Overview
Log on to OceanBase Developer Center (ODC) and click the name of the target connection to go to the corresponding connection management page. You can click Table in the left-side navigation pane to get a list of tables. To create a table, click + in the upper-right corner of the table list or click Create in the top navigation bar.
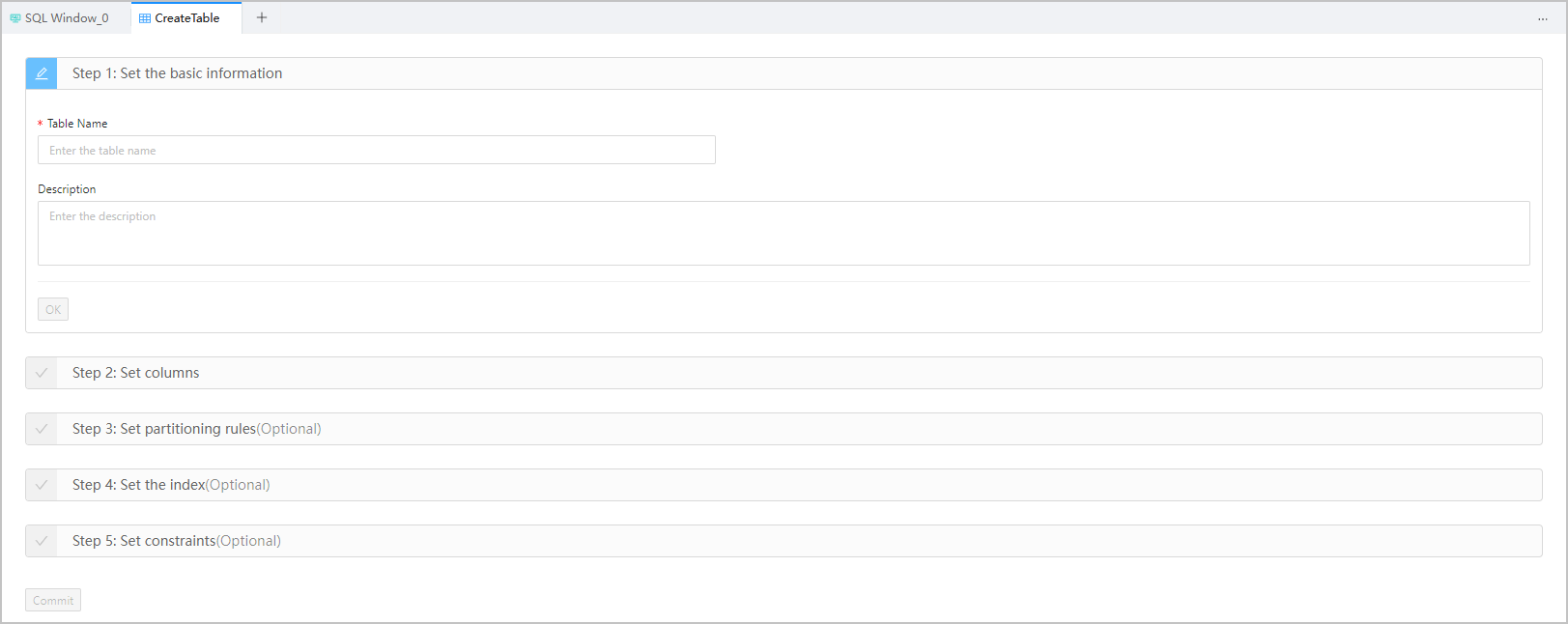
You can create a table in six steps, as shown in the preceding figure.
Set the basic information.
Set columns.
Set partitioning rules.
Set the index.
Set constraints.
Click Commit and wait for the table to be generated.
Procedure
Step 1: set the basic information
Specify the table name and description for the table. The description is optional.
Note
In MySQL mode, you also need to specify Default Character Set and Default Sorting Rule .
Step 2: set columns
The following figure and table show the information that you need to specify when you add a column.
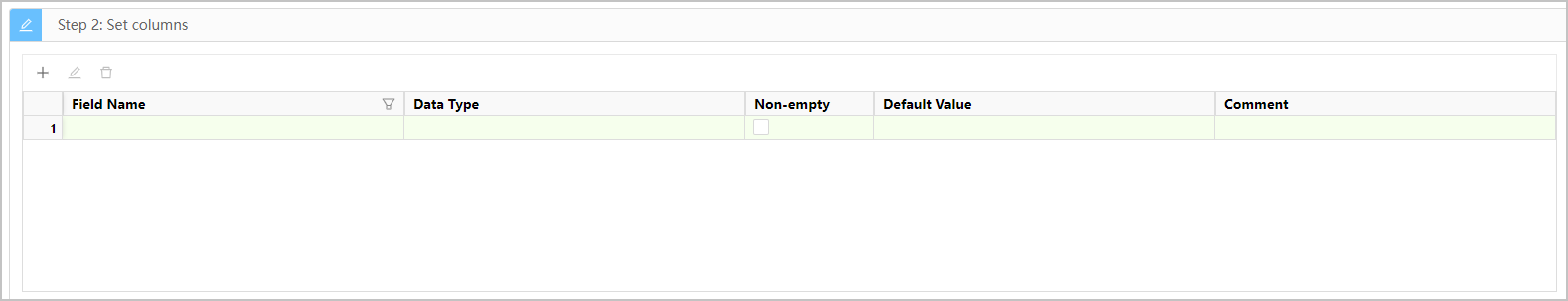
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Field Name | Specifies the name of the column. |
| Data Type | Specifies the data type of the column. |
| Non-empty | Specifies whether the value of the column must be specified. |
| Auto-increment | Specifies whether to set the column to an auto-increment column. This parameter is valid in MySQL mode. |
| Default Value | Specifies the default value of the column. |
| Comment | Provides additional information about the column. |
The column setting section also provides three buttons.
| Button | Description |
|---|---|
| Create | Click this button to add a field. |
| Edit | Click this button to edit the selected field. You can also directly double-click a cell to edit it. |
| Delete | Click this button to delete the selected field. |
Step 3: set partitioning rules
In MySQL mode, OceanBase Database supports the following six partitioning methods: Key , Hash , Range , Range_columns , List , and List_columns .
In Oracle mode, OceanBase Database supports the following three partitioning methods: List , Range , and Hash .
The definition of partition in MySQL mode is different from that in Oracle mode. So, the values of the following parameters vary in different modes. You need to specify the following parameters based on the partitioning method that you selected.
Parameter Description Partitioning Method Specifies the partitioning method. The partitioning methods supported in MySQL mode are different from those in Oracle mode. Field Specifies the field that contains the partition key. Expression Partitions are divided based on the return value of the expression. The partition expression is not supported in Oracle mode. Partition Based on the value specified for Partitioning Method , you may need to specify information such as Partition Name , Partition Quantity , Upper limit of the range , and Enumeration Value . You can add multiple partitions and drag the partitions to adjust their order.
Step 4: set the index
The following figure and table show the information that you need to specify when you set the index.
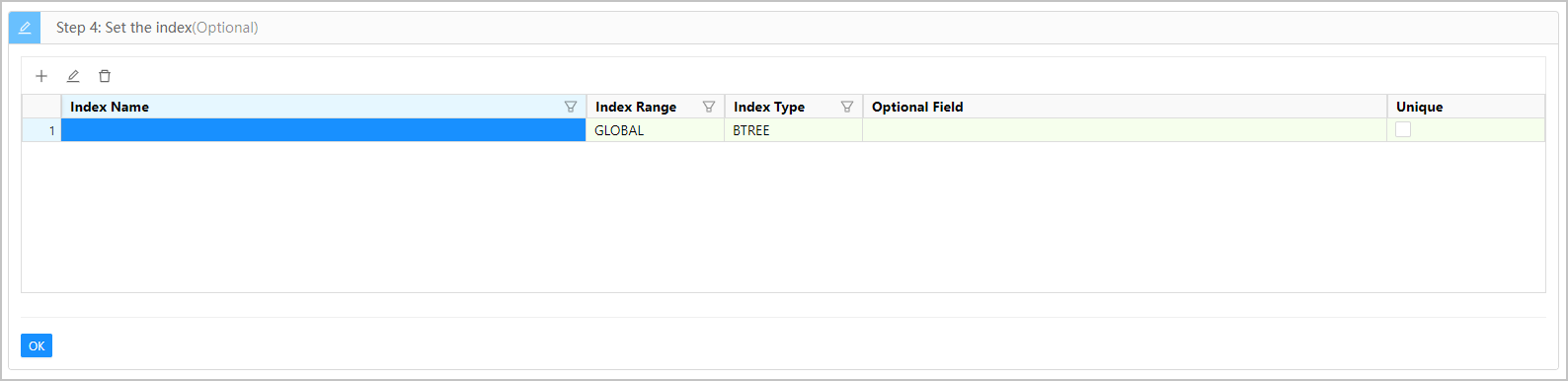
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Index Name | Specifies the name of the index. |
| Index Range | The default value is GLOBAL , indicating a global index. You can set this parameter to LOCAL only for tables with partitions. The value LOCAL indicates a local index. |
| Index Type | Only B-tree is supported. |
| Optional Field | Specifies the columns to be indexed. Pay attention to the order of the indexed columns. |
| Unique | Specifies whether the index is unique. In other words, the index is used to ensure that the constraint is unique. |
The index setting section also provides three buttons.
| Button | Description |
|---|---|
| +Create | Click this button to add an index. |
| Edit | Click this button to edit the selected index. You can also directly double-click a cell to edit it. |
| Delete | Click this button to delete the selected index. |
Step 5: set constraints
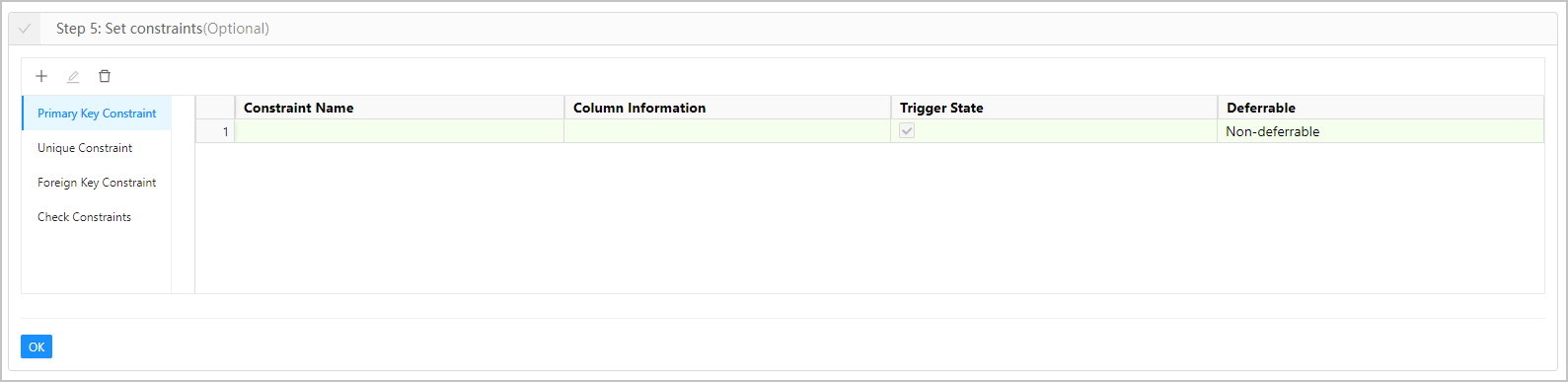
ODC supports the following four table constraints:
Primary Key Constraint : defines a primary key to uniquely identify each row of data in the table. A primary key constraint can be a field or a group of fields. You can set only one primary key constraint for a table, and you cannot edit the constraint after it is configured.
Unique Constraint : ensures that the data in a field or a group of fields is unique in the table. You can set multiple unique constraints in one table.
Foreign Key Constraint : connects one or more columns in two tables. A foreign key constraint is used to maintain the data consistency and integrity between associated tables. After you complete the setting of foreign key constraints, you cannot create new constraints or edit existing constraints.
Check Constraints : checks the data in the database based on the configured check rules when you edit the data. Data modification is allowed only after the check is passed. Check Constraints is supported only in Oracle mode.OceanBase Database supports different constraints in MySQL and Oracle modes, and different constraints require different information. Therefore, you need to specify the required information based on the constraint you selected and the requirements on the page.
Parameter Description Constraint Name Specifies the name of the constraint. Column Information Specifies one field or a group of fields as the constraint. Enabled Specifies whether to enable the created constraint. In some cases, you may need to temporarily disable the constraints. For example, when you import a large amount of data, you can disable constraints to improve the import efficiency. Deferrable Supports three types of delay status. Valid values: Verify Now , Non-deferrable , and Delayed Verification . Associated Schema Specifies the schema where the associated table is located when Foreign Key Constraint is used. The associated table is the parent table. This parameter is valid in Oracle mode. Associated Database Specifies the database where the associated table is located when Foreign Key Constraint is used. The associated table is the parent table. This parameter is valid in MySQL mode. Associated Table Specifies the associated table when Foreign Key Constraint is used. The associated table is the parent table. Associated Field Specifies the associated field when Foreign Key Constraint is used. The associated table is the parent table. Delete Specifies the action to be performed on the current table when the data in the associated table is deleted. The current table is the child table, and the associated table is the parent table. The following four types of action are supported: CASCADE , NO ACTION , RESTRICT , and SET NULL . The actions supported in MySQL mode are different from those in Oracle mode.
- In MySQL mode, you can specify CASCADE, NO ACTION, RESTRICT, and SET NULL.
- In Oracle mode, you can specify CASCADE, NO ACTION, and SET NULL.
Notice
At present, OceanBase Database does not support SET NULL .
For more information about the syntax, see CREATE TABLE, or the official documentation of MySQL or Oracle.Update Specifies the action to be performed on the current table when the data in the associated table is updated. The current table is the child table, and the associated table is the parent table. The following four types of action are supported: CASCADE , NO ACTION , RESTRICT , and SET NULL . The actions supported in MySQL mode are different from those in Oracle mode.
- In MySQL mode, you can specify CASCADE, NO ACTION, RESTRICT, and SET NULL.
- In Oracle mode, you can specify NO ACTION.
Notice
At present, OceanBase Database does not support SET NULL .
For more information about the syntax, see CREATE TABLE, or the official documentation of MySQL or Oracle.Check Condition Specifies the check rules for data verification when Check Constraints is enabled. The constraint setting section also provides three buttons.
Button Description Create Click this button to add a constraint. Edit Click this button to edit the selected constraint. You can also directly double-click a cell to edit it. Delete Click this button to delete the selected constraint.






