Purpose
You can use the JOIN clause to join tables.
A join statement is used in the database to combine two or more tables in the database based on the join conditions. The set generated by a join can be saved as a table or used as a table. A join statement combines the attributes of two tables based on their values.
Syntax
table_references:
table_reference [, table_reference ...]
table_reference:
table_factor
| joined_table
table_factor:
table_name [partition_option]
[[AS] alias] [index_hint_list]
| table_subquery [AS] alias
| ( table_references )
joined_table:
table_reference [NATURAL] [[INNER] | CROSS] JOIN table_factor [join_condition]
| table_reference outer_join_type JOIN table_factor join_condition
partition_option:
PARTITION (partition_name_list)
join_condition:
ON expression
| USING (join_column_list)
join_column_list:
column_name [, column_name ...]
outer_join_type:
[NATURAL] {LEFT | RIGHT | FULL} [OUTER]
index_hint_list:
index_hint [, index_hint ...]
index_hint:
{USE | FORCE | IGNORE} {KEY | INDEX}
[FOR {JOIN | ORDER BY | GROUP BY}] (index_list)
index_list:
index_name [, index_name ...]
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| PARTITION (partition_name_list) | The table partitions to be joined. |
| NATURAL | Indicates a natural join. NATURAL JOIN automatically joins the same columns. |
| [INNER] JOIN | Indicates an inner join. When no join condition is specified, INNER JOIN is equivalent to a comma (,). Both of them generate a Cartesian product by using the specified tables. Notice The comma (,) as an operator has a lower priority than INNER JOIN, CROSS JOIN, and LEFT JOIN. Therefore, if you use commas (,) with other join keywords, the condition of the ON clause may be invalid. |
| CROSS JOIN | In the MySQL mode of OceanBase Database, CROSS JOIN is equivalent to JOIN and INNER JOIN. |
| LEFT [OUTER] JOIN | Indicates a left outer join. If a row in the table on the left side is not found in the table on the right side, NULL is automatically filled in the join result for the table on the right side. |
| RIGHT [OUTER] JOIN | Indicates a right outer join. If a row in the table on the right side is not found in the table on the left side, NULL is automatically filled in the join result for the table on the left side. |
| FULL [OUTER] JOIN | Indicates a full join. NULL is automatically filled in the join result if no matching row is found in the table on the left or right side. |
| column_name | The name of the column used for joining. |
| index_hint | Specifies whether to use the specified index for the query.
|
| ON expression | A join condition that returns duplicate columns. This clause is applicable when columns with different names are used as join condition. |
| USING (join_column_list) | A join condition that does not return duplicate columns. This clause is applicable only when columns with the same name in the tables to be joined are used as the join condition. |
Examples
Take the a and b tables as an example.
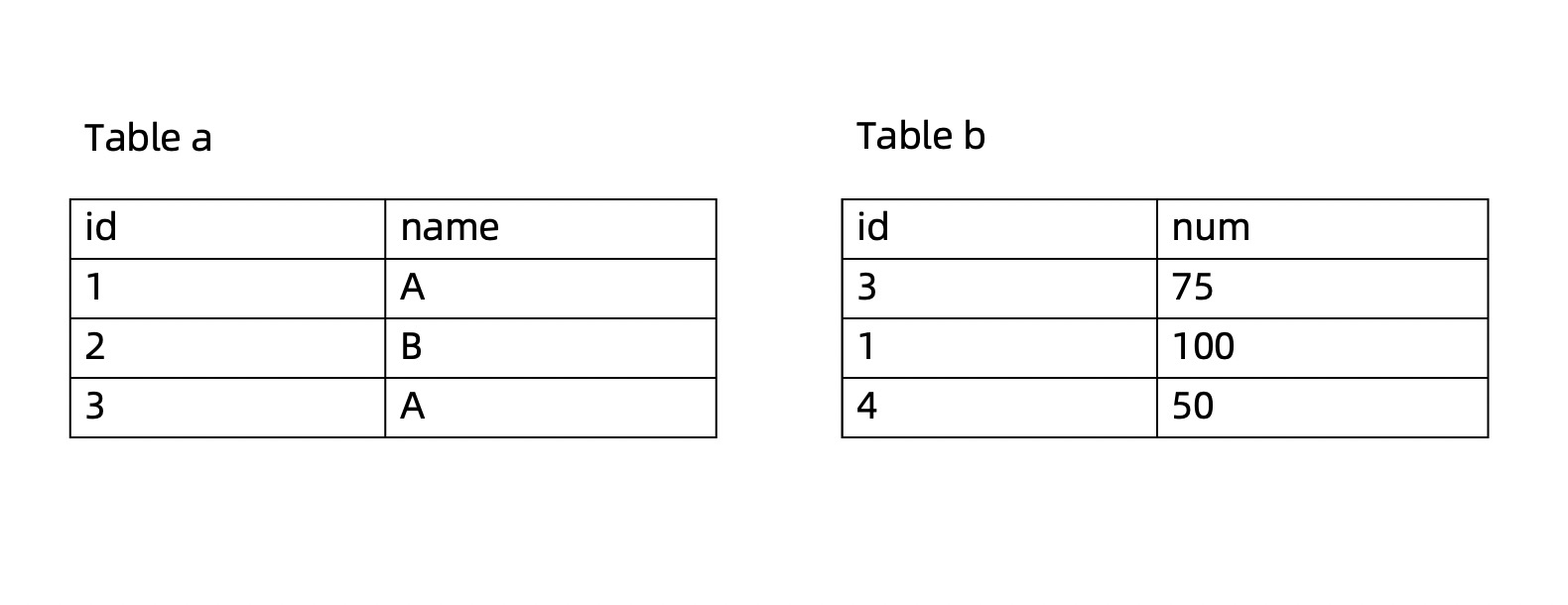
Perform an inner join on the
aandbtables.obclient> SELECT * FROM a JOIN b ON a.ID=b.ID; +------+------+------+------+ | id | name | id | num | +------+------+------+------+ | 1 | A | 1 | 100 | | 3 | A | 3 | 75 | +------+------+------+------+ 2 rows in setPerform a cross join on the
aandbtables.obclient> SELECT * FROM a CROSS JOIN b ON a.id=b.id; +------+------+------+------+ | id | name | id | num | +------+------+------+------+ | 1 | A | 1 | 100 | | 3 | A | 3 | 75 | +------+------+------+------+ 2 rows in setPerform a natural join on the
aandbtables.obclient> SELECT * FROM a NATURAL JOIN b; Empty setPerform a left outer join on the
aandbtables.obclient> SELECT * FROM a LEFT JOIN b USING(ID); +------+------+------+ | id | name | num | +------+------+------+ | 1 | A | 100 | | 2 | B | NULL | | 3 | A | 75 | +------+------+------+ 3 rows in setPerform a right outer join on the
aandbtables.obclient> SELECT * FROM a RIGHT JOIN b USING(ID); +------+------+------+ | id | num | name | +------+------+------+ | 1 | 100 | A | | 3 | 75 | A | | 4 | 50 | NULL | +------+------+------+ 3 rows in setPerform a full join on the
aandbtables.obclient> SELECT * FROM a FULL JOIN b USING(ID); +------+------+------+ | id | name | num | +------+------+------+ | 1 | A | 100 | | 2 | B | NULL | | 3 | A | 75 | | 4 | NULL | 50 | +------+------+------+ 4 rows in set






