Background information
In the information explosion era, users often need to quickly find the information they need from massive amounts of data. Online literature databases, e-commerce product catalogs, and ever-growing multimedia libraries all rely on efficient search systems to help users locate content that interests them. As data volumes keep growing, traditional keyword-based search no longer meets the need for both precision and speed. Vector search addresses this by encoding text, images, audio, and other data types into mathematical vectors and searching in vector space. Systems can then capture deeper semantic meaning and return more accurate, relevant results.
This topic walks you through building a document Q&A assistant using OceanBase's vector search capability.
Architecture
The document assistant stores documents as vectors in bulk inside OceanBase. When a user asks a question through the UI, the application uses the BGE-M3 model to embed the question into a vector and search for similar vectors in the database. After retrieving the document content for those similar vectors, the application sends that content together with the user's question to the LLM, which uses the provided documents to generate a more accurate answer.

Prerequisites
You have deployed OceanBase Database V4.3.3 or later and created a MySQL-compatible tenant. For more information about how to deploy an OceanBase cluster, see Deployment overview.
The MySQL-compatible tenant you created has the
INSERTandSELECTprivileges. For more information about how to configure privileges, see Grant direct privileges.You have created a database. For more information about how to create a database, see Create a database.
The vector search feature is enabled for the database. For more information about the vector search feature, see Perform fast vector search by using SQL.
obclient> ALTER SYSTEM SET ob_vector_memory_limit_percentage = 30;You have installed Python 3.11 or later.
You have installed Poetry.
python3 -m ensurepip python3 -m pip install poetry
Step 1: Register for an LLM platform account
Register for an Alibaba Cloud Bailian account, activate the model service, and obtain an API key.
Notice
Activating the Alibaba Cloud Bailian model service requires you to complete the process on a third-party platform. This is subject to that platform's pricing and may incur charges. Before continuing, check their official site or documentation to confirm and accept their pricing. If you do not agree, do not proceed.
Notice
This tutorial uses Qwen LLM as the example for building the Q&A chatbot. You can use other LLMs instead; if you do, update API_KEY, LLM_BASE_URL, and LLM_MODEL in the .env file accordingly.


Step 2: Build your AI assistant
Clone the code repository
git clone https://github.com/ob-labs/ChatBot.git
cd ChatBot
Install dependencies
poetry install
Set environment variables
cp .env.example .env
# If you are using Qwen for LLM, set API_KEY and OPENAI_EMBEDDING_API_KEY to the API key from the Alibaba Cloud Bailian console, update the DB_ variables with your database connection details, then save the file.
vi .env
Connect to the database
You can use the provided script to verify the database connection and confirm that the database-related environment variables are set correctly:
bash utils/connect_db.sh
# If you get a MySQL prompt, the environment variables are set correctly.
Prepare document corpus
In this step you clone the open-source documentation repository for OceanBase-related components, process the docs, generate vector data and other structured data from the documents, and insert that data into OceanBase.
Clone and process the documentation repository.
Notice
This step downloads and processes a large amount of OceanBase documentation and may take a while.
git clone --single-branch --branch V4.3.3 https://github.com/oceanbase/oceanbase-doc.git doc_repos/oceanbase-doc # If access to the GitHub repository is slow, you can clone the Gitee mirror instead: git clone --single-branch --branch V4.3.4 https://gitee.com/oceanbase-devhub/oceanbase-doc.git doc_repos/oceanbase-docStandardize the document formatting.
Some OceanBase documentation files use
====and----for first-level and second-level headings; this step converts them to standard#and##Markdown.# Convert headings to standard Markdown format. poetry run python convert_headings.py \ doc_repos/oceanbase-doc/en-US \Convert documents to vectors and insert them into OceanBase.
The
embed_docs.pyscript takes a document directory and component name, then walks all Markdown files in that directory. It splits long documents into chunks, embeds them with the embedding model to produce vectors, and inserts the chunk text, vectors, and metadata (JSON with document title, relative path, component name, chunk title, and heading hierarchy) into a single OceanBase table for retrieval.To keep things quick, we only process a few vector-search-related documents. Once the chat interface is open, questions about OceanBase vector search will get more accurate answers.
# Generate document vectors and metadata. poetry run python embed_docs.py --doc_base doc_repos/oceanbase-doc/en-US/640.ob-vector-search
Start the UI chat interface
Run the following command to start the chat interface:
poetry run streamlit run --server.runOnSave false chat_ui.py
Open the URL shown in the terminal to access the chatbot UI.
You can now view your Streamlit app in your browser.
Local URL: http://localhost:8501
Network URL: http://172.xxx.xxx.xxx:8501
External URL: http://xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx:8501 # This is the URL you can access from your browser
Application demo
Notice
This application is built from OceanBase documentation, so please ask your assistant questions about OceanBase.
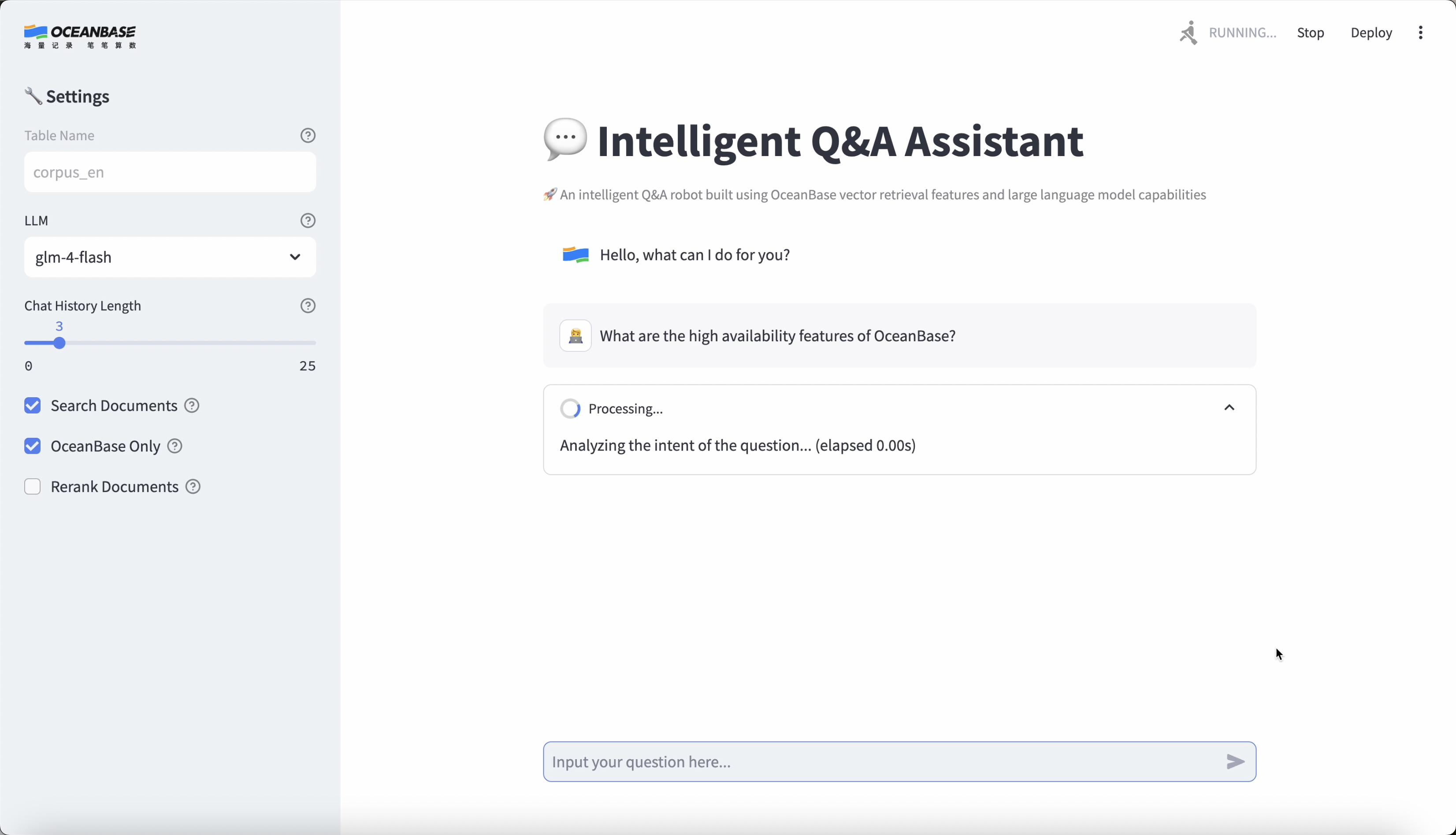
Online demo
Besides building the chatbot yourself, you can try the Document Chatbot online demo by logging in.






