You can create a tenant by using SQL statements or OceanBase Cloud Platform (OCP).
Create a tenant by using SQL statements
OceanBase Database supports two types of tenants: MySQL tenants and Oracle tenants. To create a tenant by using the CREATE TENANT statement, log on to the sys tenant as the root user (root@sys).
Syntax for creating a tenant
The syntax for creating a tenant is as follows:
CREATE TENANT [IF NOT EXISTS] tenant_name
[tenant_characteristic_list] [opt_set_sys_var];
tenant_characteristic_list:
tenant_characteristic [, tenant_characteristic...]
tenant_characteristic:
COMMENT 'string'
| {CHARACTER SET | CHARSET} [=] charsetname
| COLLATE [=] collationname
| ZONE_LIST [=] (zone [, zone...])
| PRIMARY_ZONE [=] zone
| DEFAULT TABLEGROUP [=] {NULL | tablegroup}
| RESOURCE_POOL_LIST [=](poolname [, poolname...])
| LOCALITY [=] 'locality description'
opt_set_sys_var:
{SET | SET VARIABLES | VARIABLES} system_var_name = expr [,system_var_name = expr] ...
The table below describes the parameters in the syntax.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| IF NOT EXISTS | Optional. If the tenant name already exists and IF NOT EXISTS is not specified, an error will be reported. |
| tenant_name | Like a variable, a tenant name can contain up to 128 characters, which can be letters, digits, and underscores (_). The tenant name must start with a letter or an underscore (_) and cannot be a keyword of OceanBase Database. For information about the keywords supported by OceanBase Database, see Reserved keywords (MySQL mode) and Reserved keywords (Oracle mode). |
| RESOURCE_POOL_LIST | Required. You can allocate only one resource pool to a tenant when you create the tenant. If you want to add multiple resource pools for a tenant, you can modify the resource pool of the tenant after the tenant is created.
Notice |
| DEFAULT TABLEGROUP | Optional. The default table group of the tenant. When you set it to NULL, the system disables the default table group. If this parameter is not specified, the default value is NULL. |
| COMMENT | Optional. The comment for the tenant. |
| CHARACTER SET | CHARSET | The character set of the tenant. For information about the character set, see Character sets. |
| COLLATE | The collation of the tenant. For information about the collation, see Collation. |
| ZONE_LIST | Optional. The list of zones of the specified tenant. By default, all zones in the cluster is included in the list. |
| PRIMARY_ZONE | The primary zone of the tenant. The primary zone indicates a preferred location for scheduling the leader. If a primary zone is specified, the leader tends to be scheduled to the primary zone. The primary zone is essentially a list of zones. When the primary zone list contains multiple zones, zones separated with semicolons (;) are arranged in descending order of priorities, and zones separated with commas (,) have the same priority. For example, primary_zone = 'zone1; zone2, zone3' indicates that the partition leaders of the tables of the tenant are located in zone1, zone1 has a higher priority than zone2 and zone3, and zone2 and zone3 have the same priority.
Notice For more information about the primary zone, see Primary zone. |
| LOCALITY | The distribution of replicas across the zones. For example, F@z1,F@z2,F@z3,R@z4 indicates that z1, z2, and z3 are full-featured replicas, and z4 is a read-only replica. |
| system_var_name | Optional. Specifies the system variables of the tenant.
For more information about the system variables available for tenants in OceanBase Database, see System variables. |
Examples
Create a MySQL tenant with three replicas. By default, a tenant in MySQL mode is created.
obclient> CREATE TENANT IF NOT EXISTS test_tenant CHARSET='utf8mb4', ZONE_LIST=('zone1','zone2','zone3'), PRIMARY_ZONE='zone1;zone2,zone3', RESOURCE_POOL_LIST=('pool1');Create an Oracle tenant with three replicas.
When you create an Oracle tenant, you must set the
ob_compatibility_modeparameter to specify the compatibility mode of the tenant.obclient> CREATE TENANT IF NOT EXISTS test_tenant CHARSET='utf8mb4', ZONE_LIST=('zone1','zone2','zone3'), PRIMARY_ZONE='zone1;zone2,zone3', RESOURCE_POOL_LIST=('pool1') SET ob_compatibility_mode='oracle';Create a MySQL tenant and specify the IP addresses of clients that can be connected.
obclient> CREATE TENANT IF NOT EXISTS test_tenant CHARSET='utf8mb4',ZONE_LIST=('zone1','zone2','zone3'), PRIMARY_ZONE='zone1;zone2,zone3', RESOURCE_POOL_LIST=('pool1') SET ob_tcp_invited_nodes='%' ;
Check whether the tenant is created
You can query the oceanbase.gv$tenant view to check whether the tenant is created.
Log on to the
systenant of OceanBase Database as therootuser (root@sys).Query the
oceanbase.gv$tenantview to check whether the new tenant exists in the cluster.Here is an example:
obclient> SELECT * FROM oceanbase.gv$tenant; +-----------+-------------+-----------+--------------+----------------+---------------+-----------+---------------+ | tenant_id | tenant_name | zone_list | primary_zone | collation_type | info | read_only | locality | +-----------+-------------+-----------+--------------+----------------+---------------+-----------+---------------+ | 1 | sys | zone1 | zone1 | 0 | system tenant | 0 | FULL{1}@zone1 | | 1001 | MySQL | zone1 | zone1 | 0 | | 0 | FULL{1}@zone1 | | 1002 | Oracle | zone1 | zone1 | 0 | | 0 | FULL{1}@zone1 | +-----------+-------------+-----------+--------------+----------------+---------------+-----------+---------------+ 3 rows in set
What to do next
After a tenant is created, the password of the administrator user is empty by default. The administrator user of a MySQL tenant is root and that of an Oracle tenant is SYS. You can use the obclient -h10.10.10.1 -P2883 -uusername@tenantname#clustername -p -A command to log on to the database and then change the password of the administrator user. For more information about how to change the user password, see Change a user password (MySQL mode) and Change a user password (Oracle mode).
For more information about how to connect to a database, see Connect to OceanBase Database.
Create a tenant by using OCP
To create a tenant in OCP, you can use one of the following methods:
Go to the Tenant Management page from the navigation pane and create a tenant.
Go to the Tenant Management page of a specified cluster to create a tenant.
This section describes how to create a tenant on the Tenant Management page of a specified cluster.
Prerequisites
Before you create a tenant, ensure that:
The cluster is in the running state.
When your clusters are in the primary/standby mode, you can create tenants only in the primary cluster.
For more information about tenant management in the primary/standby cluster configuration, see Tenant management.
You have permissions of the CLUSTER_MANAGER role. Otherwise, request the administrator to assign the role. For more information, see "Edit a user" in the OCP User Guide of the corresponding version.
Procedure
Log on to the OCP console.
In the left-side navigation pane, click Clusters.
In the Clusters list, find the target cluster and click its name.
In the left-side navigation pane, click Tenant Management.
In the upper-right corner of the page that appears, click Create Tenant.
Specify Basic Information.
The cluster is specified to the current cluster by default.
Select the tenant mode.
Valid values: MySQL and Oracle. Default value: MySQL.
Specify Tenant Name.
The tenant name must be 2 to 63 characters in length and can contain letters, digits, and underscores (
_).Specify a custom or randomly generated initial password for the tenant administrator account.
The password of the tenant administrator account, which can be randomly generated. The administrator account is
rootin MySQL mode. The administrator account isSYSin Oracle mode.The password must be 8 to 32 characters in length, and contain at least two uppercase letters, two lowercase letters, two digits, and two special characters. The supported special characters are ~ ! @ # % ^ & * _ - + = ` | ( ) { } [ ] : ; ' , . ? /
Specify the character set and collation of the tenant.
The supported character sets are UTF8MB4, Binary, GBK, and GB18030. Default value: UTF8MB4. You do not need to specify the collation in Oracle mode.
Specify the parameters in the Replica Settings section.
By default, the system displays configurable zones based on the zone information of the selected cluster. If you do not need to create a replica in a zone, click the Delete icon to delete the zone. The zone information fields that need to be configured and their descriptions are listed in the following table.
Field Description Replica Type The type of the replica. Valid values: - Full-featured Replica
- Read-only Replica
- Log Replica
Select multiple full-featured replicas to ensure that they are in the majority.Unit Specification OCP has a set of built-in unit specifications. You can select the specification that you need from the list of unit specifications or click Add Specification at the bottom of the list to add a custom specification. For more information, see OCP resource unit specifications. Units The number of units in the zone. The number of resource units cannot exceed the number of OBServer nodes in the zone. Zone Priority Rankings The priorities of the zones. This priority order affects the priority order of the primary zone of the systenant.
The left-side list shows all zones in the cluster.
You can select one or more zones from the list box on the left to add them to the list box on the right. By default, the priority of a zone selected earlier is higher than that of a zone selected later, and the zones selected at one time have the same priority. After you add the zones to the box on the right side, you can also drag them upward or downward to adjust their priorities. The zones in the box on the right are sorted in descending order of priorities.Specify the IP address allowlist in the Security Settings section.
In the IP Address Whitelist, you can specify a list of clients that are allowed to access this tenant. If you specify Default, the default value is %, which indicates that all client connections are allowed.
If you specify Custom, you must add the IP addresses of the OCP and OceanBase Database Proxy (ODP) servers to the allowlist. Otherwise, you cannot manage the tenant from OCP.
Configure the allowlist in the following formats:
IP address example: 10.10.10.10, 10.10.10.11.
Subnet mask example: 10.10.10.0/24.
Fuzzy match example: 10.10.10.% or 10.10.10._.
Mixed format example: 10.10.10.10, 10.10.10.11, 10.10.10.%, 10.10.10._, 10.10.10.0/24.
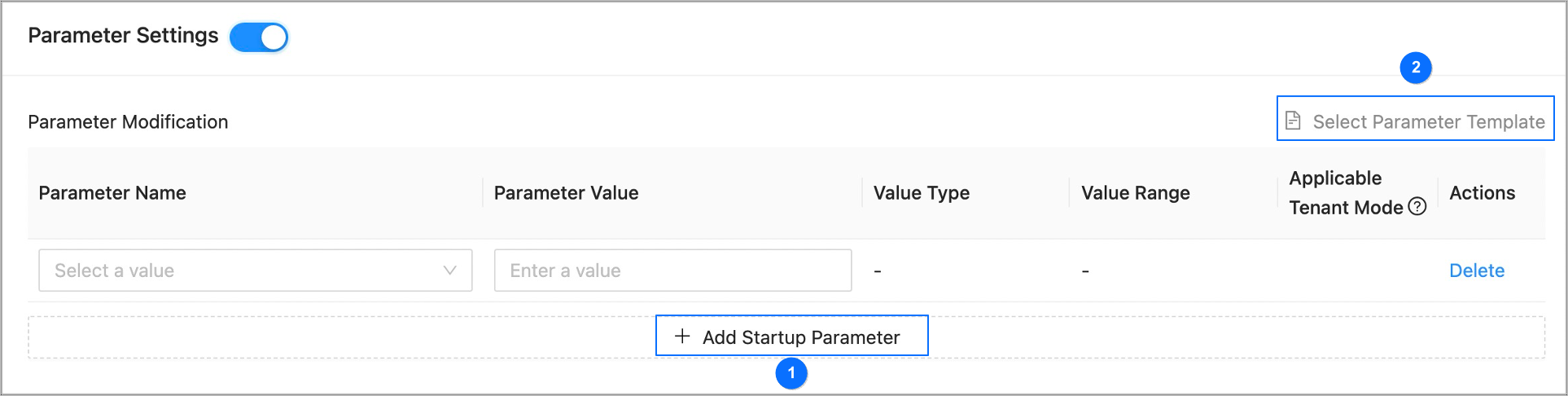
Enable the Parameter Settings section and configure the tenant parameters.
You can add startup parameters one by one and set values as shown in section ① of the following figure.
You can also move the pointer over Select Parameter Template as shown in section ② of the following figure, and select a parameter template. The system will automatically populate parameters in this section by using the template.
If you are creating a tenant in MySQL mode by using a parameter template that contains parameters that are valid only in Oracle mode, you must manually delete those parameters.
Click Submit.
In the dialog box that appears, click View Task to view the task progress.
When the task status is Completed, you can check the status of the new tenant in the Tenants list on the Tenant Management page. The new tenant is created if its status is Running.






