#docslug#/ecob/ecob/V1.1.6/establish-a-connection OceanBase Embedded SQL in C (ECOB) uses the CONNECT statement of the extended SQL statements to connect to OceanBase databases.
Syntax Description
Syntax:
Syntax 1: EXEC SQL CONNECT <:username> identified by <:password> (using <:dbstring>)
Syntax 2: EXEC SQL CONNECT <:user_password> (using <:dbstring>)
Syntax 3: EXEC SQL CONNECT <:username> identified by <:password> (AT <:dbname>) (using <:dbstring>)
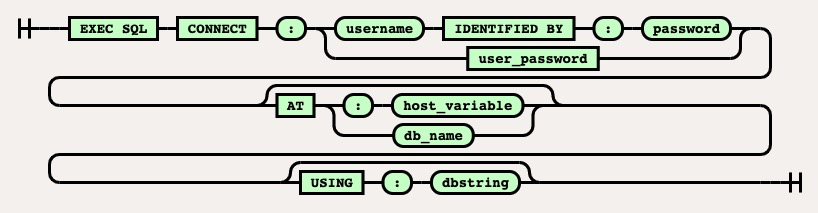 Variables:
Variables:
| Variable | Description |
|---|---|
| <:username> | Specifies the username used to connect to the OceanBase tenant in Oracle mode. The username follows the username@tenant_name format. Example: test@oracle. If ODP is used for connection, the cluster name must be added. In this case, the username follows the username@tenant_name#cluster_name format. Example: test@oracle#cluster1. |
| <:password> | Specifies the password used to connect to the OceanBase tenant in Oracle mode. |
| <:dbstring> | Specifies the service name used to connect to the OceanBase tenant in Oracle mode. This service name is the name of the string in the tnsnames.ora file specified in the TNS_ADMIN environment variable. Sample connection string in the tnsnames.ora file:demo= (DESCRIPTION= (ADDRESS=(PROTOCOL = TCP)(HOST = 10.10.10.10)(PORT = 30035)) (CONNECT_DATA= (SERVICE_NAME=TEST)) ) In this case, the value of <:dbstring> is demo. If the string follows the ip+port pattern, the <:dbstring> value can be written in the 'ip:port/dbname' format. Example: '10.10.10.10:30035/test'. |
| <:user_password> | Specifies the username and password used to connect to the OceanBase tenant in Oracle mode. Example: test@oracle/welcome1. Separate the username and password with a forward slash (/). |
Sample statement
Sample statement used to create a connection by using syntax 1 :
char * username ="**u***"; char * password = "**1***"; char * servicename = "**s***"; EXEC SQL CONNECT :username identified by :password using :servicename;Sample statement used to create a connection by using syntax 2 :
char * userpass = "**1***"; char * servicename = "**s***"; EXEC SQL CONNECT :userpass using :servicename;Sample statement used to create a connection by using syntax 3 :
char * username ="**u***"; char * password = "**1***"; char * servicename = "**s***"; char * connname = "**c***"; EXEC SQL CONNECT :username identified by :password AT :connname using :servicename;






