Alert description
This alert detects the major compaction status of an OceanBase cluster. If a zone has not completed a major compaction within three hours, the alert is triggered.
Note
A major compaction timeout does not indicate that the major compaction has stopped. The major compaction continues, but it exceeds the expected time. Therefore, you must investigate the cause and take corresponding actions.
Alerting principle
The following table lists the key parameters involved in the alerting monitoring logic.
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Monitoring metric | ob_cluster_merge_timeout_flag |
| Metric source | SQL: select zone, name, value, time_to_usec(now()) from __all_zone;
Description |
| Metric collection | zone_value |
| Monitoring expression | max(zone_value{metric_group="all_zone",name="is_merge_timeout",@LABELS}) by (@GBLABELS) |
| Metric collection interval | 1 second |
If a major compaction is automatically initiated or manually initiated, and the execution time exceeds 10800 seconds (3 hours), the flag is set and the compaction status is updated to the __all_zone table.
Note
10800 seconds is the default value of the zone_merge_timeout parameter. You can customize it based on your business needs.
The value of the Monitoring metric indicates whether the cluster compaction has timed out. An alert is triggered when this value is 1.
Note
When the monitoring metric value is 0, it indicates that the cluster compaction is normal. When the value is 1, it indicates that the cluster compaction has timed out.
Alarm rule information
| Monitoring metric | Default threshold | Duration | Detection cycle | Elimination cycle |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ob_cluster_merge_timeout_flag | 1 | 0 seconds | 60 seconds | 5 minutes |
Alarm information
| Alarm trigger method | Alarm level | Scope |
|---|---|---|
| Based on the expression of the monitoring metric | Severe | Cluster |
Alarm template
Overview
- Template: ${alarm_target} ${alarm_name}
- Example: ob_cluster=obcluster-1 OceanBase cluster merge timeout
Details
- Template: Cluster: ${ob_cluster_name}, Alarm: ${alarm_name}.
- Example: Cluster: obcluster-1, Alarm: OceanBase cluster merge timeout.
Restoration
- Template: Alarm: ${alarm_name}, OceanBase cluster merge timeout: ${recover_value}
- Example: Alarm: OceanBase cluster merge timeout, OceanBase cluster merge timeout: 0
Impact on the system
If the cluster merge times out, the storage pressure on the disk will increase. If users continue to write data, the disk will become full, blocking the server from providing services. In lower versions of OceanBase Database, a merge timeout can directly cause memory to be full, leading to write suspension in the cluster.
Possible causes
This can be due to the following reasons:
The OceanBase cluster has a large amount of data, leading to slow merges.
Disk issues are causing the merge to stall.
Low merge efficiency due to the disk medium.
Under equivalent CPU and memory configurations, the disk medium significantly affects merge efficiency. For example, a SATA mechanical disk has lower efficiency compared to an SSD.
Procedure
If the slow major compactions are caused by a large amount of data, you can increase the major compaction timeout or the number of major compaction threads. If the physical disks have problems, you need to replace the nodes.
First, determine whether the major compactions are stuck. You can view the progress of the major compactions in the OCP major compaction management page.
Go to the major compaction management page.
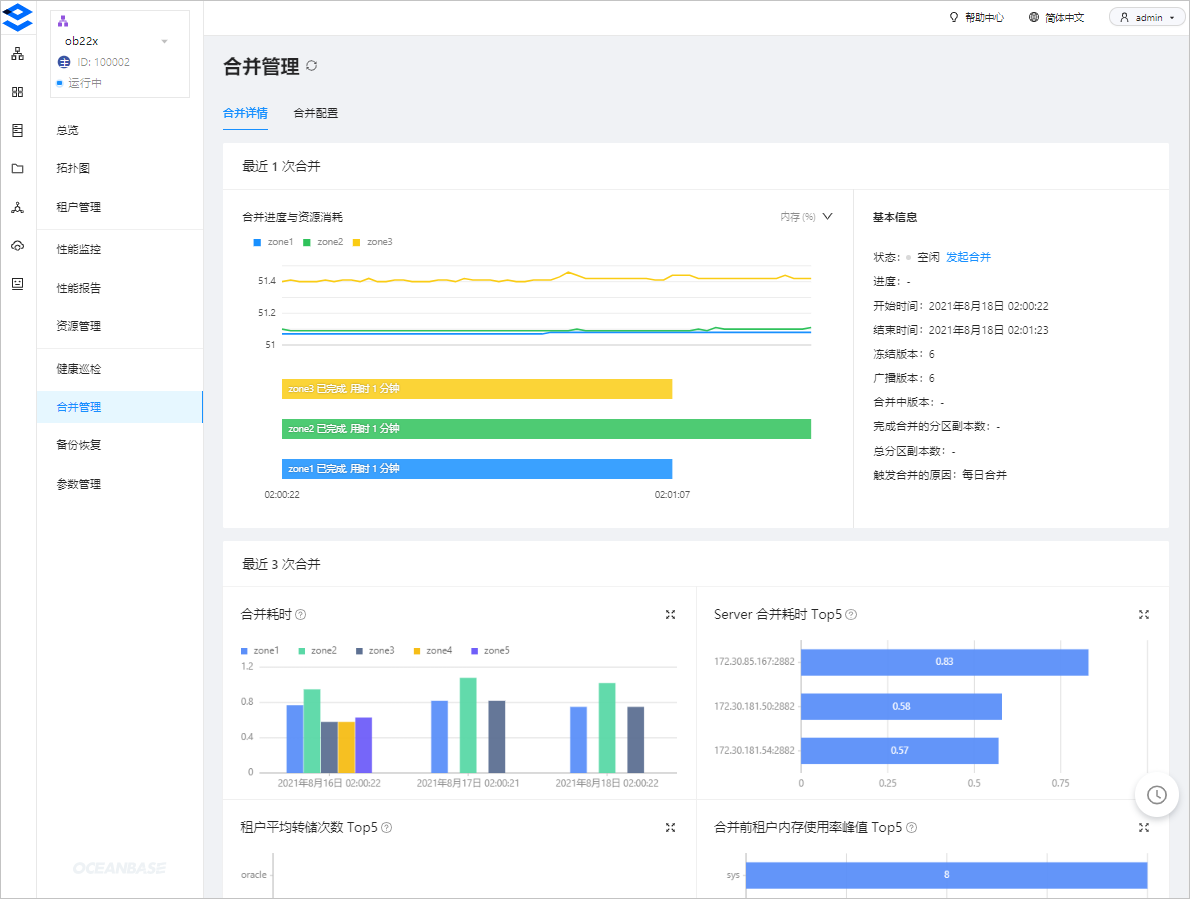
View the details of a major compaction. The details show the estimated progress, total number of partition replicas, and the number of partition replicas completed in the major compaction. If the number of partition replicas completed increases every minute, the major compaction is not stuck.
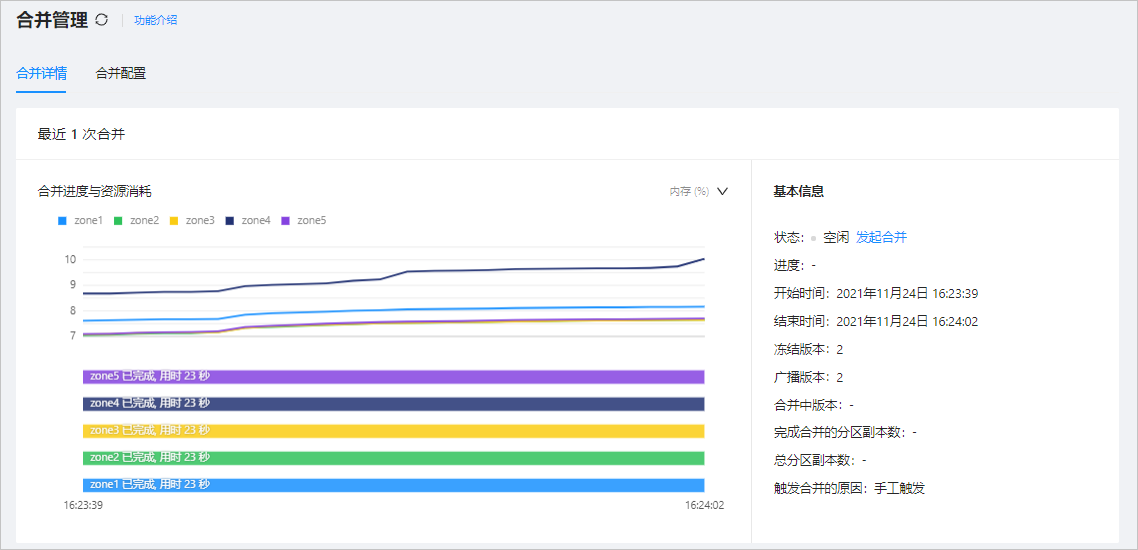
View the statistics of a major compaction. Generally, if the business data has not changed much in recent days, a significant increase in the major compaction time compared to the last three major compactions may indicate an issue.
If the major compactions are stuck, refer to Handle major compaction errors in OceanBase clusters to identify the faulty OBServer node. If needed, you can replace the faulty OBServer node. For more information, see Replace an OBServer node.
If the major compactions are not stuck, proceed to the next step.
The increased major compaction time may be due to the growth of business data or the physical disks. In this case, you can increase the major compaction timeout or the number of major compaction threads. Perform the following steps:
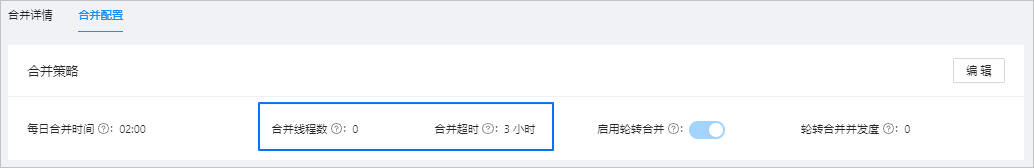
Choose Overview > Major Compaction Management > Major Compaction Configuration > Major Compaction Strategy.
Click Edit.
Modify Merge Threads and Major Compaction Timeout Period.
Click Save.






