This topic describes the execution time distribution of different types of SQL statements, to help you understand the overall SQL statement execution status. The data for SQL request analysis originates from the TopSQL diagnostic data.
Prerequisites
For a tenant in MySQL mode, the password box of the OceanBase Cloud Platform (OCP) user must contain the password of the tenant.
For a tenant in Oracle mode, the password box of the OCP user must contain the password of the SYS tenant in the cluster.
Procedure
You can view SQL request analysis by using one of the following methods.
Method 1:
Log on to the OceanBase Cloud Platform (OCP) console.
In the left-side navigation pane, click Autonomous Services to go to the Real-time Diagnostics page.
The SQL Diagnostics page automatically appears.
Method 2:
Log on to the OceanBase Cloud Platform (OCP) console.
To go to the O&M page of the tenant.
In the left-side navigation pane, click SQL Diagnostics to go to the SQL Diagnostics page.
The following takes Method 1 as an example.
Log on to the OceanBase Cloud Platform (OCP) console.
In the left-side navigation pane, click Autonomous service.
In the Cluster Details section, click the name of the target cluster.
By default, the SQL Diagnostics tab of the Real-time Diagnostics page appears.
Click View Request Analysis .
On the request analysis details page, you can view the trend chart of execution time distribution and the request statistics list. By default, the system displays data of the last 30 minutes. If you change the statistical period, the system automatically updates Distribution of Execution Time and Request Statistics List based on the specified period.
View the trend chart of execution duration distribution.
Distribution of Execution Duration displays the execution duration distribution of SQL statements in the specified time range. By default, the system displays all SQL statements. You can select an SQL statement type (SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE, REPLACE, or others) to view the execution duration distribution of the specific SQL statement type.
The execution duration is categorized into seven intervals as follows and calculated once every minute:
Interval Description [0,1] ms The proportion of SQL executions that take greater than or equal to 0 ms and less than or equal to 1 ms. (1,2] ms The proportion of SQL executions that take more than 1 ms and less than or equal to 2 ms. (2,3] ms The proportion of SQL executions that take more than 2 ms and less than or equal to 3 ms. (3,10] ms The proportion of SQL executions that take more than 3 ms and less than or equal to 10 ms. (10,100] ms The proportion of SQL executions that take more than 10 ms and less than or equal to 100 ms. (0.1,1]s The proportion of SQL executions that take more than 0.1s and less than or equal to 1s. >1s The proportion of SQL executions that take more than 1s. 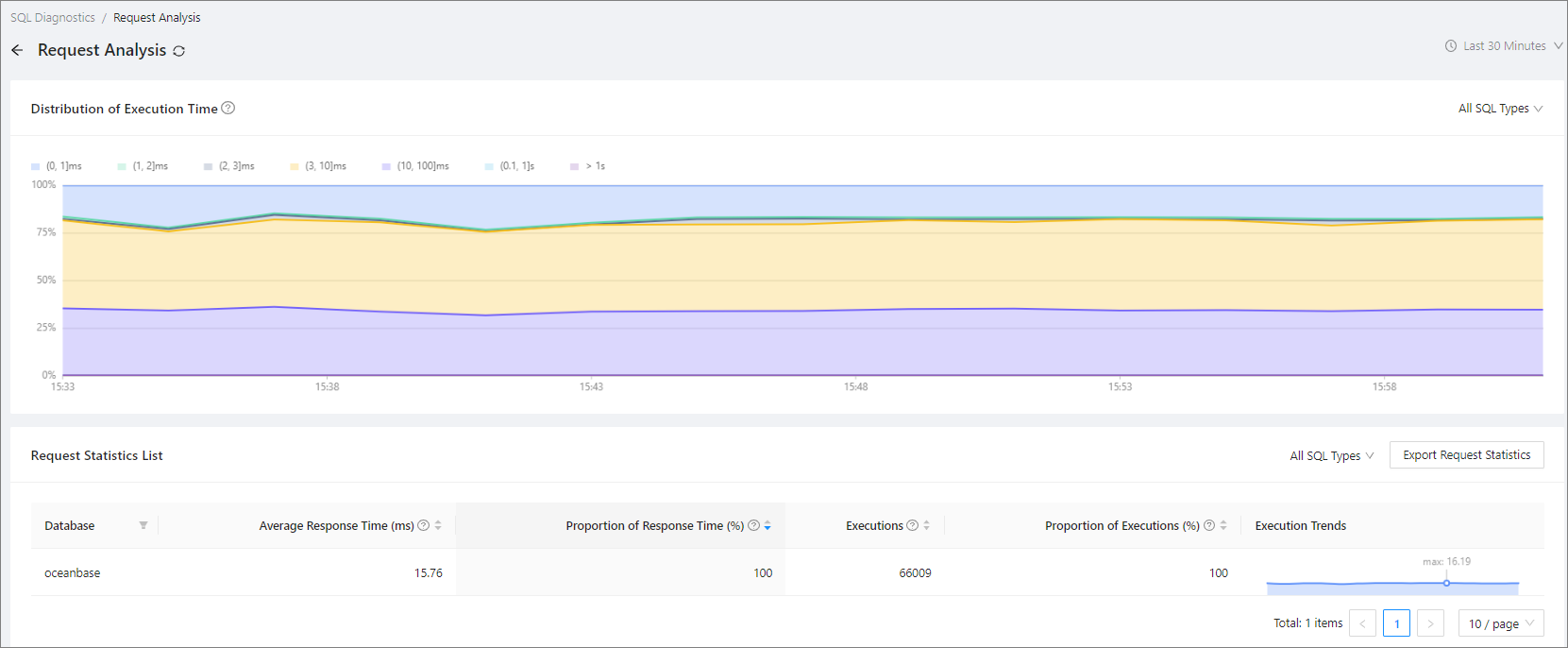
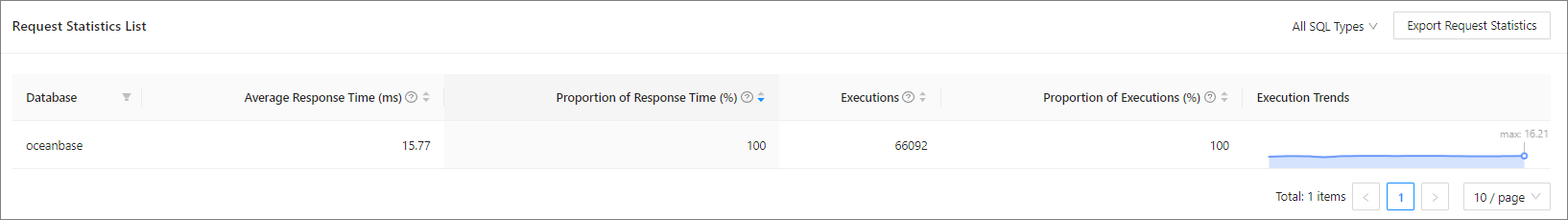
View the request statistics list.
Request Statistics List shows the average response time, proportion of response time, number of executions, proportion of executions, and execution trend (based on the average response time) of the database requests. You can perform the following operations on Request Statistics List:
Filter databases by database type.
Sort the database requests by average response time, proportion of response time, number of executions, or proportion of executions. By default, the system sorts the database requests by response time.
Select an SQL type from the drop-down list in section ① in the figure to view the execution duration distribution of a specific SQL type.
Click Export Request Statistics in section ② in the figure to export the request statistics list in Excel format.