The protection mode defines whether the primary cluster synchronously or asynchronously transfer logs to different standby clusters, how the standby clusters receive the logs, and whether the data is lossless.
OceanBase Database provides two fields to specify the protection mode and the status of the primary and standby clusters: PROTECTION_MODE and PROTECTION_LEVEL. This topic describes the values of the fields in two scenarios.
Switch from the maximum performance mode to the maximum protection mode
By default, the primary and standby clusters are in maximum performance mode. In this mode, the primary cluster asynchronously transfers logs to all standby clusters. The data of the standby clusters is out-of-sync with that of the primary cluster and is lossy. Both the protection mode and protection level of the primary and standby clusters are displayed as MAXIMUM PERFORMANCE.
In maximum protection mode, the primary cluster synchronously transfers logs to the standby cluster that is in SYNC mode so that the data of the standby clusters is lossless. The entire process of this mode is not atomic, and intermediate states exist. The following figure shows the state transition process of the <PROTECTION_MODE, PROTECTION_LEVEL> tuple when the protection mode switches from maximum performance to the maximum protection.
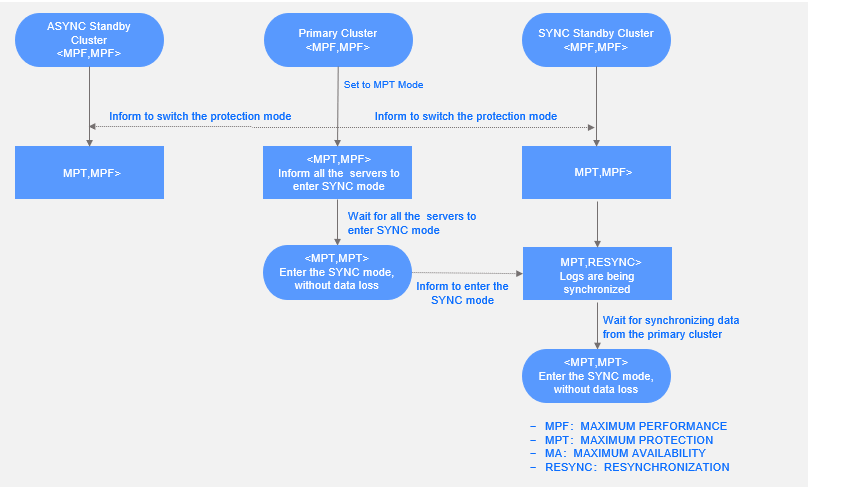 The state transitions are described as follows:
The state transitions are described as follows:
Initial status of the primary and standby clusters
The primary and standby clusters are in maximum performance mode. Both
PROTECTION_MODEandPROTECTION_LEVELareMAXIMUM PERFORMANCE.Status of the primary cluster after it receives the protection mode switchover command:
PROTECTION_MODEof the primary cluster changes toMAXIMUM PROTECTION, andPROTECTION_LEVELof the primary cluster is stillMAXIMUM PERFORMANCE. Then, the primary cluster instructs all servers to synchronously transfer logs to the standby cluster that is inSYNCmode.After all servers enter the SYNC mode,
PROTECTION_LEVELof the primary cluster changes toMAXIMUM PROTECTION, indicating that the primary cluster enters the SYNC mode.Notice
Data writes are not interrupted in this process. Only the logs written after the primary cluster enters the SYNC mode are synchronously transferred, and the previously committed logs are not affected.
Status of a standby cluster in
SYNCmode after it perceives the protection mode switchover:PROTECTION_MODEof the standby cluster changes toMAXIMUM PROTECTION, andPROTECTION_LEVELof the standby cluster is stillMAXIMUM PERFORMANCE.After the primary cluster enters the SYNC mode,
PROTECTION_LEVELof the standby cluster changes toRESYNCHRONIZATION, indicating that the logs are being synchronized to the standby cluster. In this state, the standby cluster synchronizes logs from the primary cluster.After logs are synchronized,
PROTECTION_LEVELof the standby cluster changes toMAXIMUM PROTECTION, indicating that the data of the standby cluster is consistent with that of the primary cluster and is losses.
Status of a standby cluster in
ASYNCmode after it perceives the protection mode switchover:PROTECTION_MODEof the standby cluster changes toMAXIMUM PROTECTION. The standby cluster is in ASYNC mode, soPROTECTION_LEVELof the standby cluster is alwaysMAXIMUM PERFORMANCE.
Switch from the maximum performance mode to the maximum availability mode
The maximum availability mode combines the maximum performance and maximum protection modes. In maximum availability mode, the primary cluster has two states: synchronously transferring logs to the standby cluster that is in SYNC mode, and asynchronously transferring logs to the standby cluster that is in SYNC mode. The primary cluster dynamically switches between the two states, affecting the status of the standby clusters. The following figure shows the state transition process of the <PROTECTION_MODE, PROTECTION_LEVEL> tuple when the protection mode switches from maximum performance to maximum availability. The state transitions are described as follows: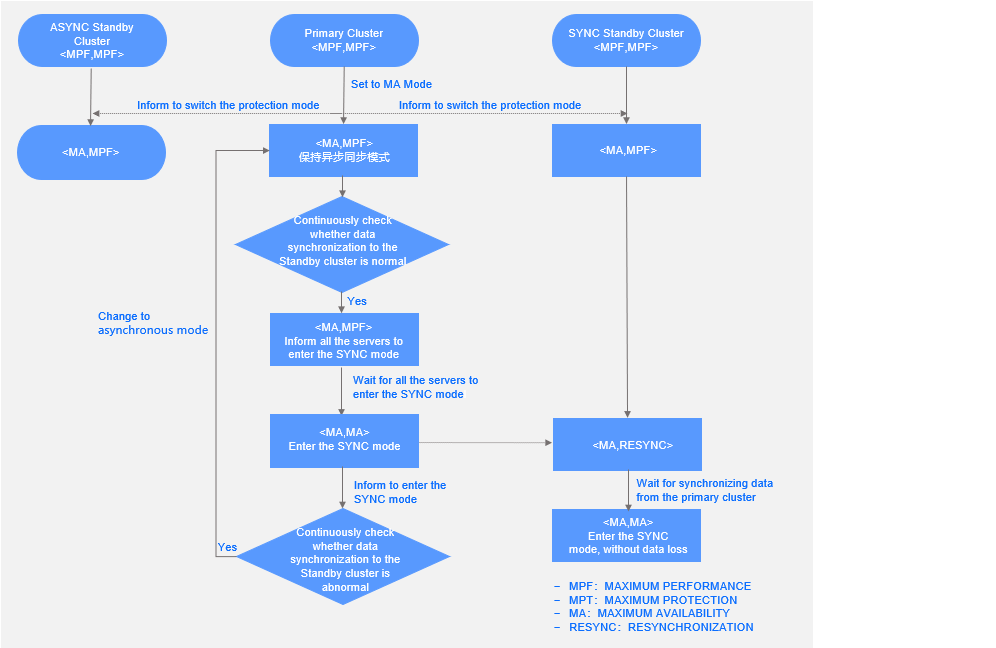
Initial status of the primary and standby clusters
The primary and standby clusters are in maximum performance mode. Both
PROTECTION_MODEandPROTECTION_LEVELareMAXIMUM PERFORMANCE.Status of the primary cluster after it receives the protection mode switchover command:
PROTECTION_MODEof the primary cluster changes toMAXIMUM AVAILABILITY, andPROTECTION_LEVELof the primary cluster is stillMAXIMUM PERFORMANCE, indicating that the primary cluster is still in ASYNC mode.Then, the primary cluster constantly checks whether log synchronization to the standby clusters. If yes, the primary cluster instructs all servers to synchronously transfer logs to the standby cluster that is in
SYNCmode.After all servers enter the SYNC mode,
PROTECTION_LEVELof the primary cluster changes toMAXIMUM AVAILABILITY, indicating that the primary cluster enters the SYNC mode.The primary cluster remains in SYNC mode. If the primary cluster detects a log synchronization exception in the standby cluster in
SYNCmode, the primary cluster is automatically downgraded to the ASYNC mode, andPROTECTION_LEVELof the primary cluster changes toMAXIMUM PERFORMANCE.
Status of a standby cluster in
SYNCmode after it perceives the protection mode switchover:PROTECTION_MODEof the standby cluster changes toMAXIMUM AVAILABILITY.Same the case in the maximum protection mode, after the primary cluster enters the SYNC mode,
PROTECTION_LEVELof the standby cluster changes toRESYNCHRONIZATION, indicating that logs are being synchronized to the standby cluster.After logs are synchronized,
PROTECTION_LEVELof the standby cluster changes toMAXIMUM AVAILABILITY, indicating that the standby cluster is in SYNC mode, and the data of the standby cluster is consistent with that of the primary cluster and is losses.
Status of a standby cluster in
ASYNCmode after it perceives the protection mode switchover:PROTECTION_MODEof the standby cluster changes toMAXIMUM AVAILABILITY. The standby cluster is in ASYNC mode, soPROTECTION_LEVELof the standby cluster is alwaysMAXIMUM PERFORMANCE.
As can be learned from the foregoing two scenarios, PROTECTION_MODE is shared across the primary and standby clusters, and indicates the data protection capabilities of the primary and standby clusters in the current configurations.
The values of PROTECTION_MODE are described as follows:
MAXIMUM PERFORMANCE: The maximum performance mode. In this mode, the primary cluster asynchronously transfers logs to all standby clusters.MAXIMUM PROTECTION: The maximum protection mode. In this mode, the primary cluster synchronously transfers logs to the standby cluster that is inSYNCmode.MAXIMUM AVAILABILITY: The maximum availability mode. In this mode, the primary cluster synchronously transfers logs to the standby cluster that is inSYNCmode and can be automatically downgraded to the ASYNC mode as required.
PROTECTION_LEVEL is specific to clusters and has different meanings for the primary cluster and the standby clusters. PROTECTION_LEVEL of the primary cluster specifies whether the primary cluster synchronously transfers logs to standby clusters. PROTECTION_LEVEL of a standby cluster indicates whether the standby cluster is in SYNC mode and whether data is lossless.
The values of PROTECTION_LEVEL are described as follows:
MAXIMUM PERFORMANCE: indicates that the primary and standby clusters are in ASYNC mode.MAXIMUM PROTECTION: indicates that the primary cluster synchronously transfers logs to the standby cluster that is inSYNCmode with maximum protection, or indicates that a standby cluster is in SYNC mode and data is lossless.MAXIMUM AVAILABILITY: indicates that the primary cluster synchronously transfers logs to the standby cluster that is inSYNCmode with maximum availability, or indicates that the standby cluster is in SYNC mode and data is lossless.RESYNCHRONIZATION: indicates that logs are being synchronized to the standby cluster. This state is unavailable for the primary cluster.
The following table describes the protection levels of the primary and standby clusters in different protection modes.
| Protection mode | Primary cluster at the MAXIMUM PERFORMANCE level | Primary cluster at the MAXIMUM PROTECTION level | Primary cluster at the MAXIMUM AVAILABILITY level |
|---|---|---|---|
| MAXIMUM PERFORMANCE | * Protection level of standby clusters in SYNC mode: MAXIMUM PERFORMANCE * Protection level of standby clusters in ASYNC mode: MAXIMUM PERFORMANCE |
N/A | N/A |
| MAXIMUM PROTECTION | If the primary cluster is temporarily at the MAXIMUM PERFORMANCE level: * Protection level of standby clusters in SYNC mode: MAXIMUM PERFORMANCE * Protection level of standby clusters in ASYNC mode: MAXIMUM PERFORMANCE |
* Protection level of standby clusters in SYNC mode: MAXIMUM PROTECTION or RESYNCHRONIZATION * Protection level of standby clusters in ASYNC mode: MAXIMUM PERFORMANCE |
N/A |
| MAXIMUM AVAILABILITY | * Protection level of standby clusters in SYNC mode: MAXIMUM PERFORMANCE * Protection level of standby clusters in ASYNC mode: MAXIMUM PERFORMANCE |
N/A | * Protection level of standby clusters in SYNC mode: MAXIMUM AVAILABILITY or RESYNCHRONIZATION * Protection level of standby clusters in ASYNC mode: MAXIMUM PERFORMANCE |
View the protection mode and protection level of a cluster
Log on to the cluster and check the PROTECTION_MODE and PROTECTION_LEVEL columns in the V$OB_CLUSTER view.
obclient> SELECT PROTECTION_MODE, PROTECTION_LEVEL FROM V$OB_CLUSTER;
+--------------------+--------------------+
| PROTECTION_MODE | PROTECTION_LEVEL |
+--------------------+--------------------+
| MAXIMUM PROTECTION | MAXIMUM PROTECTION |
+--------------------+--------------------+
1 row in set






