This topic describes how to create a database in MySQL mode.
Create a database by using an SQL statement
You can use the CREATE DATABASE statement to create a database.
Examples:
Create a database named
test2and specify the character set asUTF8.obclient> CREATE DATABASE test2 DEFAULT CHARACTER SET UTF8; Query OK, 1 row affectedCreate a database named
test3that supports read and write operations.obclient> CREATE DATABASE test3 READ WRITE; Query OK, 1 row affectedCreate a read-only database named
test4.obclient> CREATE DATABASE test4 READ ONLY; Query OK, 1 row affectedFor more information about the syntax of the
CREATE DATABASEstatement, see CREATE DATABASE.
Create a database in OCP
You can also create a database for a MySQL tenant in OceanBase Cloud Platform (OCP).
Before you create a database, make sure that the password box of the current OCP user contains the root password of the tenant. Otherwise, the creation fails. To create a database in OCP, perform the following steps.
Log on to the OCP console.
In the left-side navigation pane, click Tenants to go to the Tenants page.
In the tenant list, find the required tenant and click the tenant name. The Overview page appears.
In the left-side navigation pane, click Database Management. The Database Management page appears.
In the upper-right corner of the page, click Create Database.
In the panel that appears, enter the database information.
Field Description Database Name The database name. The name must be 2 to 128 characters in length and can contain lowercase letters, digits, and underscores (_). The name must start with a letter. Character Set The character set of the database. Valid values: - utf8mb4: encodes data into variable-length characters. The maximum length of an encoded character is 4 bytes.
- binary: encodes data into characters with a fixed length of 1 byte.
- gbk: encodes data into 2-byte characters.
- gb18030: encodes data into 1-byte, 2-byte, or 4-byte characters.
Collation The collation of the specified character set.
Valid collations for the utf8mb4 character set:- utf8mb4_bin: compares the binary values of characters. Characters are case-sensitive in this collation.
- utf8mb4_general_ci: does not follow the Unicode rules and may generate undesirable sorting and comparison results in specific scenarios that involve particular languages or character sets. Characters are case-insensitive in this collation.
- utf8mb4_unicode_ci: follows the standard Unicode rules to perform sorting and comparison. This collation can provide accurate results for various languages. Characters are case-insensitive in this collation.
Valid collation for the binary character set: binary.
Valid collations for the gbk character set:- gbk_bin: compares characters based on the encoded values. Characters are case-sensitive in this collation.
- gbk_chinese_ci: Characters are case-insensitive in this collation.
Valid collations for the gb18030 character set:- gb18030_bin: Characters are case-sensitive in this collation.
- gb18030_chinese_ci: Characters are case-insensitive in this collation.
Read-only Specifies whether the database is read-only. - Yes: Only the
rootuser under the current tenant has read/write permissions on the database. - No: All users under the current tenant have read/write permissions on the database.
Zone Priority The priorities of the zones. This is an advanced setting. 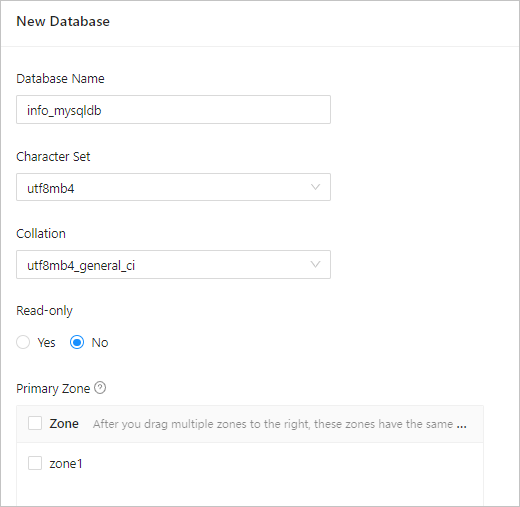
Click Submit.






