OceanBase Database provides cluster-level and tenant-level parameters. You can set these parameters to make sure that the behaviors of OceanBase Database meet your business requirements.
For more information about the parameters, see Overview of configuration management.
Parameter levels
OceanBase Database provides cluster-level and tenant-level parameters. You can set these parameters to control the load balancing, major compaction time, major compaction mode, resource allocation, and module switches of the entire cluster. For more information, see Overview of system parameters.
Cluster-level parameters apply to all OBServer nodes in the cluster. For more information about cluster-level parameters, see Cluster-level parameters.
Tenant-level parameters apply to OBServer nodes in the current tenant. For more information about tenant-level parameters, see Tenant-level parameters.
Note
Parameters whose names start with an underscore (_), such as
_ob_max_thread_num, are hidden parameters. Hidden parameters are used by developers only for troubleshooting or emergency O&M. This topic does not describe hidden parameters, nor does it involve any.
Considerations
- Before you modify parameters, save the original values.
- Assess the expected effects to be achieved after the modification.
- You can set cluster-level parameters only in the
systenant. You cannot set cluster-level parameters in a user tenant or perform this operation in a sys tenant by specifying a user tenant. For example, theALTER SYSTEM SET memory_limit='100G' TENANT='test_tenant'statement will cause an error becausememory_limitis a cluster-level parameter.
View and modify parameters
The following table describes privileges of different tenants to view and modify parameters.
| Tenant type | Parameters that can be viewed | Parameter that can be configured |
|---|---|---|
sys tenant |
Cluster-level parameters and tenant-level parameters
Note |
Cluster-level parameters and tenant-level parameters
Note |
| User tenant | Cluster-level parameters, and tenant-level parameters of the current tenant | Tenant-level parameters of the current tenant |
The following table describes the data types of parameters in OceanBase Database.
| Data type | Description |
|---|---|
| BOOL | The Boolean type. Valid values: true and false. |
| CAPACITY | The unit of capacity. Valid values: b (bytes), k (KB), m (MB), g (GB), t (TB), and p (PB). The unit is case-insensitive. Default value: m. |
| DOUBLE | The Double (double-precision floating-point) type. A value of this data type occupies a storage space of 64 bits, contains 16 valid digits, and is accurate to 15 digits after the decimal point. |
| INT | The Int64 type. A value of this data type can be a positive integer, negative integer, or 0. |
| MOMENT | The type that represents a moment in hh:mm format, such as 02:00. Special value: disable, which indicates that no time is specified. This data type applies only to the major_freeze_duty_time parameter. |
| STRING | Strings. The user-specified string value. |
| STRING_LIST | The type that represents a list of strings separated with semicolons (;). |
| TIME | The time type. The following time units are supported: us (microseconds), ms (milliseconds), s (seconds), m (minutes), h (hours), and d (days). If no suffix is added to a value of this data type, the unit s is used by default. The unit is case-insensitive. |
Query parameters by using an SQL statement
SQL syntax:
SHOW PARAMETERS [LIKE 'pattern' | WHERE expr] [TENANT = tenant_name]
Note
- In the
systenant, you can query the tenant-level and cluster-level parameters of the current tenant. You can also query parameters of all tenants or a specified tenant by specifying theTENANTkeyword.- In a user tenant, you can query the tenant-level parameters of the current tenant and cluster-level parameters of the sys tenant.
- A column attribute specified in the
WHERE exprclause must be a column attribute in the execution results of theSHOW PARAMETERSstatement.
Here are examples for querying parameters by using the SHOW PARAMETERS statement:
obclient> SHOW PARAMETERS WHERE scope = 'tenant';
obclient> SHOW PARAMETERS WHERE svr_ip != 'XXX.XXX.XXX.XXX';
obclient> SHOW PARAMETERS WHERE INFO like '%ara%';
obclient> SHOW PARAMETERS LIKE 'large_query_threshold';
+-------+----------+-----------------+----------+-----------------------+-----------+-------+------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+---------+---------+---------+-------------------+
| zone | svr_type | svr_ip | svr_port | name | data_type | value | info | section | scope | source | edit_level |
+-------+----------+-----------------+----------+-----------------------+-----------+-------+------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+---------+---------+---------+-------------------+
| zone1 | observer | XXX.XXX.XXX.XXX | 2882 | large_query_threshold | NULL | 5s | threshold for execution time beyond which a request may be paused and rescheduled as a \'large request\'. Range: [1ms, +∞) | TENANT | CLUSTER | DEFAULT | DYNAMIC_EFFECTIVE |
+-------+----------+-----------------+----------+-----------------------+-----------+-------+------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+---------+---------+---------+-------------------+
1 row in set (0.01 sec)
The following table describes the column attributes in the execution results.
| Column name | Description |
|---|---|
| zone | The zone where the parameter exists. |
| svr_type | The server type. |
| svr_ip | The IP address of the server. |
| svr_port | The port of the server. |
| name | The name of the parameter. |
| data_type | The data type of the parameter. Valid values: NUMBER, STRING, CAPACITY, and so on. |
| value | The value of the parameter.
Note |
| info | The description of the parameter. |
| section | The category of the parameter. Valid values:
|
| scope | The application scope of the parameter. Valid values: TENANT and CLUSTER.
|
| source | The source of the current value. Valid values:
|
| edit_level | Defines the modification behavior of the parameter. Valid values:
|
Modify parameters by using an SQL statement
MySQL mode
SQL syntax:
ALTER SYSTEM [SET]
parameter_name = expression [SCOPE = {SPFILE | BOTH}] [COMMENT [=] 'text']
[ TENANT [=] ALL|tenant_name ] {SERVER [=] 'ip:port' | ZONE [=] 'zone'};
The parameters are described as follows:
parameter_name: the name of the parameter to be modified.expression: the value of the parameter after modification.COMMENT 'text': the comment to be added for the modification. This parameter is optional. We recommend that you specify this parameter.SCOPE: the effective scope of the modification. Default value:BOTH. Valid values:SPFILE: indicates that only the parameter value in the internal table is modified. The modification takes effect after the OBServer node is restarted. This value is valid only for the parameters that take effect upon a restart.BOTH: indicates that both the parameter values in the internal table and the memory are modified. The modification takes effect immediately, and remains effective after the OBServer node is restarted.
TENANT: used in thesystenant to specify the tenants whose tenant-level parameters are to be modified. Valid values:ALL: all tenants.tenant_name: a specified tenant.
SERVER: the server for which the parameter is to be modified.ZONE: indicates that the parameter is modified for the specific server type of the specified cluster. If this parameter is not specified, the parameter is modified for the specific server type of all clusters.
Note
- When you modify multiple parameters at a time, separate the parameters with commas (,). For example,
ALTER SYSTEM SET clog_max_unconfirmed_log_count = 400,auto_broadcast_location_cache_rate_limit = 500;.- You can modify tenant-level parameters directly in the current tenant or in the
systenant by specifying theTENANTkeyword.- The
ALTER SYSTEMstatement allows you to specify either a zone or an OBServer node, not both. You can specify only one zone or OBServer node at a time. If you do not specify a zone or an OBServer node, the modification of a cluster-level parameter takes effect on all OBServer nodes in the cluster, and the modification of a tenant-level parameter takes effect on the OBServer node where the current tenant is deployed in the cluster.- The value of the
scopeparameter in the execution results of theSHOW PARAMETERSstatement specifies whether a parameter is a cluster-level or tenant-level parameter.
- If the value of
scopeisCLUSTER, the parameter is a cluster-level parameter.- If the value of
scopeisTENANT, the parameter is a tenant-level parameter.
Examples
Note
Before you modify a parameter, you can view the current value of the parameter. For more information, see Query parameters by using an SQL statement.
Example of modify cluster-level parameters:
For more information about cluster-level parameters, see Cluster-level parameters.
Example of modifying the clog_max_unconfirmed_log_count parameter:
obclient> ALTER SYSTEM SET auto_broadcast_location_cache_rate_limit = 1500;
Query OK, 0 rows affected
Example of modify tenant-level parameters:
For more information about tenant-level parameters, see Tenant-level parameters.
Example of modifying the
clog_max_unconfirmed_log_countparameter:obclient> ALTER SYSTEM SET clog_max_unconfirmed_log_count = 400; Query OK, 0 rows affectedExample of modifying the
clog_max_unconfirmed_log_countparameter for a specified zone:obclient> ALTER SYSTEM SET clog_max_unconfirmed_log_count = 400 ZONE='z1'; Query OK, 0 rows affectedExample of modifying the
clog_max_unconfirmed_log_countparameter for a specified OBServer node:obclient> ALTER SYSTEM SET clog_max_unconfirmed_log_count = 400 SERVER='XXX.XXX.XXX.XXX:XXXXX'; Query OK, 0 rows affectedExample of modifying the
clog_max_unconfirmed_log_countparameter in the sys tenant for all tenants:obclient> ALTER SYSTEM SET clog_max_unconfirmed_log_count = 400 TENANT='ALL'; Query OK, 0 rows affectedExample of modifying the
clog_max_unconfirmed_log_countparameter in the sys tenant for a specified tenant:obclient> ALTER SYSTEM SET clog_max_unconfirmed_log_count = 400 TENANT='Oracle'; Query OK, 0 rows affectedNote
After the statement is executed, the parameter is modified for all the specified tenants.
Oracle mode
SQL syntax:
ALTER SYSTEM SET parameter_name = expression
The parameters are described as follows:
parameter_name: the name of the parameter to be modified.expression: the value of the parameter after modification.
Note
- When you modify multiple parameters at a time, separate the parameters with commas (,).
- In Oracle mode, you can set only tenant-level parameters. For more information about tenant-level parameters, see System parameters in System Reference.
- You can modify tenant-level parameters directly in the current tenant or in the sys tenant by specifying the
TENANTkeyword.
Examples
Example of modifying the clog_max_unconfirmed_log_count parameter:
obclient> ALTER SYSTEM SET clog_max_unconfirmed_log_count = 400;
View cluster-level parameters in OCP
Log on to the OCP console. The Clusters page automatically appears.
In the Clusters list, find the target cluster and click its name.
In the left-side navigation pane of the page that appears, click Parameter Management.
The Parameters page automatically appears. You can view all parameters of the current cluster on the Parameters page.
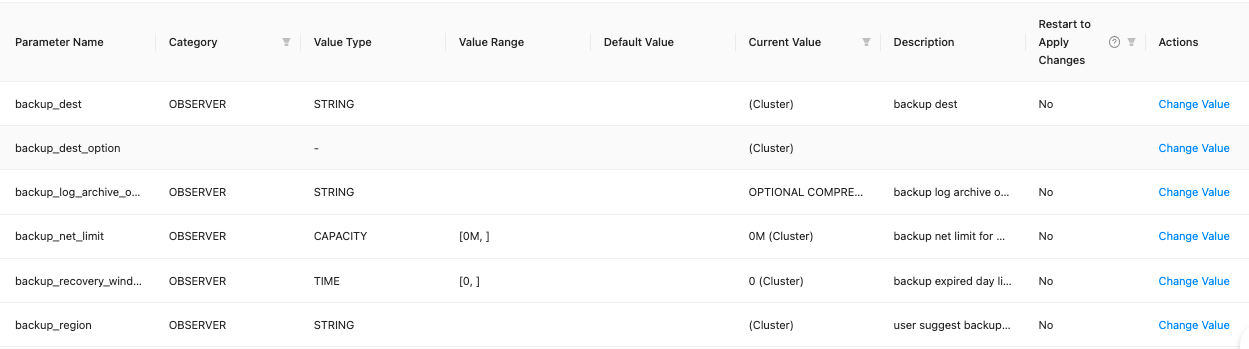
Note
- In the Current Value column, a value followed by (Cluster) takes effect at the cluster level. As shown in the preceding figure, the current value of backup_region is 0 (Cluster), which indicates that the value 0 takes effect at the cluster level.
- In the Current Value column, a value followed by (Custom) does not take effect at the cluster level. For example, 2d;1d (Custom) indicates that the value 2d applies to a specific zone and the value 1d applies to a specific OBServer node. You can click each value to view the object to which it applies.
In the search box on the Parameters page, enter part of a parameter name for fuzzy search.
In the search results, find the specified parameter.
Modify cluster-level parameters in OCP
Log on to the OCP console.
The Clusters page automatically appears.
In the Clusters list, find the target cluster and click its name.
In the left-side navigation pane of the page that appears, click Parameter Management.
(Optional) In the search box of the Parameters page, enter a parameter name to perform a fuzzy search.
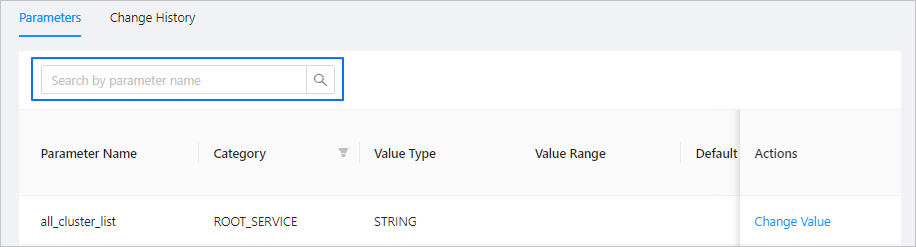
Find the target parameter and click Change Value in the Actions column.
In the dialog box that appears, modify the parameter value and the effective scope, and then click OK.
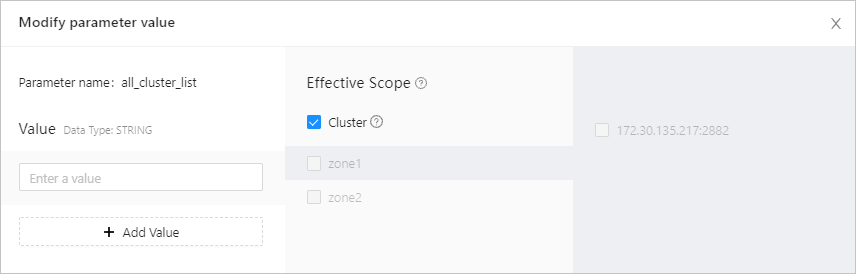
Cluster-level parameters of OceanBase Database have three effective scopes: Global (also known as Cluster), Zone, and Server. You can select the scope as needed when you modify the values.
The default effective scope is Cluster. If you need to narrow the effective scope down to Zone or Server, unselect Cluster in the Effective Scope column. Then, a list of zones in the cluster appears. Select a zone as prompted. If you select a zone and then select a server in the zone, the parameter takes effect on the selected server.
If you want to apply different parameter values in different scopes, you can select Add Value in the Value column. For example, you can set the value of backup_concurrency to 10 in Zone 1, 12 in Zone 2, and 20 on Server 1. In the three record rows that appear, and select the corresponding effective scope in each row that appears.
Note
If multiple rows of values are displayed after you click Add Value, modify the parameter values from the top down. For each successful modification operation, a record is generated on the Change History tab.
View tenant-level parameters in OCP
Prerequisites
The password of the root user in the password box and the allowlist settings are correct.
Procedure
Log on to the OCP console.
In the left-side navigation pane, click Tenant. On the Tenants list page, click the name of the target tenant.
In the left-side navigation pane of the page that appears, click Parameter Management.
On the Parameters page, you can view all parameters of the current cluster.
You can view the name, value type, value range, default value, current value, description, and read-only attribute of each parameter.
Default Value indicates the default value for the newly created tenant. Read-only indicates whether the parameter can be modified. For parameters that can be modified, the Change Value icon is displayed in the Actions column.
Modify tenant-level parameters in OCP
Log on to the OCP console.
In the left-side navigation pane, click Tenants.
In the Tenants list, find the target tenant and click its name.
In the left-side navigation pane of the page that appears, click Parameter Management.
(Optional) In the search box of the Parameters page, enter a parameter name to perform a fuzzy search.
Find the parameter to be modified and click Change Value.
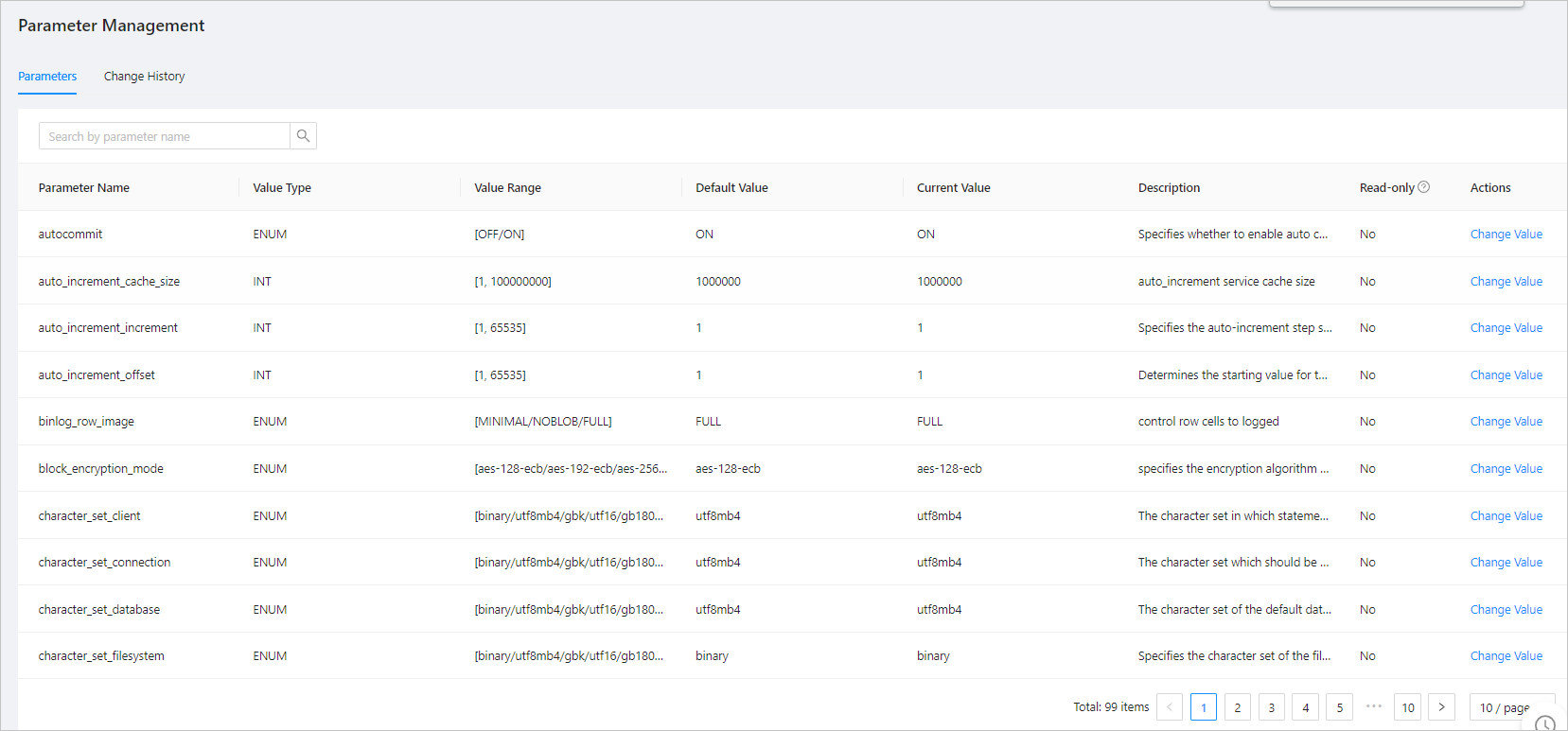
In the dialog box that appears, modify the parameter value.
Click Submit.
More information
For more information about the parameters, see Overview of system parameters in System Reference.






