The syntax of SELECT is complex. This topic describes the syntax of common SELECT statements and aggregate SELECT statements.
Purpose
You can use this statement to query data from a table.
Syntax
SELECT
[/*+ hint statement */]
[ALL DISTINCT UNIQUE SQL_CALC_FOUND_ROWS]
select_expr_list
[FROM from_list [WHERE condition]]
[GROUP BY group_expression_list [WITH ROLLUP] [HAVING condition]]
[ORDER BY order_expression_list]
[limit_clause]
[FOR UPDATE [opt_for_update_wait]];
select_expr:
table_name.*
table_alias_name.*
expr [[AS] column_alias_name]
from_list:
DUAL
table_reference [, table_reference ...]
table_reference:
simple_table
joined_table
simple_table:
table_factor [partition_option]
[sample_clause [opt_seed]]
[[AS] table_alias_name][index_hint]
(select_stmt [sample_clause [opt_seed])
[AS] table_alias_name [index_hint]
(table_reference_list) [index_hint]
joined_table:
table_reference [NATURAL][INNER] JOIN simple_table [join_condition]
table_reference outer_join_type JOIN simple_table join_condition
partition_option:
PARTITION (partition_name_list)
sample_clause:
SAMPLE [BLOCK] [ ALL BASE INCR] (sample_percent)
opt_seed:
SEED(integer)
index_hint:
{USE FORCE IGNORE} {KEY INDEX}
[FOR {JOIN ORDER BY GROUP BY}] (index_list)
index_list:
index_name [, index_name ...]
partition_name_list:
partition_name [, partition_name ...]
outer_join_type:
[NATURAL]{LEFT RIGHT FULL} [OUTER]
join_condition:
ON expression
condition:
expression
group_expression_list:
group_expression [, group_expression ...]
group_expression:
expression [ASC DESC]
order_expression_list:
order_expression [, order_expression ...]
order_expression:
expression [ASC DESC]
limit_clause:
LIMIT {[offset,] row_count row_count OFFSET offset}
opt_for_update_wait:
WAIT { DECIMAL INTNUM }
NOWAIT NO_WAIT
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| ALL DISTINCT UNIQUE SQL_CALC_FOUND_ROWS | A database table may contain duplicate values.
|
| select_expr | Specifies the expressions or column names that you want to query. Multiple values must be separated with commas (,). You can also use an asterisk (*) to represent all columns. |
| AS othername | Renames the output fields. |
| FROM table_references | Specifies the table or tables from which data is to be retrieved (multi-table query is supported). |
| WHERE where_conditions | (Optional) Specifies a filter condition. Only the data that meets the condition is included in the query result. where_conditions is an expression. |
| GROUP BY group_by_list | Summarizes data by class. |
| WITH ROLLUP | Summarizes groups to produce higher-level aggregations, also known as hyper-aggregations, and additional rows. |
| HAVING search_conditions | The HAVING clause is similar to the WHERE clause, but the HAVING clause can use an accumulation function such as SUM or AVG. |
| SAMPLE [BLOCK] [ ALL BASE INCR] (sample_percent) | Scans only a part of records.
|
| SEED integer | The sampling seed. Value range: [0, 4294967295]. The same result is always returned for the same seed. |
| {USE FORCE IGNORE} {KEY INDEX} [FOR {JOIN ORDER BY GROUP BY}] (index_list) | Specifies whether to use the specified index for the query.
|
| SQL_CALC_FOUND_ROWS | Displays the query results in ascending (ASC) or descending (DESC) order. The default value is ASC. |
| [LIMIT {[offset,] row_count row_count OFFSET offset}] | Forces the SELECT statement to return the specified number of records. LIMIT supports one or two numeric arguments. The argument must be an integer constant.
|
| FOR UPDATE | Imposes an exclusive lock on all the rows in the query results to prevent other concurrent transactions from changing or reading the rows in some transaction isolation levels.
|
| PARTITION(partition_list) | Specifies the partition information of the table to be queried. Example: partition(p0,p1...). |
Examples
Take table a as an example.
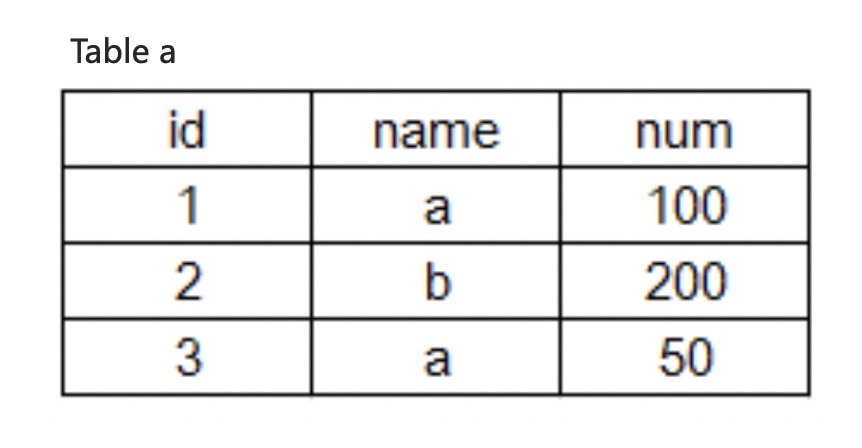
Query the data in the
namefield from tablea.obclient> SELECT name FROM a; +------+ name +------+ a b a +------+Deduplicate the query results of the
namefield.obclient> SELECT DISTINCT name FROM a; +------+ name +------+ a b +------+Query the
id,name, andnumvalues from tablea, divide thenumvalues by 2, and name the output column asavg.obclient> SELECT id, name, num/2 AS avg FROM a; +------+------+----------+ id name avg +------+------+----------+ 1 a 50.0000 2 b 100.0000 3 a 25.0000 +------+------+----------+Return the values of the corresponding
id,name, andnumfields based on the filter conditionname = 'a'from tablea.obclient> SELECT id, name, num FROM a WHERE name = 'a'; +------+------+------+ id name num +------+------+------+ 1 a 100 3 a 50 +------+------+------+Query the
idandnamevalues from tablea, calculate the sum of thenumvalues byname, and return the calculation results.obclient> SELECT id, name, SUM(num) FROM a GROUP BY name; +------+------+----------+ id name SUM(num) +------+------+----------+ 1 a 150 2 b 200 +------+------+----------+Query the
idandnamevalues from tablea, calculate the sum of thenumvalues byname, and return the rows with a sum of less than160.obclient> SELECT id, name, SUM(num) as sum FROM a GROUP BY name HAVING SUM(num) < 160; +------+------+------+ id name sum +------+------+------+ 1 a 150 +------+------+------+Query the
id,name, andnumvalues from tablea, and sort the result set by thenumcolumn inASCorder.obclient> SELECT * FROM a ORDER BY num ASC; +------+------+------+ id name num +------+------+------+ 3 a 50 1 a 100 2 b 200 +------+------+------+Query the
id,name, andnumvalues from tablea, and sort the result set by thenumcolumn inDESCorder.obclient> SELECT * FROM a ORDER BY num DESC; +------+------+------+ id name num +------+------+------+ 2 b 200 1 a 100 3 a 50 +------+------+------+Query the
id,name, andnumvalues from tablea, and useLIMITto forcibly return two result rows starting from the second row.obclient> SELECT * FROM a LIMIT 1,2; +------+------+------+ id name num +------+------+------+ 2 b 200 3 a 50 +------+------+------+You can use the
SELECT ... FOR UPDATEstatement to apply a row lock to a table. If you use theLIMIT 1clause, the operator is pushed down to the table scan step during query optimization, and only the rows returned byLIMITare locked.obclient> SELECT * FROM a LIMIT 1 FOR UPDATE;If you use the
ORDER BYclause, the query results are sorted first, and theLIMIT 1clause is executed. In this case, all the selected rows are locked.obclient> SELECT * FROM a ORDER BY id LIMIT 1 FOR UPDATE;






