A tenant is a container for various database objects and resources such as CPU, memory, and I/O. You can create tenants in a cluster as needed.
You can create tenants in one of the following two ways:
Create a tenant on the Tenant Overview page.
Create a tenant on the Tenant Management page of the specified cluster.
This topic describes how to create a tenant on the Tenant Management page of the specified cluster.
Prerequisites
The cluster where you want to create the tenant is the running primary cluster.
You have the ADMIN or TENANT_MANAGER role, or a role that has permissions to manage the cluster.
Procedure
Log on to the OCP console. The Cluster Overview page automatically appears.
In the Clusters section on the Cluster Overview page, select the target cluster and click its name.
In the left-side navigation pane on the page that appears, click Tenant Management .
In the upper-right corner of the page that appears, click Create Tenant .
Specify the Basic Information .
The current cluster is selected by default.
Enter the Tenant Name . The tenant name can contain uppercase and lowercase letters, digits, and underscores (_). It must be 2 to 64 characters in length.
Specify the Zone Information .
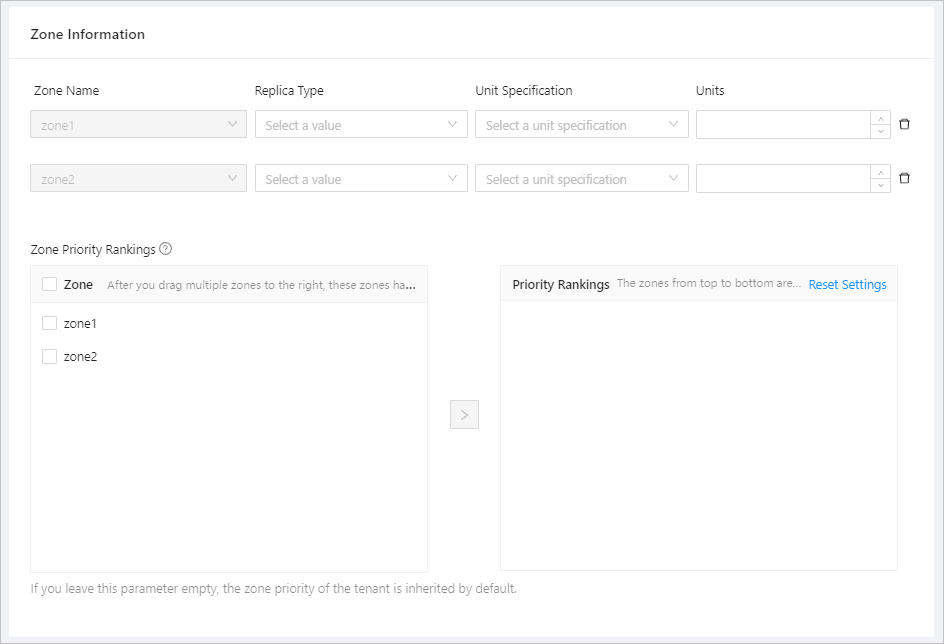
Configure the replica type, unit specification, and unit quantity for z1, z2, and z3.
The page provides a list of zones that can be configured based on the zone information of the cluster. You can click the Delete icon to delete the zones that do not need replica distribution.
Select a replica type from the drop-down list. Full-featured, read-only, and log replicas are supported.
You can use the built-in unit specifications or click Add Specification at the bottom of the drop-down list to add a custom specification.
Specify the number of units in the zone. Ensure that the number of units does not exceed the number of servers.
Specify the Zone Priority Rankings . If you drag multiple zones to the right at a time, these zones have the same priority.
Complete the Basic Settings .
Set the Administrator Password . The password can be generated randomly.
In MySQL mode, the administrator account is "root".
In Oracle mode, the administrator account is "SYS". The password must be 8 to 32 characters in length and can contain at least two digits, two uppercase letters, two lowercase letters, and two special characters. Special characters include . _ + @ # $ %
Set the Tenant Mode .
It supports Oracle and MySQL tenant modes.
The Oracle mode is supported only for OceanBase Database V2.1 and later.
Set the Character Set .
In MySQL mode, the supported character sets are utf8mb4, binary, gbk, and gb18030. Default value: utf8mb4.
In Oracle mode, the supported character sets are utf8mb4, gbk, and gb18030. Default value: utf8mb4.
Optional. Set the remarks.
Set the IP Address Whitelist .
You can specify a list of clients that are allowed to log on to this tenant here. Default value: %, indicating that all client connections are allowed. When you configure the whitelist, you must add the IP addresses of the OCP server and the OBProxy server to it. Otherwise, you cannot manage the tenant from OCP.
Default configuration: All IP addresses are allowed.
Custom configuration: You can set an IP address whitelist to allow access from IP addresses in the whitelist.
Configure the whitelist in the following formats:
IP address example: 10.10.10.10,10.10.10.11
Subnet mask example: 10.10.10.0/24
Fuzzy match example: 10.10.10.% or 10.10.10._
Mixed format example: 10.10.10.10,10.10.10.11,10.10.10.%,10.10.10._,10.10.10.0/24
Note
% indicates that all clients can connect to this tenant.

Click Submit .






