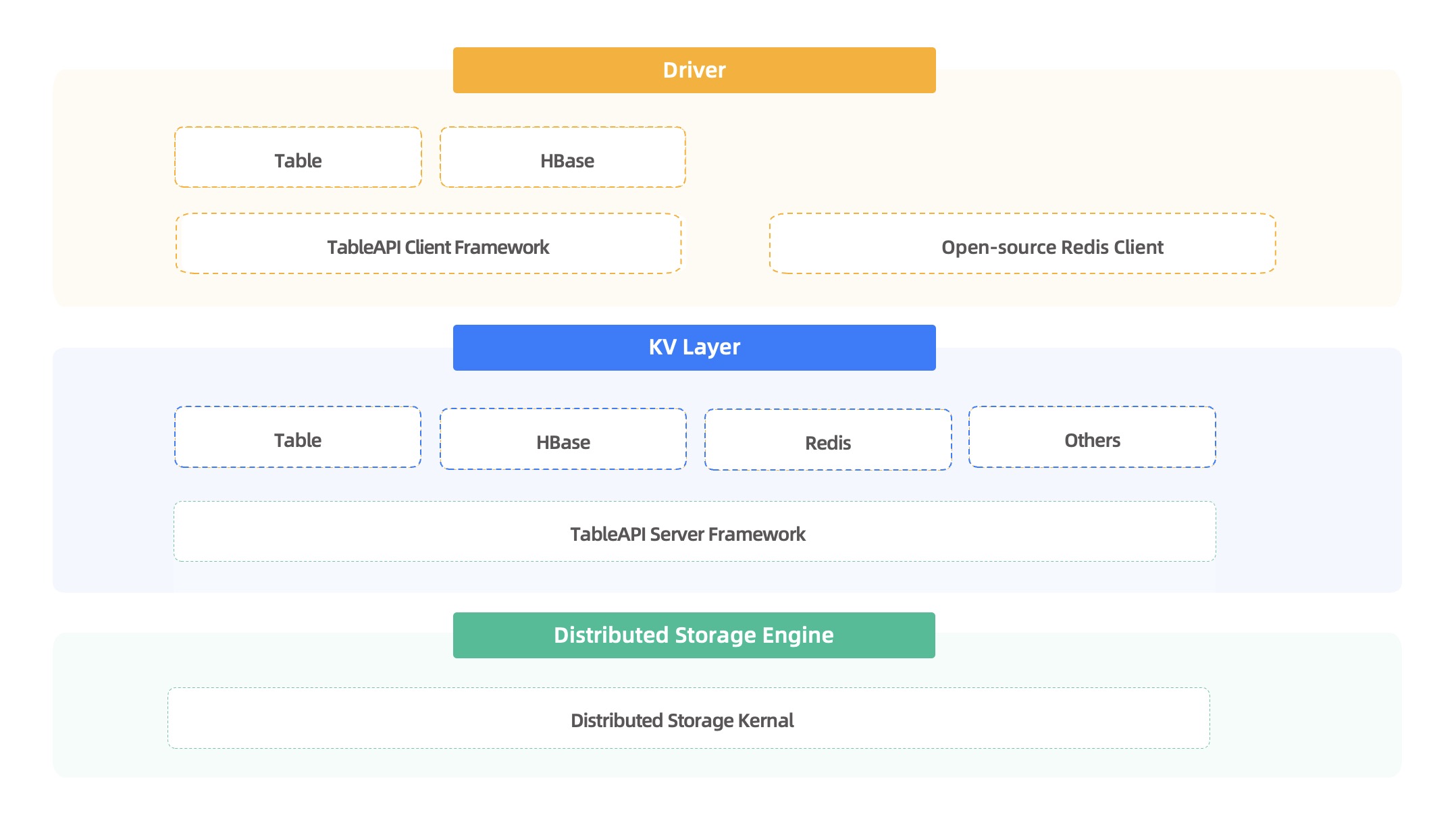
The following figure shows the multi-model architecture of OceanBase Database. This topic focuses on the KV architecture.
TableAPI framework
TableAPI comprises two parts: database server and client.
- TableAPI server: a computing framework encapsulated in OBKV based on the distributed storage engine of OceanBase Database. The framework provides basic table-based computing services.
- TableAPI client: provides an RPC API for interaction with the TableAPI server. In addition, the client integrates routing and high reliability capabilities.
KV layer
The KV layer comprises the TableAPI server framework and model layers. In the preceding figure, table, HBase, and Redis are called model layers in OBKV. A model layer provides model computing capabilities and converts specific models into table models. For example:
- The HBase model layer implements HBase features such as multiple data versions, sparse columns, wide tables, filters, and row locks. It also maps operations performed on rows and cells in HBase as operations on rows in OceanBase Database.
- The Redis model layer implements all kinds of commands of Redis and converts operations performed on data structures in Redis to operations on tables in OceanBase Database.
- The table model layer supports the add, delete, modify, and query operations on table data, as well as secondary indexes. It can also be used as a simple KV database.
Driver layer
The implementation of the driver varies depending on the model. For example:
- The OBKV-HBase model uses the native driver of OBKV and implements HBase APIs at the API layer. Business can call the APIs to interact with the OBKV server through the TableAPI client.
- The OBKV-Redis model uses an open source driver. Since the model is compatible with the native Redis protocol, business can directly use any open source client that supports the Redis protocol to interact with the OBKV server.






