Description
This alert is triggered when a zone of an OceanBase cluster fails to be compacted in three hours.
Note
Major compaction timeout does not mean that the major compaction has stopped. Instead, the major compaction is still in progress. The timeout alert is sent to remind you that the operation remains unfinished after the expected finish time. You need to find out the causes and take necessary actions.
Principle
The following table describes the key parameters that are involved in the monitoring and alerting logic.
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Metric | ob_cluster_merge_timeout_flag |
| Source | SQL: select zone, name, value, time_to_usec(now()) from __all_zone; Note: The value of the value field is used as the value of the zone_value metric, and the values of other fields are used as labels. |
| Collected metric | zone_value |
| Metric expression | max(zone_value{metric_group="all_zone",name="is_merge_timeout",@LABELS}) by (@GBLABELS) |
| Collection cycle | 1 second |
For a major compaction task that is initiated automatically or manually, after the task run time exceeds 10,800 seconds (three hours), the flag bit is set and the major compaction status is updated in the __all_zone table.
Note
The default value of the zone_merge_timeout parameter is 10,800 seconds, which can be customized.
The value of the metric indicates the cluster compaction timeout status. Valid values: 0 and 1.
Note
When the value is 0, the cluster compaction is normal. When the value is 1, the cluster compaction timed out and the alert is triggered.
Alert rule
| Metric | Default threshold | Duration | Detection cycle | Time before clearance |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ob_cluster_merge_timeout_flag | 1 | 0 seconds | 60 seconds | 5 minutes |
Alert information
| Trigger method | Alert level | Scope |
|---|---|---|
| Metric expression | Critical | Cluster |
Alert templates
Overview: /${alarm_target} /${alarm_name}
Details: /${alarm_target} /${alarm_name}
Overview example: ob_cluster=C1-1000. OceanBase cluster compaction timed out.
Details example: ob_cluster=C1-1000. OceanBase cluster compaction timed out.
Impact on the system
When a major compaction times out, the storage pressure of the disk increases. If users go on writing data to it, the disk will be full, blocking services of the server. When you use OceanBase Database of an earlier version, the memory will be used up and the cluster will stop writing.
Possible causes
This problem is commonly found in the following scenarios:
The OceanBase cluster has a huge amount of data to compact.
An error occurred with the disk.
The major compaction efficiency of the disk medium is low.
When the CPU and memory specifications are the same, the major compaction efficiency depends on the disk medium. For example, a Serial Advanced Technology Attachment (SATA) disk has a lower major compaction efficiency than that of a Solid State Disk (SSD).
Suggested solutions
If the problem is caused by a huge amount of data, modify the timeout value or thread parameters for major compaction. If the problem is caused by a disk failure, replace the corresponding OBServer. For more information, see Exception handling for OceanBase cluster compaction.
Check whether the major compaction is stuck on the Compaction Management page of the OCP console.
Go to the Compaction Management page.
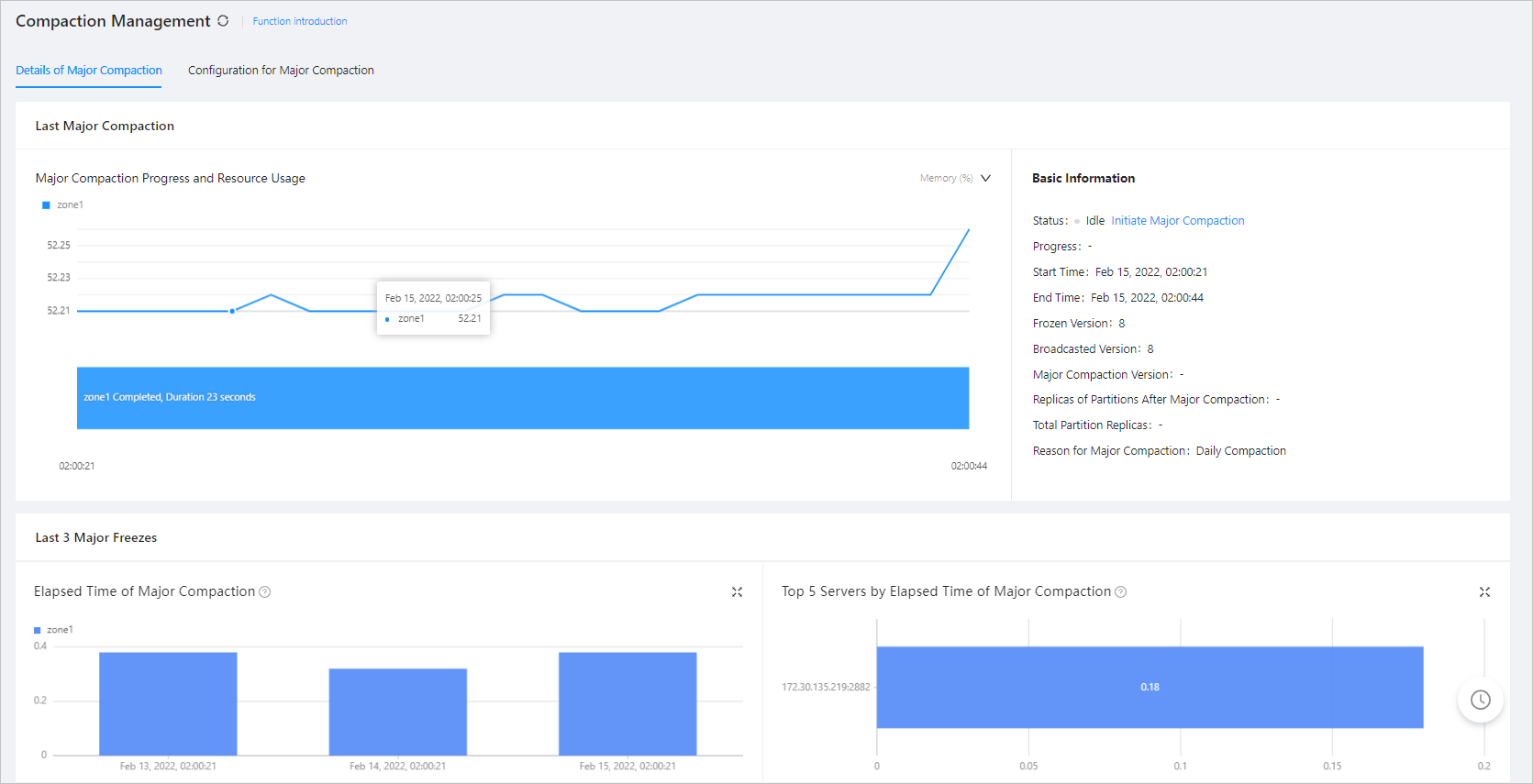
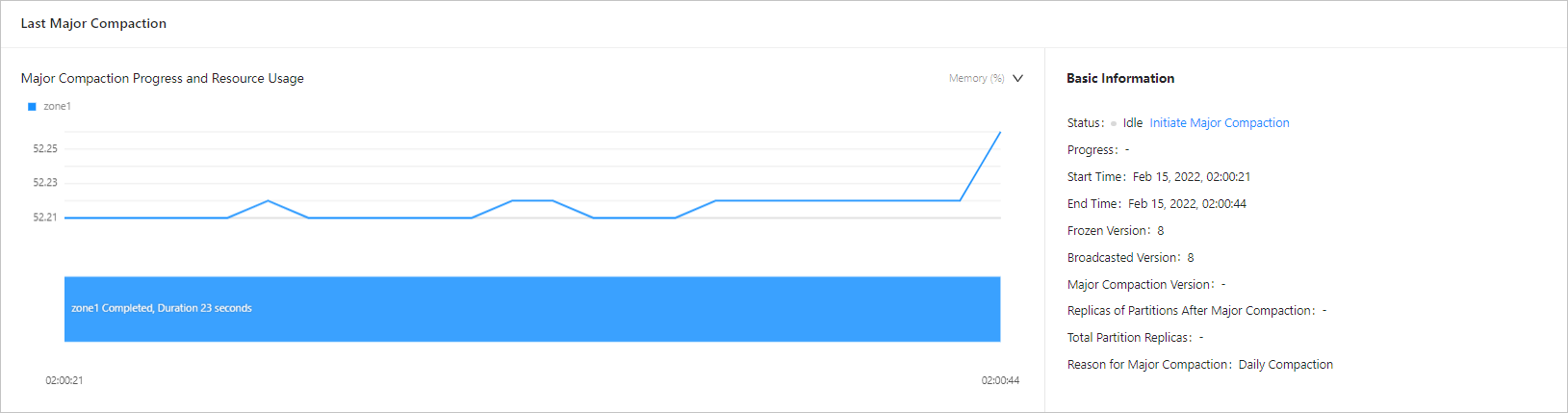
View the major compaction details on the Details of Major Freeze tab. The following figure shows the estimated end time, total partition replicas, and replicas of partitions after major compaction on this tab. Check the replicas of partitions after major compaction every minute. If the number increases, the major compaction is not stuck.
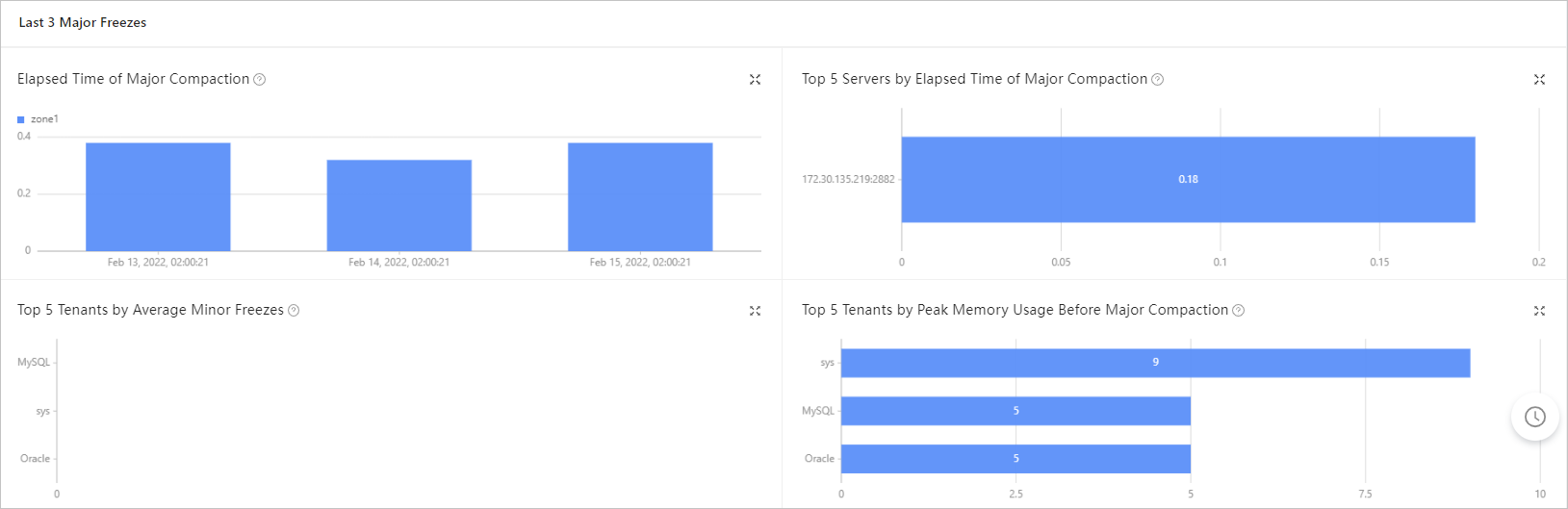
View the major compaction statistics. If the elapsed time of major compaction significantly increases compared with the last three major compactions with no business traffic surge in the recent days, an error may have occurred.
Based on the preceding analysis, if the major compaction is stuck, check for the faulty OBServer. For more information, see Exception handling for OceanBase cluster compaction.If the faulty OBServer must be replaced, replace it. For more information, see Replace an OBServer.
Based on the preceding analysis, if the major compaction is not stuck, go to the next step.
Check whether a large amount of business data needs to be compacted or the major compaction efficiency of the disk medium is low.
Adjust the timeout value or thread number for major compaction. Perform the following steps:
Choose Cluster Overview > Compaction Management > Configuration for Major Freeze > Major Freeze Strategy .
Click Modify .
Modify the Worker Threads for Major Freeze and Major Freeze Timeout Period parameters.

Click Save .






