You can use the CREATE TYPE statement to specify the name, method, and other attributes of a type.
Applicability
This topic applies only to OceanBase Database Enterprise Edition. OceanBase Database Community Edition provides only the MySQL mode.
You can use the CREATE TYPE statement to create or replace the specifications of the following types:
Abstract data type (ADT)
Independent variable array (VARRAY) type
Independent nested table type
Incomplete object type
An incomplete object type is a type created by using a forward type definition. An incomplete object type has a name but no attributes or methods. It can be referenced by other types and can be used to define types that reference each other. However, you must first create a complete type before you use it to create table columns, object columns, or nested table columns.
The CREATE TYPE BODY statement is built in with the code for implementing the type.
Note
- If you create a type whose specification declares only attributes but no methods, you do not need to create the type body.
- You can use the
CREATE TYPEstatement to create nested tables and the VARRAY type, but not associative arrays. You can define three collection types in a PL block or package.
Prerequisites
To create a type in your own schema, you must have the CREATE TYPE system privilege. To create a type in the schema of other users, you must have the CREATE ANY TYPE system privilege. You can obtain these privileges directly or through roles.
The owner of a type must be explicitly granted the EXECUTE object privilege or the EXECUTE ANY TYPE system privilege, to access all other types referenced in the definition of this type. The owner of a type cannot obtain these privileges through roles.
If the owner of a type wants to grant other users the access privilege on this type, the type owner must first be granted the EXECUTE object privilege by using GRANT OPTION, or the EXECUTE ANY TYPE system privilege by using ADMIN OPTION. Otherwise, the type owner does not have sufficient privileges to grant other users the access privilege on this type.
Syntax
Note
This topic describes the syntax of some important syntax nodes only.
The syntax of
create_type_stmtis as follows: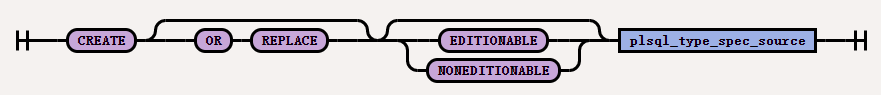
The syntax of
plsql_type_spec_sourceis as follows:
The syntax of
object_type_defis as follows:
The syntax of
attr_and_element_specis as follows: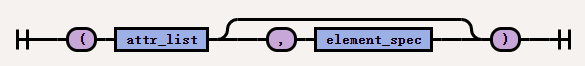
The syntax of
element_specis as follows:
The syntax of
el_element_spec_list_ccis as follows: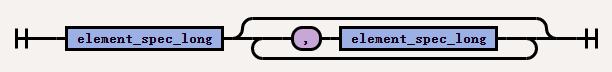
The syntax of
element_spec_longis as follows:
The syntax of
inheritance_final_instantiable_clauseis as follows: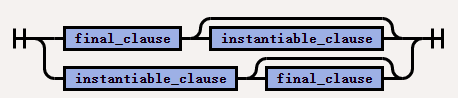
The syntax of
inheritance_overriding_instantiable_clauseis as follows: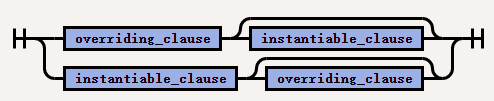
The syntax of
subprogram_specis as follows: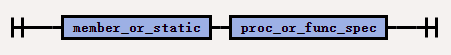
The syntax of
proc_or_func_specis as follows: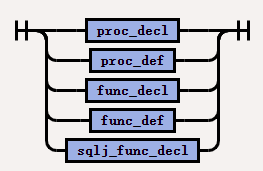
Semantics
| Syntax | Keyword or syntax node | Description |
|---|---|---|
| create_type_stmt | OR REPLACE | Re-creates this type (if any) and recompiles it. Before the type is redefined, users granted the access privilege can still access this type without the need to obtain the access privilege again. If any function-based index depends on this type, the database marks this index as DISABLED. |
| plsql_type_spec_source | pl_schema_name | The name of the schema containing the type. The default value is your own schema. |
| plsql_type_spec_source | TYPE | The ADT name, nested table type, or VARRAY type. |
| plsql_type_spec_source | varray_type_def | Creates a type as an orderly set of elements of the same data type. |
| plsql_type_spec_source | nested_table_type_def | Creates a nested table of the type specified by datatype. |
| object_type_def | object_type_def | Creates an ADT. The variables that form the data structure are referred to as attributes. Member subprograms that define ADT behaviors are referred to as methods. You need to use the AS OBJECT keyword when you create an ADT. |
| object_type_def | AS OBJECT | Creates a schema-level ADT. A schema-level ADT is sometimes referred to as a root ADT. |
| attr_and_element_spec | element_spec | Specifies each attribute of the ADT. |
| subprogram_spec | subprogram_spec | Declares a subprocedure. |
| subprogram_spec | member_or_static |
|
| subprogram_spec | proc_or_func_spec | Specifies the parameter and data type of the stored procedure or function. If this subprocedure does not contain the definition of the stored procedure or function, you must use the CREATE TYPE BODY statement to make the definition. If you want to create a subtype, the name of the stored procedure or function cannot be the same as the name (regardless of whether it is inherited) of any attribute declared in the supertype link. |






