This topic briefly describes the features and architectures of the multi-zone mode of OceanBase Cloud Platform (OCP).
Applicability
This topic applies only to OceanBase Cloud Platform Enterprise Edition. OceanBase Cloud Platform Community Edition does not support the multi-zone mode.
Features
To improve the high availability of OCP, an OCP cluster can be deployed across multiple zones. Each zone is mapped to one or more physical Internet data centers (IDCs) and provides a separate API access point.
For an OceanBase cluster that is deployed across IDCs, its replicas are generally distributed across IDCs. When this multi-replica cluster is managed by an OCP cluster in non-multi-zone mode, cross-IDC O&M is required. If these IDCs are deployed in different cities, the O&M requires higher bandwidth and suffers higher latency. This is a problem that must be solved for remote replica management in OCP.
To solve this problem, you can manage multi-replica OceanBase clusters in multi-zone mode of OCP. In multi-zone mode, each zone can be mapped to one or more IDCs. You can allocate an OCP cluster to each of the busy zones or every zone. Each OCP node manages OceanBase cluster replicas in its zone and provides a separate access URL. However, the content that you can view and manage in OCP is the same for all zones.
For more information about deploying OCP in multi-zone mode, see Deploy OCP. You can take the following actions in the OCP console:
Note
You can enable the multi-zone mode by deploying an OCP cluster across the zones of IDCs and regions that your business involves. You need to plan these IDCs and regions before you deploy the OCP cluster.
You cannot enable the multi-zone mode in the OCP console. To turn the deployment mode of an existing OCP cluster into the multi-zone mode, we recommend that you contact OceanBase Technical Support for assistance because this process involves a lot of changes.
View all zones, IDCs of each zone, OCP node of each zone, and the IDCs that are not associated with any zones. For more information, see View details of multiple zones.
Modify the configurations of the multi-zone mode. For more information, see Manage multi-zone parameters.
Multi-zone architectures
The multi-zone mode of OCP applies to O&M of OceanBase clusters that have replicas distributed across different IDCs. In non-multi-zone mode, the O&M requires high bandwidth and suffers high latency if the preceding IDCs are geologically far from each other. In the multi-zone mode, IDCs are associated with zones and the O&M of these IDCs are performed in the OCP nodes of the corresponding zones. The following examples briefly describe the principles of two typical multi-zone architectures.
Three IDCs in one city (one OCP cluster across multiple zones)
The following figure shows the architecture of an OCP cluster deployed across three IDCs in the same city in multi-zone mode.
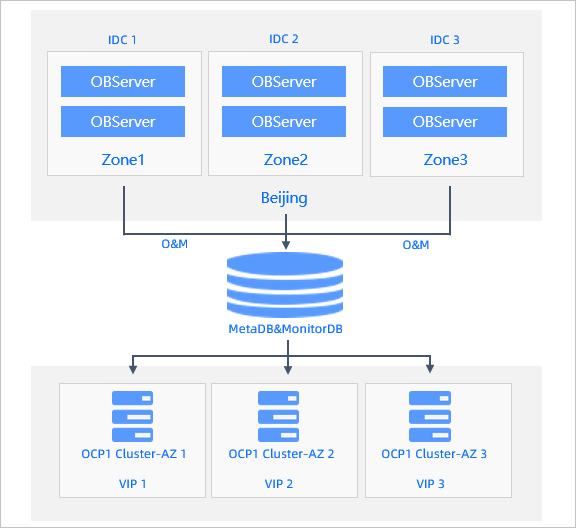
The figure shows a three-replica OceanBase cluster, whose zones are deployed in three IDCs in the same city. Each zone handles an equivalent amount of business traffic.
If the OceanBase cluster is managed by a non-multi-zone OCP cluster, the OCP cluster is deployed in one of the three IDCs. Cross-IDC O&M is required for OBServers in the other two IDCs. When the business traffic of the OceanBase cluster increases, the communication between the OCP cluster and OBServers in other IDCs is limited by the bandwidth. The distance also leads to higher latency.
If the OceanBase cluster is managed in multi-zone mode, the IDCs, zones, and OCP Cluster 1 interact in the following ways:
Zone 1: IDC 1 is associated with this zone. Business in this zone is managed by the OCP node allocated for this zone in OCP Cluster 1. The OCP node is accessed through Virtual IP Address 1 (VIP 1).
Zone 2: IDC 2 is associated with this zone. Business in this zone is managed by the OCP node allocated for this zone in OCP Cluster 1. The OCP node is accessed through VIP 2.
Zone 3: IDC 3 is associated with this zone. Business in this zone is managed by the OCP node allocated for this zone in OCP Cluster 1. The OCP node is accessed through VIP 3.
The OCP node allocated for a zone is installed in the IDC of the zone and manages the business in the zone. When the business volume increases, the OceanBase cluster can be efficiently managed within OCP Cluster 1 with low latency.
Three IDCs in different cities (multiple OCP clusters across multiple zones)
The following figure shows the architecture of two OCP clusters deployed across three IDCs in different cities in multi-zone mode.
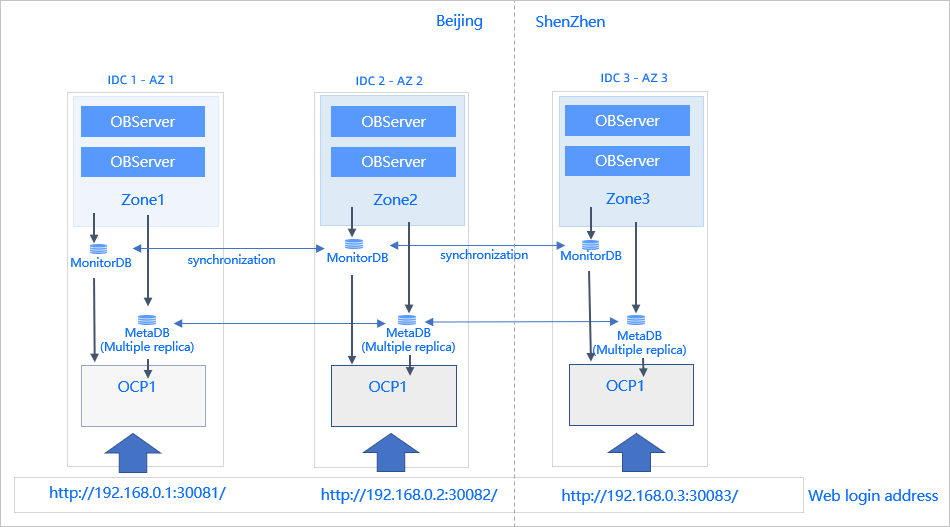
The figure shows a three-replica OceanBase cluster that has two zones respectively deployed in two IDCs in Beijing and one zone in an IDC in Shenzhen. Most of the business traffic is managed in Beijing.
Assume that the OceanBase cluster is managed by a non-multi-zone OCP cluster, say OCP Cluster 1, which is deployed in one of the IDCs in Beijing. Cross-IDC O&M is required for OBServers in the other IDC in Beijing and even the IDC in Shenzhen. When the business volume of the OceanBase cluster increases, the interaction between the OCP cluster and OBServers in other IDCs is limited by the bandwidth. The latency is also very high due to the long distance between the IDCs.
If the OceanBase cluster is managed in multi-zone mode, the IDCs, zones, and OCP cluster 1 interact in the following ways:
Zone 1: IDC 1 is associated with this zone and is installed with an OCP node of OCP Cluster 1 to manage the business of this zone. This OCP node is accessed through VIP 1.
Zone 2: IDC 2 is associated with this zone and is installed with an OCP node of OCP Cluster 1 to manage the business of this zone. This OCP node is accessed through VIP 2.
Zone 3: IDC 3 is associated with this zone and is installed with an OCP node of OCP Cluster 1 to manage the business of this zone. This OCP node is accessed through VIP 3.
The OCP node allocated for a zone is installed in the IDC of the zone and manages the business in the zone. When the business volume increases, the OceanBase cluster can be efficiently managed within OCP Cluster 1 with low latency. While the OCP node of each zone is accessed through a separate VIP, the content accessed is the same. The preceding figure shows that the MetaDB read and written by the OCP node of a zone has three replicas. These three replicas enable fast reads and writes in the three zones and always have consistent data.






