The multi-replica mechanism of OceanBase clusters provides rich disaster recovery capabilities. When a failure at the server, IDC, or city level occurs, an automatic failover is performed with no data loss. This achieves a recovery point objective (RPO) of 0. The primary/standby cluster architecture is an important supplement to the high availability (HA) capabilities of OceanBase Database. If the primary cluster is unavailable (the majority of replicas fail), the standby cluster takes over the services. Lossless switchover (RPO = 0) and lossy switchover (RPO > 0) are supported to minimize service downtime.
OceanBase Database allows you to create, maintain, manage, and monitor one or more standby clusters. A standby cluster accommodates a hot backup for the production cluster, that is, the primary cluster. The administrator can allocate resource-intensive table-related operations to standby clusters to improve system performance and resource utilization.
Primary cluster
The primary cluster is the production cluster and the only cluster that accepts business writes and strong consistency reads. It plays the PRIMARY role.
Standby cluster
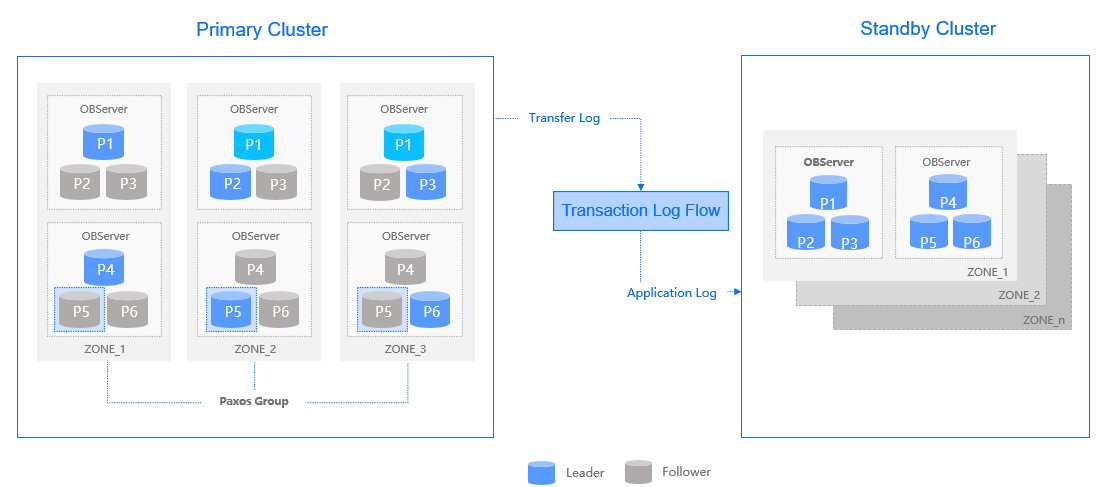
A standby cluster is a physical copy of the primary cluster to ensure transaction consistency. It plays the PHYSICAL STANDBY role. The primary cluster automatically transfers REDO logs to the standby cluster. The standby cluster persists the transferred REDO logs and replays them to restore the user data and schemas. This way, the standby cluster maintains physical data consistency with the primary cluster.
Configuration example
The following figure shows a typical primary/standby cluster configuration, including one primary cluster and one standby cluster. They synchronize data by transmitting REDO logs. You can deploy the primary and standby clusters in different locations to meet different disaster recovery requirements.