You can use hints to manage distributed execution plans to improve SQL query performance.
The distributed execution framework supports hints such as ORDERED, LEADING, USE_NL, USE_HASH, and USE_MERGE.
PARALLEL hint
The PARALLEL hint specifies the degree of parallelism (DOP) of distributed execution. Three workers are activated to perform scanning in parallel, as shown in the following example:
obclient> SELECT /*+ PARALLEL(3) */ MAX(L_QUANTITY) FROM tbl1;
OceanBase Database also supports table-level PARALLEL hints. The syntax is as follows:
/*+ PARALLEL(table_name n) */
If the global DOP and table-level DOP are both specified, the table-level DOP does not take effect.
Notice
In complex queries, the scheduler can schedule the parallel execution of two data flow objects (DFOs). In this case, the number of activated workers is two times the degree of parallelism, which means PARALLEL × 2.
ORDERED hint
The ORDERED hint specifies the join order in a parallel execution plan. The order of items in the FROM clause is strictly followed.
In the following example, customer is forced to be the table on the left of the join, whereas orders is the table on the right, and a nested loop join is used:
obclient> CREATE TABLE lineitem(
l_orderkey NUMBER(20) NOT NULL ,
l_linenumber NUMBER(20) NOT NULL ,
l_quantity NUMBER(20) NOT NULL ,
l_extendedprice DECIMAL(10,2) NOT NULL ,
l_discount DECIMAL(10,2) NOT NULL ,
l_tax DECIMAL(10,2) NOT NULL ,
l_shipdate DATE NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY(L_ORDERKEY, L_LINENUMBER));
Query OK, 1 row affected
obclient> CREATE TABLE customer(
c_custkey NUMBER(20) NOT NULL ,
c_name VARCHAR(25) DEFAULT NULL,
c_address VARCHAR(40) DEFAULT NULL,
c_nationkey NUMBER(20) DEFAULT NULL,
c_phone CHAR(15) DEFAULT NULL,
c_acctbal DECIMAL(10,2) DEFAULT NULL,
c_mktsegment CHAR(10) DEFAULT NULL,
c_comment VARCHAR(117) DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY(c_custkey));
Query OK, 1 row affected
obclient> CREATE TABLE orders(
o_orderkey NUMBER(20) NOT NULL ,
o_custkey NUMBER(20) NOT NULL ,
o_orderstatus CHAR(1) DEFAULT NULL,
o_totalprice DECIMAL(10,2) DEFAULT NULL,
o_orderdate DATE NOT NULL,
o_orderpriority CHAR(15) DEFAULT NULL,
o_clerk CHAR(15) DEFAULT NULL,
o_shippriority NUMBER(20) DEFAULT NULL,
o_comment VARCHAR(79) DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY(o_orderkey,o_orderdate,o_custkey));
Query OK, 1 row affected
obclient> INSERT INTO lineitem VALUES(1,2,3,6.00,0.20,0.01,'01-JUN-02');
Query OK, 1 row affected
obclient> INSERT INTO customer VALUES(1,'Leo',null,null,'1390000****',null,'BUILDING',null);
Query OK, 1 row affected
obclient> INSERT INTO orders VALUES(1,1,null,null,'01-JUN-20',10,null,8,null);
Query OK, 1 row affected
obclient>SELECT /*+ ORDERED USE_NL(orders) */o_orderdate, o_shippriority
FROM customer, orders WHERE c_mktsegment = 'BUILDING' AND
c_custkey = o_custkey GROUP BY o_orderdate, o_shippriority;
+-------------+----------------+
| O_ORDERDATE | O_SHIPPRIORITY |
+-------------+----------------+
| 01-JUN-20 | 8 |
+-------------+----------------+
1 row in set
The ORDERED hint is useful in writing an SQL statement. If you know the optimal join order, you can write table names in order after FROM and add the ORDERED hint.
LEADING hint
The LEADING hint specifies which tables are joined first in a parallel query plan. The order of tables in the LEADING hint is also the join order. It is more flexible than the ORDERED hint.
Notice
If ORDERED and LEADING hints are used at the same time, only the ORDERED hint takes effect.
PQ_DISTRIBUTE hint
The PQ_DISTRIBUTE hint, or PQ hint, specifies how the data is distributed in a parallel query plan. It changes the data distribution mode during a distributed join.
The syntax of the PQ hint is as follows:
PQ_DISTRIBUTE(tablespec outer_distribution inner_distribution)
The parameters are described as follows:
tablespecspecifies the target table, which is the table on the right of the join.outer_distributionspecifies the data distribution mode for the table on the left.inner_distributionspecifies the data distribution mode for the table on the right.
Data of these two tables can be distributed in one of the following modes:
HASH,HASHBROADCAST,NONENONE,BROADCASTPARTITION,NONENONE,PARTITIONNONE,NONE
The two modes that include the word PARTITION require partitions in the table on the left or right, and the partitioning key serves as the join key. If the requirement is not satisfied, the PQ hint is invalid.
obclient> CREATE TABLE t1(c1 INT PRIMARY KEY, c2 INT, c3 INT, c4 DATE);
Query OK, 0 rows affected
obclient> CREATE INDEX i1 ON t1(c3);
Query OK, 0 rows affected
obclient> CREATE TABLE t2(c1 INT(11) NOT NULL, c2 INT(11) NOT NULL, c3 INT(11) NOT NULL, PRIMARY KEY (c1, c2, c3)) PARTITION BY KEY(c2) PARTITIONS 4;
Query OK, 0 rows affected
obclient> EXPLAIN BASIC SELECT /*+USE_PX PARALLEL(3) PQ_DISTRIBUTE
(t2 BROADCAST NONE) LEADING(t1 t2)*/ * FROM t1 JOIN t2 ON
t1.c2 = t2.c2;
Query Plan:
================================================
|ID|OPERATOR |NAME |
------------------------------------------------
|0 |EXCHANGE IN DISTR | |
|1 | EXCHANGE OUT DISTR |:EX10001|
|2 | HASH JOIN | |
|3 | EXCHANGE IN DISTR | |
|4 | EXCHANGE OUT DISTR (BROADCAST)|:EX10000|
|5 | PX BLOCK ITERATOR | |
|6 | TABLE SCAN |t1 |
|7 | PX BLOCK ITERATOR | |
|8 | TABLE SCAN |t2 |
================================================
USE_NL hint
The USE_NL hint specifies to use a nested loop join. The table specified in the USE_NL hint must be the table on the right of JOIN.
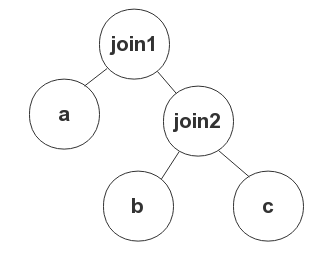
In the following example, if you want join1 to be a nested loop join, write the hint as LEADING(a, (b,c)) USE_NL((b,c)).
When used together with the ORDERED or LEADING hint, the USE_NL hint is ignored if the table specified in the USE_NL hint is not the table on the right.
USE_HASH hint
The USE_HASH hint specifies to use a hash join. The table specified in the USE_HASH hint must be the table on the right of the join.
Notice
If neither the ORDERED hint nor the LEADING hint is used and tables specified in the join order generated by the optimizer are not to be directly joined, the USE_HASH hint is ignored.
USE_MERGE hint
The USE_MERGE hint specifies to use a merge join. The table specified in the USE_MERGE hint must be the table on the right of the join.
Notice
If neither the ORDERED hint nor the LEADING hint is used and tables specified in the join order generated by the optimizer are not to be directly joined, the USE_MERGE hint is ignored.






