This topic describes how to call an API operation of OceanBase Cloud Platform (OCP) in the HTTP mode, using the Query clusters operation as an example.
Request structure
A complete HTTP request includes a request URI, a request method , a request header , and a request body .
Request URI
A request URI consists of the following parts:
{scheme}://{endpoint}/{resource-path}?{query-string}
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| scheme | The transport protocol, which is typically HTTP or HTTPS. |
| endpoint | The endpoint of OCP, for example, xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx:8080, which is determined by the specific deployment. |
| resource-path | The resource path of the API. For more information about the resource path of each API, see the "Request path" section in the documentation of the corresponding API. For example, the resource path for the Query clusters API is /api/v2/ob/clusters. |
| query-string | The query parameters, which are optional key-value pairs in the format of a=10&b=hello. Separate query-string and resource-path with a question mark (?). |
The following example is a complete URI of the Query clusters API:
http://xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx:8080/api/v2/ob/clusters
Request method
A request method is an HTTP method, which can be GET, PUT, POST, or DELETE. The request methods of each API are described in the corresponding API documentation.
For example, in the request path GET /api/v2/ob/clusters, the request method of the Query clusters API is GET.
Request header
A request header contains the additional information of the request, such as the language and authentication information.
| Parameter | Required | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Content-Type | Yes | The type of the message body. The OCP uses the application/json type message body uniformly. | application/json |
| Accept-Language | No | The language supported by the client. OCP APIs support internationalization, and can return content in the specified language based on the language settings of the client. | en-US, en, q=0.9 zh-CN |
| Authorization | Yes | The authentication information. OCP APIs use the Basic authentication in compliance with the HTTP specification. The user name and password are encoded in Base64. | Basic Zm9vOmJhcg== |
Request body
The request body is optional. It contains the service data sent to the server. OCP APIs use request bodies in the unified JSON format.
Authentication description
OCP APIs use client authentication in the HTTP Basic authentication mode.
When being called, the API use the Authorization attribute in the request header to pass the user/password in Base64 encoding.
For example, assume that the password of the user foo is bar. When user foo calls an OCP API, the following request header must be passed:
Authorization: Basic Zm9vOmJhcg==
Where, Zm9vOmJhcg== is the Base64 encoding of foo:bar.
Response structure
OCP APIs return data in a unified data structure, except for some special APIs. Data structure of the basic return result:
| Parameter | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| data | Object | Single-value data, list data, or paged data. |
| ├─ contents | Array | ├── indicates that the content is affiliated with the parameter in the previous row. |
| successful | Boolean | Whether the request is successful. |
| timestamp | Datetime | The timestamp when the server completes the request. |
| duration | Integer | The time that the server takes to process the request, in milliseconds. |
| status | Integer | The encoding in compliance with the HTTP Status specification. |
| traceId | String | The trace ID of the request. This trace ID is used for troubleshooting. |
| server | String | The address of the server that responds to the request. |
Call example
cURL
You can use the cURL tool to call APIs. In the following example, the user admin:hello calls the Query tenants API of an OCP application with the IP address xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx. Where, YWRtaW46aGVsbG8= is the Base64 encoding of admin:hello.
curl "http://xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx/api/v2/ob/clusters/1/tenants" \
-H "Authorization: Basic YWRtaW46aGVsbG8="
cURL also allows you to use a plaintext password to call an API.
curl "http://xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx/api/v2/ob/clusters/1/tenants" \
--user admin:hello
Note
However, the use of a plaintext password reduces security, so proceed with caution.
Internationalization
OCP APIs support internationalization. The API returns the content in the specified language based on the language settings of the client. You can refer to the API documentation to check whether an attribute support internationalization.
An OCP API uses the Accept-Language attribute in the request header to specify the language option of the client.
Throttling
OCP provides the throttling feature to prevent users from accessing OCP too frequently. When creating an OCP user, the system administrator can set a throttling strategy for the user. Resources subject to throttling include global paths, which include all HTTP requests except for static resources. Fine-grained access control allows you to set access limits for different types of resources in OCP. The throttling window can be set to 10s, 1 min, 1 h, and 1 day. 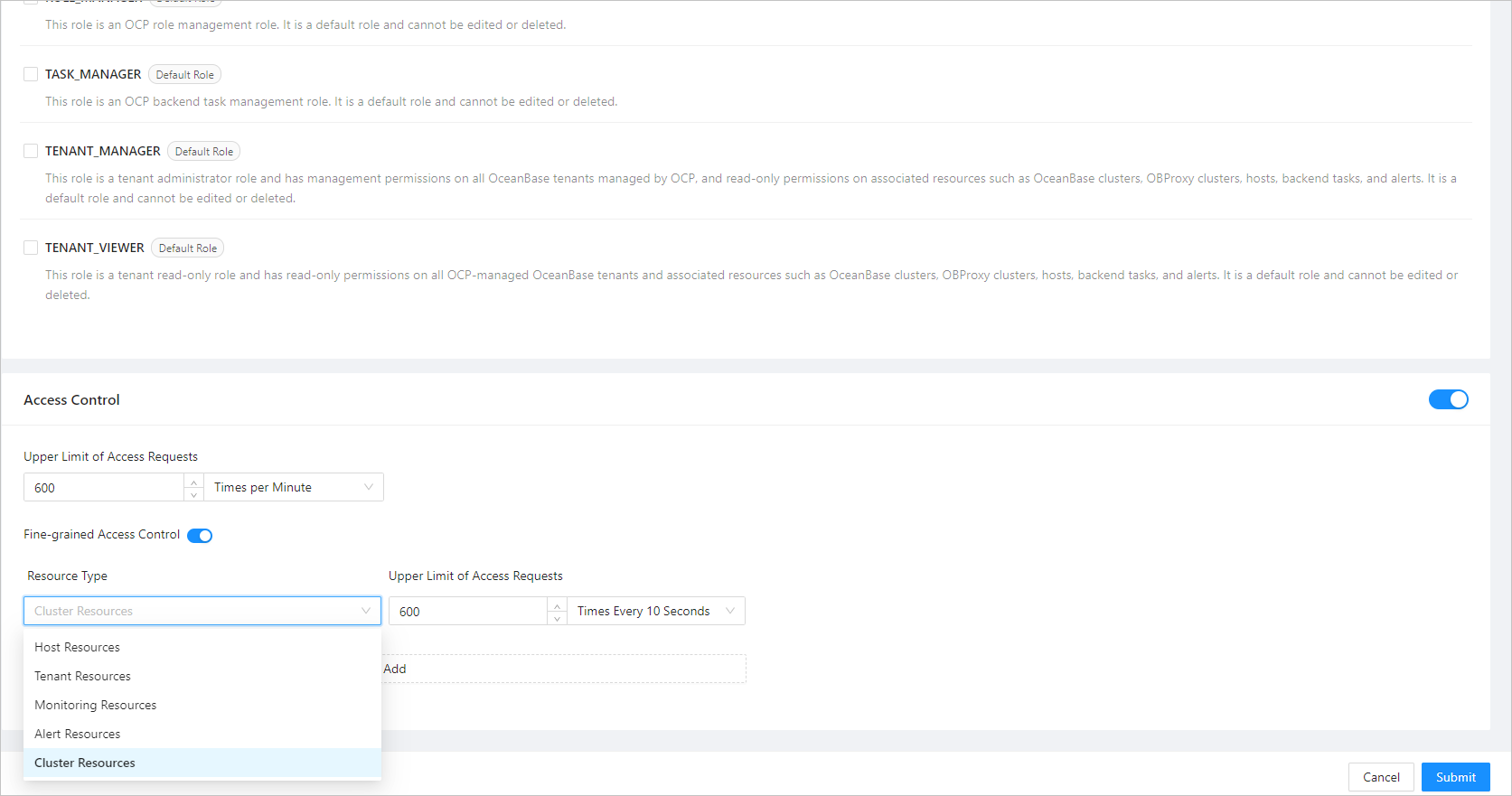
You can enable or disable the throttling feature by setting the ocp.iam.rate-limit.enabled system parameter. The default value is true, indicating that throttling is enabled.
When throttling is enabled, the returned header contains the following information:
RateLimit-Limit: The upper limit of access requests in the current time window, for example, 10.RateLimit-Remaining: The number of remaining access times in the current time window, such as "7".RateLimit-Reset: The countdown to the reset of the throttling time window, such as "53".
When a user accesses the corresponding resource interface exceeds the specified threshold in the time window, the request is rejected due to throttling, and the HTTP code 429 is returned. Return result:
{
"duration":0,
"error":{
"code":0,
"message":"Excessive number of requests. You have exceeded the request limit for the current throttling window."
},
"server":"xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx",
"status":429,
"successful":false,
"timestamp":"2020-12-03T09:38:24.194+08:00",
"traceId":""
}






