Purpose
You can use the JOIN clause to join tables.
A join statement is used in the database to combine two or more tables in the database based on the join conditions. The set generated by a join can be saved as a table or used as a table. A join statement combines the attributes of two tables based on their values.
Syntax
table_references:
table_reference [, table_reference ...]
table_reference:
table_factor
| joined_table
table_factor:
table_name [partition_option]
[[AS] alias] [index_hint_list]
| table_subquery [AS] alias
| ( table_references )
joined_table:
table_reference [NATURAL] [[INNER] | CROSS] JOIN table_factor [join_condition]
| table_reference outer_join_type JOIN table_factor join_condition
partition_option:
PARTITION (partition_name_list)
join_condition:
ON expression
| USING (join_column_list)
join_column_list:
column_name [, column_name ...]
outer_join_type:
[NATURAL] {LEFT | RIGHT | FULL} [OUTER]
index_hint_list:
index_hint [, index_hint ...]
index_hint:
{USE | FORCE | IGNORE} {KEY | INDEX}
[FOR {JOIN | ORDER BY | GROUP BY}] (index_list)
index_list:
index_name [, index_name ...]
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| PARTITION (partition_name_list) | The table partitions to be joined. |
| NATURAL | Indicates a natural join. NATURAL JOIN automatically joins the same columns. |
| [INNER] JOIN | Indicates an inner join. When no join condition is specified, INNER JOIN is equivalent to a comma (,). Both of them generate a Cartesian product by using the specified tables. Notice: The comma (,) as an operator has a lower priority than INNER JOIN, CROSS JOIN, and LEFT JOIN. Therefore, if you use commas (,) with other join keywords, the condition of the ON clause may be invalid. |
| CROSS JOIN | In the MySQL mode of OceanBase Database, CROSS JOIN is equivalent to JOIN and INNER JOIN. |
| LEFT [OUTER] JOIN | Indicates a left outer join. If a row in the table on the left side is not found in the table on the right side, NULL is automatically filled in the table on the right side. |
| RIGHT [OUTER] JOIN | Indicates a right outer join. If a row in the table on the right side is not found in the table on the left side, NULL is automatically filled in the table on the left side. |
| FULL [OUTER] JOIN | Indicates a full join. NULL is automatically filled if no matching row is found in the table on the left or right side. |
| column_name | The name of the column used for joining. |
| index_hint | Specifies whether to use the specified index for the query.
|
| ON expression | A join condition that returns duplicate columns. This parameter is applicable when columns with different names are used as join condition. |
| USING (join_column_list) | A join condition that does not return duplicate columns. This parameter is applicable only when columns with the same name in the joined tables are used as the join condition. |
Examples
Take tables a and b as examples.
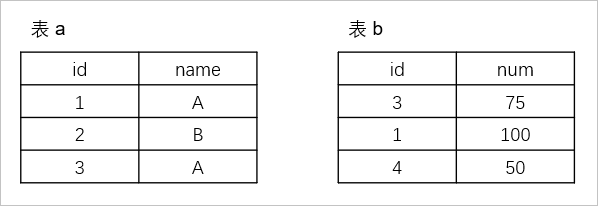
Perform an inner join on tables
aandb.obclient> SELECT * FROM a JOIN b ON a.ID=b.ID; +------+------+------+------+ | id | name | id | name | +------+------+------+------+ | 1 | A | 1 | 100 | | 3 | A | 3 | 75 | +------+------+------+------+ 2 rows in setPerform a cross join on tables
aandb.obclient> SELECT * FROM a CROSS JOIN b ON a.id=b.id; +------+------+------+------+ | id | name | id | name | +------+------+------+------+ | 1 | A | 1 | 100 | | 3 | A | 3 | 75 | +------+------+------+------+ 2 rows in setPerform a natural join on tables
aandb.obclient> SELECT * FROM a NATURAL JOIN b; Empty setPerform a left outer join on tables
aandb.obclient> SELECT * FROM a LEFT JOIN b USING(ID); +------+------+------+ | id | name | name | +------+------+------+ | 1 | A | 100 | | 2 | B | NULL | | 3 | A | 75 | +------+------+------+ 3 rows in setPerform a right outer join on tables
aandb.obclient> SELECT * FROM a RIGHT JOIN b USING(ID); +------+------+------+ | id | name | name | +------+------+------+ | 1 | 100 | A | | 3 | 75 | A | | 4 | 50 | NULL | +------+------+------+ 3 rows in setPerform a full join on tables
aandb.obclient> SELECT * FROM a FULL JOIN b USING(ID); +------+------+------+ | id | name | name | +------+------+------+ | 1 | A | 100 | | 2 | B | NULL | | 3 | A | 75 | | 4 | NULL | 50 | +------+------+------+ 4 rows in set






