OceanBase Database supports global CPU resource isolation for frontend and backend tasks in all tenants.
Overview
In a high-performance computing environment, reasonable resource allocation and isolation are decisive in ensuring system stability and improving efficiency. An effective resource isolation strategy can prevent resource contention and interference between tasks, thereby improving the resource utilization efficiency and overall service quality. At present, OceanBase Database allows you to configure different unit configs for tenants to implement resource isolation between the tenants, and use the DBMS_RESOURCE_MANAGER system package to configure resource isolation within a tenant.
Before you enable global CPU resource isolation for frontend and backend tasks on an OBServer node, the OBServer node supports CPU resource isolation between tenants and within a tenant, as shown in the following figure:

The isolation hierarchy is shown as a tree structure. The strategies of resource isolation between tenants depend on the unit configs of the tenants. The strategies of resource isolation between tasks within a tenant are determined by the DBMS_RESOURCE_MANAGER system package.
After you enable global CPU resource isolation for frontend and backend tasks, the system creates a tenant-level sub-control group (cgroup) based on backend tasks. The backend sub-cgroup can be understood as a virtual tenant. The MAX_CPU value of the virtual tenant is the same as the value of the global_background_cpu_quota parameter, and the MIN_CPU value of the virtual tenant is 1. The following figure shows the isolation hierarchy after global CPU resource isolation is enabled for frontend and backend tasks.
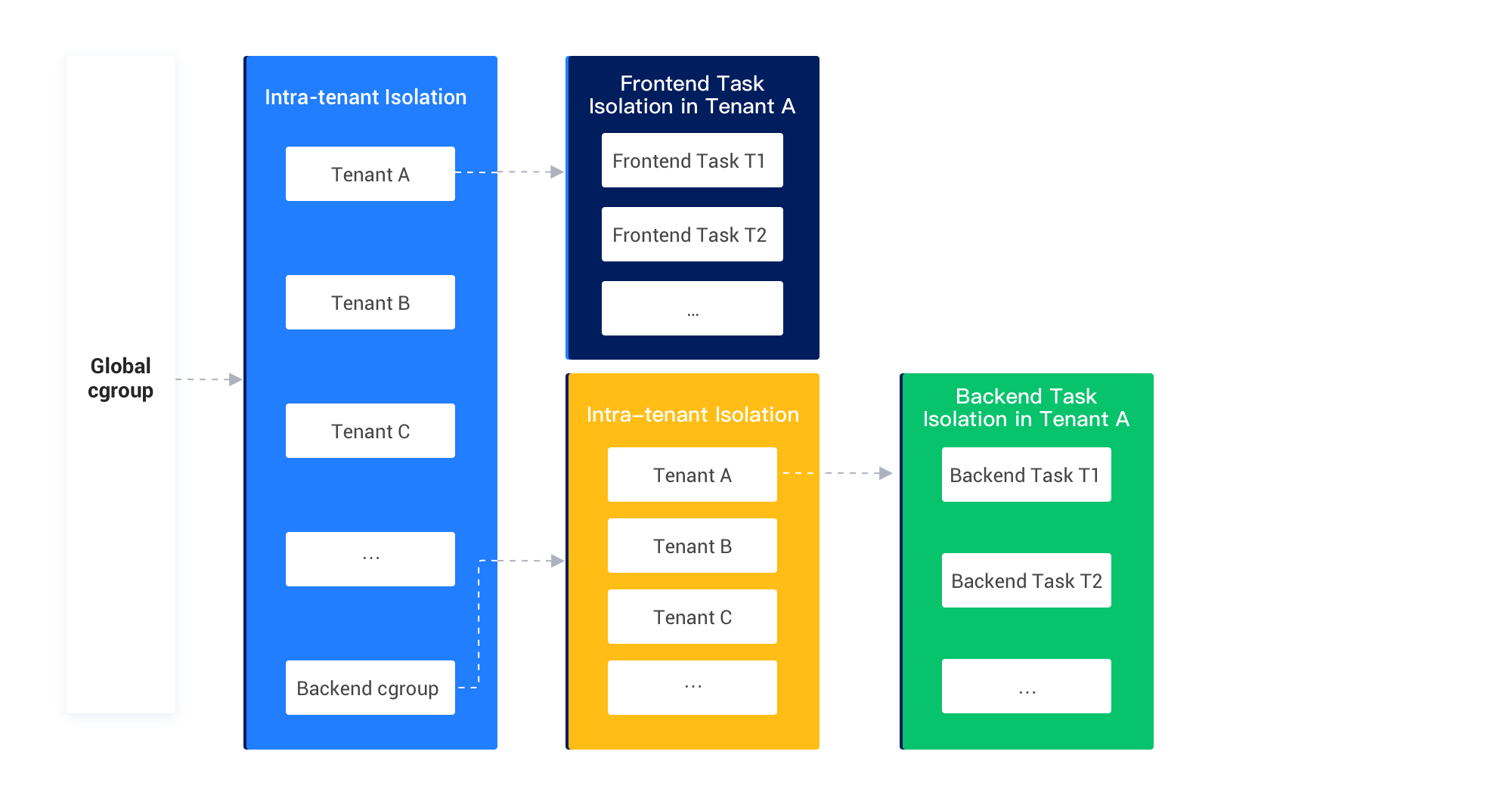
After you enable global CPU resource isolation for frontend and backend tasks, the maximum CPU resources available to all backend tasks are limited by the global_background_cpu_quota parameter even if you do not specify strategies of resource isolation within a tenant. This prevents backend tasks from affecting frontend tasks.
Scenarios
We recommend that you enable global CPU resource isolation for frontend and backend tasks in the following scenarios:
You expect global resource isolation for backend tasks to prevent them from affecting frontend tasks.
You want to avoid calculation or configuration of complex strategies of resource isolation between tenants and within a tenant, especially when a large number of tenants are deployed.
Prerequisites
You have configured the cgroup directory and enabled the cgroup feature on the OBServer node. For more information, see Configure cgroups.
Considerations
CPU resources can be isolated between tenants. After you enable global CPU resource isolation for frontend and backend tasks, the maximum CPU resources available to backend tasks of each tenant are limited by the
global_background_cpu_quotaparameter and are equal tomin(MAX_CPU of the tenant, global_background_cpu_quota).Notice
In OceanBase Database V4.2.1 and later, CPU resources for the
systenant are not limited, to avoid impact on requests from thesystenant.CPU resources can be isolated within a tenant. After you enable global CPU resource isolation for frontend and backend tasks, you can use the
DBMS_RESOURCE_MANAGERsystem package to configure resource isolation within a tenant. The maximum CPU resources available to each backend task of the tenant are calculated based on the maximum CPU resources available to all backend tasks of the tenant and are equal tomin(global_background_cpu_quota, MAX_CPU of the tenant) * UTILIZATION_LIMIT within the resource group.
Enable global CPU resource isolation for frontend and backend tasks
In OceanBase Database, global CPU resource isolation for frontend and backend tasks is controlled by the following two parameters:
enable_global_background_resource_isolationThis parameter specifies whether to enable global CPU resource isolation for frontend and backend tasks. It is a cluster-level parameter. The default value is
False, which specifies to disable global CPU resource isolation for frontend and backend tasks. In this case, CPU resources for frontend and backend tasks are isolated within a tenant. The setting takes effect only after you restart the OBServer node.The value
Truespecifies to enable global CPU resource isolation for frontend and backend tasks. In this case, CPU resources for backend tasks are limited independently of tenants.For more information about the
enable_global_background_resource_isolationparameter, see enable_global_background_resource_isolation.global_background_cpu_quotaThis parameter specifies the CPU quota available to backend tasks. It is a cluster-level parameter. The default value is
-1, which specifies that the CPU resources available to backend tasks are limited by the cgroup.For more information about the
global_background_cpu_quotaparameter, see global_background_cpu_quota.
To enable global CPU resource isolation for frontend and backend tasks, perform the following steps:
Log in to the
systenant of the cluster as therootuser.Execute the following statement to enable global CPU resource isolation for frontend and backend tasks:
obclient> ALTER SYSTEM SET enable_global_background_resource_isolation = True;Specify the CPU quota available to backend tasks based on your business needs.
The value must be less than the CPU quota available to the current OBServer node.
obclient> ALTER SYSTEM SET global_background_cpu_quota = 3;Restart the OBServer node for the setting to take effect.
After the setting takes effect, the system creates a
backgrounddirectory at the same level as all tenants in the original cgroup directory structure. Thebackgrounddirectory acts as a cgroup directory for backend tasks. The system also creates cgroup directories corresponding to all tenants in thebackgrounddirectory.
What to do next
Global CPU resource isolation for frontend and backend tasks limits the CPU resources for backend tasks from a global perspective. If you expect finer-grained resource isolation for backend tasks, you can use the DBMS_RESOURCE_MANAGER system package to configure resource isolation within a tenant. For more information, see Configure resource isolation within a tenant.






