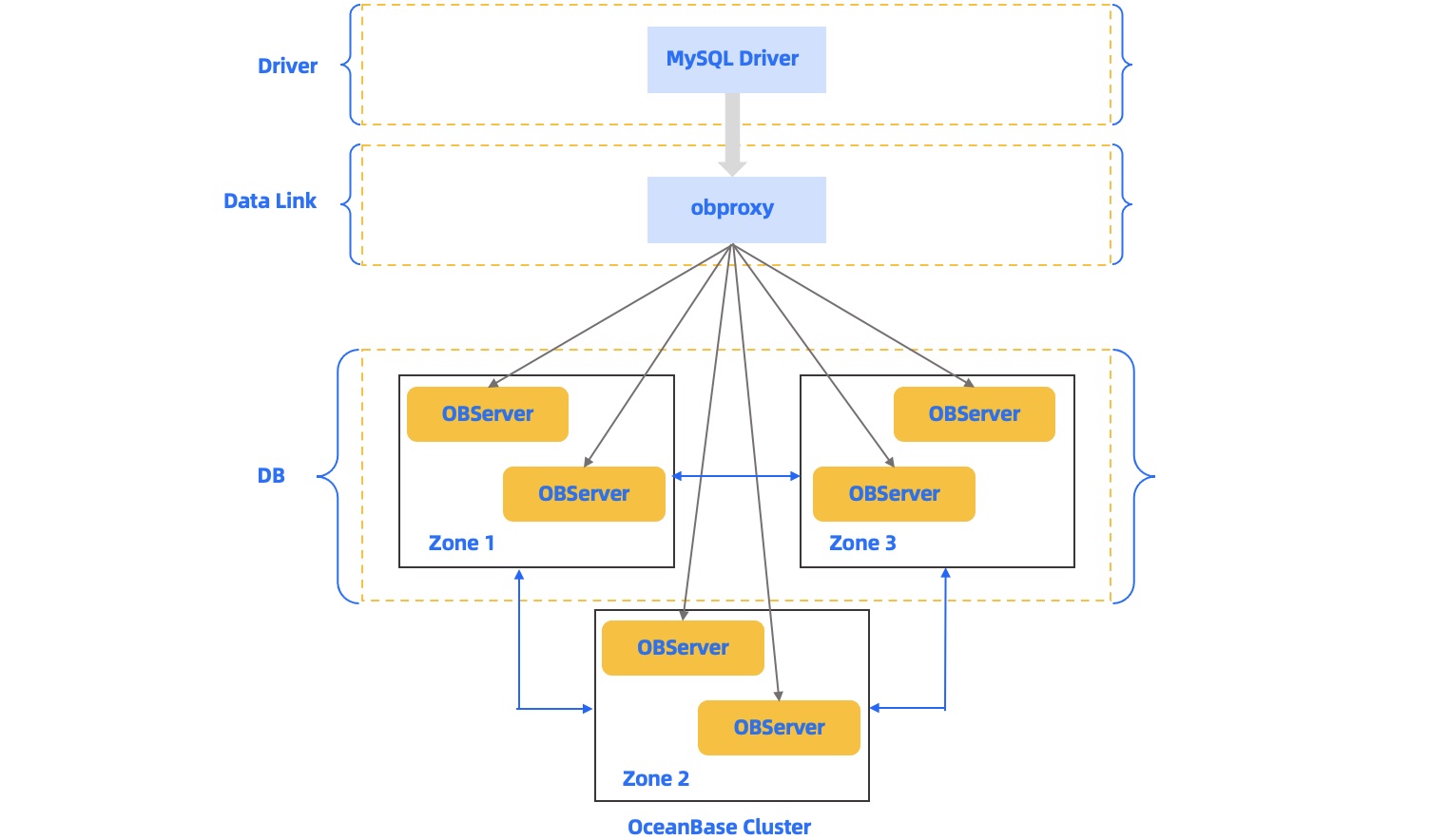
The three parts communicate over the following two protocols:
MySQL protocol: The data link layer communicates with the driver layer and the database layer over the extended MySQL protocol.
OB-RPC protocol: This is an RPC protocol for the communication between OBServers, and the communication between OBServers and liboblog and ob_admin.
The data link layer and the database components, such as OBServer, liboblog, and ob_admin, all support SSL/TLS encrypted communication. The communication depends on OpenSSL or a third-party SSL library to enable secure and encrypted data transmission.
Supported methods for loading private keys or certificates
The communication between OBServers, liboblog, and ob_admin depends on the libeasy library. Therefore, they all support the following two methods for loading private keys and certificates: the local file mode and the BKMI mode.
Local file mode
CA certificates, user certificates, and private keys are stored in the
wallet/directory and are loaded based on the configuration. This mode is not secure.BKMI mode
The basic key management infrastructure (BKMI) serves as a warehouse in which keys and certificates are generated and hosted. BKMI assigns the application identity private key and identity information to a user such as an OBServer. When the user needs to load a private key, it uses an URL to access the BKMI, obtains the encrypted private key from BKMI, and then uses the application identity private key to decrypt the application private key and load the configuration. This mode is highly secure.
Enable transmission encryption
You can perform the following steps to enable transmission encryption for an OBServer:
Specify the method for loading the private key, user certificate, or CA certificate.
To use the local file mode, run the following command:
alter system set ssl_external_kms_info = ' { "ssl_mode":"file" }';or
alter system set ssl_external_kms_info = '';To use the BKMI mode, run the following command:
alter system set ssl_external_kms_info = ' { "ssl_mode":"bkmi", "kms_host":"http://xxx", the url of the BKMI main site. "root_cert": the content of the CA certificate. "private_key": the application identity private key that BKMI provides for the user to decrypt the encrypted application private key, which is also obtained from BKMI. "PRIVATE_KEY_PHRASE":"123456", the password used to decrypt the application identity private key that BKMI assigns to the user. "SCENE":"ANT", the scenario. "CALLER":"xxx", the username that is assigned by BKMI to call the service. "CERT_NAME":"xxx", the name of the user certificate. "PRIVATE_KEY_NAME":"xxx", the name of the user private key. "KEY_VERSION":"1" }';Configure the corresponding SSL-enabled protocol.
alter system set ssl_client_authentication = 'TRUE'; SSL is enabled for MySQL communication when the parameter is set to TRUE.Configure an SSL allowlist for RPC communication. The TCP connections between OBServers are persistent connections. To enable SSL-encrypted RPC communication, restart the OBServers.
An allowlist is required to enable SSL-encrypted RPC communication. alter system set _ob_ssl_invited_nodes='ALL'; Enable SSL for the entire cluster. alter system set _ob_ssl_invited_nodes='123.12.21.12, 128.191.11.12'; Enable SSL only for OBServers of the specified IP addresses.
Check whether transmission encryption is enabled for an OBServer
The most straightforward approach is to capture packets from the MySQL and RPC ports of the OBServer to check whether the packets are encrypted. You can also use the following method:
Use the SYS tenant account to log on to the OBServer from OBClient or a MySQL client and query the
ssl_key_expired_timefield of theoceanbase.__all_virtual_server_stattable to check whether SSL is enabled.This field records the expiration time of the SSL certificate used by the current OBServer when SSL is enabled. The time is displayed in UTC in microseconds.
obclient> select svr_ip, svr_port,zone, ssl_key_expired_time, from_unixtime(ssl_key_expired_time/1000000) from oceanbase.__all_virtual_server_stat; +--------------+----------+-------+----------------------+---------------------------------------------+ | svr_ip | svr_port | zone | ssl_key_expired_time | from_unixtime(ssl_key_expired_time/1000000) | +--------------+----------+-------+----------------------+---------------------------------------------+ | xx.xx.xx.xx | 13212 | zone1 | 1871860075 | 2029-04-26 09:07:55 | +--------------+----------+-------+----------------------+---------------------------------------------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec)
Check whether SSL is enabled on the MySQL port
Log on to an OBServer from OBClient or a MySQL client and run the \s command to view the SSL field, as shown in the following example:
obclient> \s
--------------
obclient Ver 1.1.8 Distrib 5.7.24, for Linux (x86_64) using EditLine wrapper
Connection id: 3221506046
Current database: test
Current user: root@11.166.79.39
SSL: Cipher in use is DHE-RSA-AES128-GCM-SHA256
Current pager: less
Using outfile: ''
Using delimiter: ;
Server version: 5.7.25 OceanBase 2.2.60 (r1-63cbd3084a3283523f09d6ba20795f77b95e046b) (Built Jun 30 2020 10:10:29)
Protocol version: 10
Connection: xx.xx.xx.xx via TCP/IP
Server characterset: utf8mb4
Db characterset: utf8mb4
Client characterset: utf8mb4
Conn. characterset: utf8mb4
TCP port: 13213
Active --------------
Check whether SSL is enabled on the RPC port
Open the OBServer.log file, search for "rpc connection accept", and then check the value of use_ssl. If the value is True, SSL is enabled for RPC communication. Otherwise, SSL is disabled.






