As the core component to ensure the high availability of OceanBase Database, the backup and restore module protects data security by preventing misoperations and damages to the storage media. If data is lost due to misoperations or damage to the storage media, you can restore the data.
Overview
OceanBase Database supports the backup, restore, and management of data in two types of storage media: Object Storage Service (OSS) and Network File System (NFS).
OceanBase Database supports physical backup of clusters, including the physical backup of all tenants except the sys tenant within the cluster. Physical backup data includes baseline data and log archive data. Therefore, physical backup consists of log archiving and data backup.
Log archiving refers to the automatic backup of log data. OBServer nodes regularly archive log data to the specified backup path without manual triggering.
The interval for log archiving is calculated as follows:
Log archiving interval = checkpoint_interval/2You can set the value of
checkpoint_intervalas needed. For more information, see Configure backup parameters.Data backup refers to the backup of data, and includes full backup and incremental backup:
Full backup refers to the backup of all macroblocks.
Incremental backup refers to the backup of macroblocks that are added or modified since the last backup.
OceanBase Database supports tenant-level restore, which allows you to create a tenant based on existing data backups. You can execute the ALTER SYSTEM RESTORE TENANT statement to restore a tenant. The tenant restore process consists of the restore and recovery of system tables and user tables in the tenant. Restoring the tables means to restore the required baseline data to the OBServer node of the target tenant, whereas recovering the tables means to restore the logs corresponding to the baseline data to the OBServer node.
OceanBase Database allows you to back up clusters and tenants, and manually clear specified backup data or automatically clear expired backup data.
Physical backup architecture
The following figure shows the physical backup architecture of OceanBase Database.
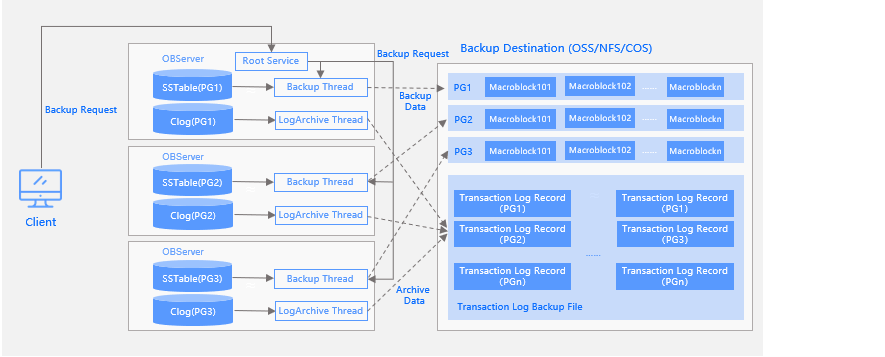
After you log on to the backup cluster by using the sys tenant account, you must first execute an SQL statement to initiate log archiving. You can perform a baseline backup only after log archiving is completed.
Log archiving regularly backs up logs to the backup destination. You need to execute the alter system archivelog statement only once, and the log backup will continue in the background. During log archiving, the leader of each partition group (PG) regularly archives logs of the PG to the specified path of the backup medium, and RootService regularly checks the log archiving progress and updates it to the internal table.
Data backup is user-triggered. Generally, full backup is triggered on each Saturday, and incremental backup is triggered on Tuesday and Thursday each week. When you initiate a data backup request, the request is first forwarded to the node running RootService. RootService generates a data backup task based on the current tenant and the PGs of the tenant. The backup task is then distributed to OBServer nodes for parallel execution. The OBServer nodes back up the metadata and macroblocks of the PGs to the specified backup directories, and the macroblocks are managed by PG.
OceanBase Database allows you to use OSS and NFS as the backup destination. Directory structure at the backup destination and the file types under each directory:
data
tenant_data_backup_info // The information about the baseline backup data of a tenant.
tenant_backup_set_file_info // The information that is more comprehensive than tenant_data_backup_info.
backup_set_1_full_date // A full backup set, ended with a date such as backup_set_1_full_20211014.
backup_set_info // The information about the current backup.
single_backup_set_info // The information about the current backup, which is more comprehensive than backup_set_info.
backup_1 // The backup_set_id is 1.
sys_pg_list
normal_pg_list
sys_meta_index_file_<task_id>// The index on the system table. It points to the corresponding PG meta files based on the PG key.
normal_meta_index_file_<task_id> // The index on a regular table.
meta_file_<task_id> // A file that records information such as the meta data and the list of macroblocks.
data // Versions are not differentiated.
pgkey
major_data // The baseline data.
macro_block_1.<sub_task_id>
macro_block_index_1
macro_block_2.<sub_task_id>
macro_block_index_2
minor_data // The minor compaction data.
task_id_1
macro_block_1.<sub_task_id>
macro_block_index_1
task_id_2
macro_block_2.<sub_task_id>
macro_block_index_2
backup_set_2_inc_date // An incremental backup set, ended with a date such as backup_set_2_inc_20211014.
backup_set_info // The information about the current backup.
single_backup_set_info
backup_2
sys_pg_list
normal_pg_list
sys_meta_index_file_<task_id>
normal_meta_index_file_<task_id>
meta_file_<task_id>
data
...
clog
backup_piece_info // The backup piece-related information.
tenant_clog_backup_info
roundid_pieceid_date // Example: 1_1_20211014
single_piece_info
archive_key
tableid_partition_id // Example: 1100611139403779_0
...
data
tableid // Example: 1100611139403779
partition_id // Example: 0
1 // The data file.
2
...
index
tableid // Example: 1100611139403779
partition_id // Example: 0
1 // The index file.
2
..
Physical restore architecture
The following figure shows the physical restore architecture of OceanBase Database.
To start physical restore, perform the following two steps:
In the target cluster, execute the
CREATE RESOURCE POOLstatement to create a resource pool for tenant restore.Execute the
ALTER SYSTEM RESTORE TENANTstatement to schedule a tenant restore task.The system executes the
RESTORE TENANTstatement in the following process:Create a tenant for restore.
Restore the system table data of the tenant.
Restore the system table logs of the tenant.
Modify and restore the metadata of the tenant.
Restore the user table data of the tenant.
Restore the user table logs of the tenant.
Complete the restore operation.
The restore of a single PG is to copy the metadata and macroblock data of the PG to the specified OBServer node to create a PG with only baseline data, and then copy the logs of the PG to the MemTable of the PG on the specified OBServer node. In this process, minor compactions may be triggered if the number of logs is large.






