Description
You can execute the SAVEPOINT statement to perform a partial rollback of a transaction.
Syntax
- Create a savepoint:
SAVEPOINT spname
- Roll back to a savepoint:
ROLLBACK [WORK] to [SAVEPOINT] spname
- Delete a savepoint:
RELEASE SAVEPOINT spname
Parameters
- spname: specifies the name of the savepoint. Savepoints are unique within a transaction. If the specified name of a savepoint already exists, the new savepoint overwrites the existing savepoint. After a savepoint is created, the transaction can be rolled back to the savepoint. You can also execute the
ROLLBACKstatement to roll back the entire transaction.
Examples
Assume that a transaction has executed the following statements:
| sql_no | Statement | Partition |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | update... | p1, p4 |
| savepoint sp1 | ||
| 2 | update... | p2, p4 |
| 3 | update... | p3, p5 |
| savepoint sp2 | ||
| 4 | update... | p1, p3, p6 |
| 5 | update... | p1, p5 |
| savepoint sp3 | ||
| 6 | select... | |
| 7 | update... | p5, p6 |
| savepoint sp4 |
Record a savepoint
You can create savepoints before you submit transactions. You must connect the transaction savepoints into a linked list based on the order in which the savepoints are created. The preceding transaction contains seven SQL statements and four savepoints. The following figure shows the linked list of savepoints, where each node records a mapping from the spname to the sql_no.
List of transaction participants
To roll back all changes after an SQL statement is executed in a transaction, the participants and sql_no of each statement must be recorded. The preceding transaction executes seven SQL statements and involves six partitions from p1 to p6.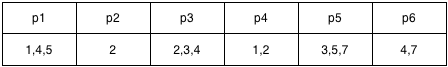
Roll back to a savepoint
- Find the sql_no that corresponds to the spname based on the savepoint linked list.
Assume that you have executed the ROLLBACK to SAVEPOINT sp2 statement. In the linked list of savepoints, sp2 corresponds to sql_no:3.
- Find the partitions that correspond to the sql_no based on the list of transaction participants.
The query result shows that the statements whose sql_no values are greater than 3 involve partitions p1, p3, p5, and p6.
- Roll back the data in partitions
The scheduler initiates a rollback request to the partitions obtained in Step 2. All changes caused by the transaction after sp2 are rolled back in these partitions. Some changes caused by this transaction in p1, p3, and p5 are rolled back, and all changes in p6 are rolled back.
- Update the transaction participant list
ApsaraDB for OceanBase modifies the transaction participant list and deletes the information about operations that have sql_no greater than 3 from the transaction participant list. p6 is deleted from the transaction participant list because all changes in p6 are rolled back.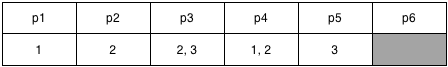
- Delete an invalid savepoint
After you execute the ROLLBACK to SAVEPOINT sp2 statement, the system deletes savepoints sp3 and sp4. In this case, you cannot roll back to sp3 or sp4.






