After the backup succeeds, you can enable the automatic data clearing feature based on your business needs. The system automatically clears backup data that meets requirements when this feature is enabled. OceanBase supports automatic backup data clearing only at the cluster level.
Considerations
The clearing of the archive log data depends on data backup. Before you clear archive log data, confirm that a data backup file exists. If no data backup file exists, the archive log data cannot be cleared.
Only data stored in the backup destination specified in
backup_destcan be automatically cleared. If the destination of a backup is changed, the backup data must be manually cleared upon expiration.At least one copy of backup data is retained after automatic clearing. If only one copy of valid backup data exists, this data copy will never expire.
When you clear backup data from the Network File System (NFS), the system directly clears backup files that meet the requirements. When you clear backup data from the Object Storage Service (OSS), the backup file clearing mode is specified by the
delete_modeparameter inbackup_dest. For more information, see Preparations for backup.
Set related parameters to enable automatic backup clearing
(Recommended) Enable automatic data clearing by using the backup_dest_option parameter
Log on to the
systenant as therootuser.Configure the backup clearing strategy in
backup_dest_option.The clearing of backup data is determined by the
auto_delete_obsolete_backupandrecovery_windowparameters inbackup_dest_option. For more information about the setting method and description of these parameters, see Preparations for backup.For more information about the
backup_dest_optionparameter, see backup_dest_option.Parameters are as follows:
auto_delete_obsolete_backupThis parameter specifies whether to enable automatic data clearing. If
auto_delete_obsolete_backupis set to true, the system automatically clears expired backup data.recovery_windowThis parameter specifies the time window for restoring backup data. The system determines whether a copy of backup data has expired based on this time window.
All backup data earlier than the latest backup data that meets the following condition is considered expired:
current time - backup point in time >= recovery_window.``For example, the setting
recovery_window='7d'indicates that the data backed up within the last 7 days must be restorable, and the backup data beyond this restore window is considered expired.The following example shows how to determine whether backup data has expired after you specify
recovery_window, as shown in the following figure.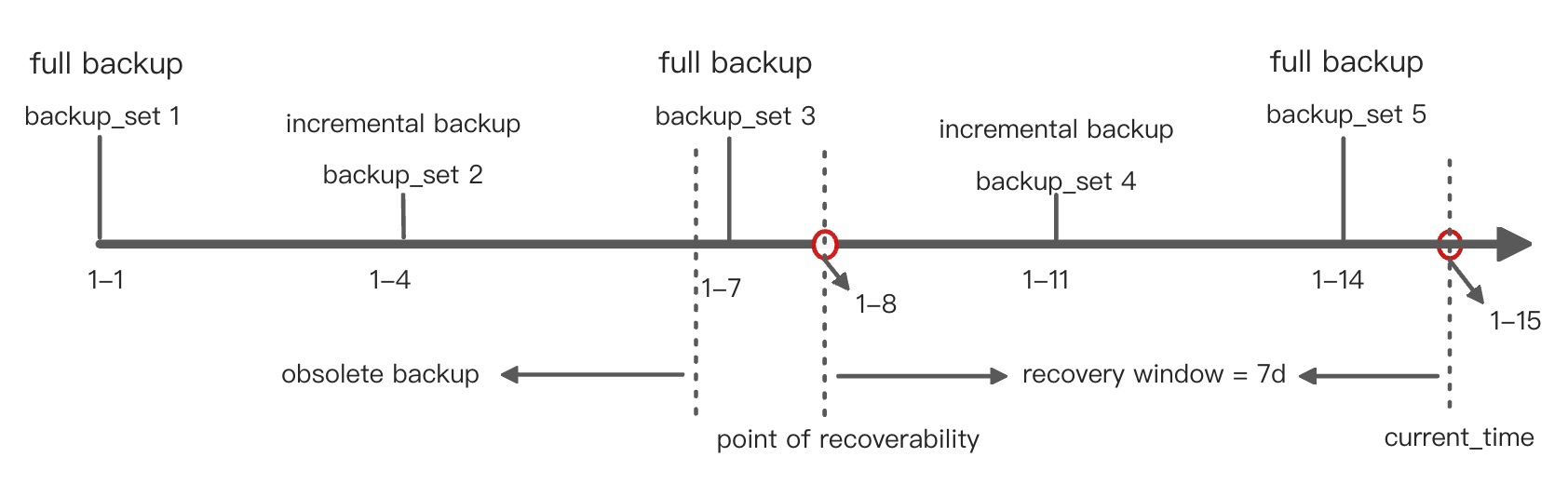
When automatic data clearing is enabled, the system clears expired data on the basis of one full backup and multiple incremental backups. As shown in the preceding figure.
First batch of backup data: full backup file
backup_set 1on January 1 + incremental backup filebackup_set 2on January 4Second batch of backup data: full backup file
backup_set 3on January 7 + incremental backup filebackup_set 4on January 11Third batch of backup data: full backup file
backup_set 5on January 14
The current time is January 15, and the earliest restore point is January 8. That is, the backup data from January 8 to January 15 can be restored. The restore of the incremental backup file
backup_set 4on January 11 depends on the full backup filebackup_set 3on January 7. Therefore, the system retainsbackup_set 3and considers the backup data earlier than January 7 expired. That is,backup_set 1andbackup_set 2are expired. When automatic data clearing is enabled, the expired backup data will be cleared.Note
If you have created a backup strategy and set a full backup cycle in OCP, reserve the disk space for backup based on the following formula when automatic clearing is enabled:
Minimum disk space reserved for backup = Disk space occupied by the maximal full data backups that can be retained + Disk space occupied by the maximal log backups that can be retained + Additional disk space to be reserved
In the formula:
Maximum full data backups that can be retained (unit: times): recovery_window/Full backup cycle + 2
Maximum log backups that can be retained (unit: days): Maximum full data backups that can be retained × Full backup cycle
Additional disk space to be reserved: (Disk space occupied by data backups that are retained + Disk space occupied by log backups that are retained) × 30%
This calculation formula does not take incremental backup into consideration. Therefore, if you have set an incremental backup strategy, you must also consider the disk space occupied by all incremental backups between full backups.
Enable automatic data clearing by specifying the auto_delete_expired_backup parameter
Notice
The cluster-level parameter
auto_delete_expired_backupcan enable the automatic clearing of the backup data. However, the use of this parameter will be discontinued in future versions. We recommend that you use thebackup_dest_optionparameter to enable automatic data clearing``.
Log on to the
systenant as therootuser.Execute the following statement to set the restore time window of backup data by specifying the
backup_recovery_windowparameter:obclient>ALTER SYSTEM SET backup_recovery_window = <restorable window>;The
backup_recovery_windowparameter in this statement is equivalent to therecovery_windowparameter inbackup_dest_option.For example:
obclient> ALTER SYSTEM SET backup_recovery_window = '7d';Execute the following statement to enable automatic clearing of backup data by using the
auto_delete_expired_backupparameter.obclient> ALTER SYSTEM SET auto_delete_expired_backup = 'True';
Trigger condition of automatic clearing
After you enable automatic clearing of backup data, the system triggers an automatic clearing task when the trigger condition is met.
Automatic clearing interval = min(recovery_window/2, 1d)
When the difference between the current time and time of last successful automatic clearing is greater than automatic clearing interval, the system triggers an automatic clearing task. In general, the interval between two adjacent automatic clearing tasks cannot exceed one day.
For more information about the recovery_window parameter, see Enable automatic data clearing by using the backup_dest_option parameter. You can query the END_TIME field in the view oceanbase.CDB_OB_BACKUP_CLEAN_HISTORY to obtain the time of last successful automatic clearing. Perform the following steps:
Log on to the sys tenant as the root user.
Query the
oceanbase.CDB_OB_BACKUP_CLEAN_HISTORYview to obtain the time of last successful automatic clearing.For example:
obclient> SELECT * FROM oceanbase.CDB_OB_BACKUP_CLEAN_HISTORY WHERE tenant_id = 1 AND type = 'DELETE OBSOLETE BACKUP' AND ERROR_MSG='' ORDER BY END_TIME DESC LIMIT 1; +-----------+--------+---------+----------------------------+----------------------------+-------------+------------------------+--------+------------------+-----------+-------------------------------------------+ | TENANT_ID | BS_KEY | COPY_ID | START_TIME | END_TIME | INCARNATION | TYPE | STATUS | PARAMETER | ERROR_MSG | COMMENT | +-----------+--------+---------+----------------------------+----------------------------+-------------+------------------------+--------+------------------+-----------+-------------------------------------------+ | 1 | 3 | 0 | 2022-10-28 11:23:51.330579 | 2022-10-28 11:23:52.928141 | 1 | DELETE OBSOLETE BACKUP | STOP | 1666927131324508 | | server:xxx, trace_id:xxx | +-----------+--------+---------+----------------------------+----------------------------+-------------+------------------------+--------+------------------+-----------+-------------------------------------------+ 1 row in setFields in query results are as follows:
BS_KEYindicates the job ID of the clearing task.COPY_IDindicates the copy_id of the clearing task. The value of this field is not 0 only when you use the backup clearing command to clear the specified secondary backup.END_TIMEindicates the time when the clearing task ends.STATUSindicates the status of the clearing task. If the task is recorded in a historical task view, the value of theSTATUSfield isSTOP.ERROR_MSGrecords the description of a failed clearing task. If the clearing task succeeded, this field is empty.
Possible causes of an empty query result:
A clearing task is being performed. You can check the
oceanbase.__all_virtual_backup_clean_infotable for ongoing tasks. After all clearing tasks (including manual and automatic tasks) are completed and the automatic clearing interval arrives, the system performs the next automatic clearing task.Backups have never been automatically cleared before. In this case, the system immediately performs an automatic clearing task right after you enable automatic data clearing.
Enable automatic data clearing in OCP
When you create a backup strategy in OceanBase Cloud Platform (OCP), you can enable Clear Expired Backup so that the system automatically clears expired backup data. For more information, see Perform a backup for clusters in OCP.
What to do next
In addition to automatically clearing backup data, you can manually clear the backup data. In manual backup data clearing mode, you can clear specified backup data or clear expired backup data. For more information, see Manually clear backup data for clusters.
OceanBase Database allows you to stop backup data clearing. For more information, see Stop backup data clearing for clusters.






